
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol.

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.
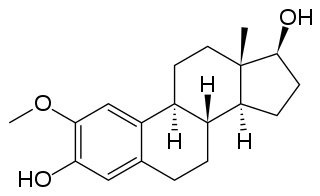
2-Methoxyestradiol is a natural metabolite of estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol (2-OHE2). It is specifically the 2-methyl ether of 2-hydroxyestradiol. 2-Methoxyestradiol prevents the formation of new blood vessels that tumors need in order to grow (angiogenesis), hence it is an angiogenesis inhibitor. It also acts as a vasodilator and induces apoptosis in some cancer cell lines. 2-Methoxyestradiol is derived from estradiol, although it interacts poorly with the estrogen receptors. However, it retains activity as a high-affinity agonist of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER).

Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester. E2S itself is biologically inactive, but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen. Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues. Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol. E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol. Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S. High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.

2-Hydroxyestradiol (2-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17β-triol, is an endogenous steroid, catechol estrogen, and metabolite of estradiol, as well as a positional isomer of estriol.

16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol. It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis.

A catechol estrogen is a steroidal estrogen that contains catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) within its structure. The catechol estrogens are endogenous metabolites of estradiol and estrone and include the following compounds:

Estriol glucuronide (E3G), or oestriol glucuronide, also known as estriol monoglucuronide, as well as estriol 16α-β-D-glucosiduronic acid, is a natural, steroidal estrogen and the glucuronic acid conjugate of estriol. It occurs in high concentrations in the urine of pregnant women as a reversibly formed metabolite of estriol. Estriol glucuronide is a prodrug of estriol, and was the major component of Progynon and Emmenin, estrogenic products manufactured from the urine of pregnant women that were introduced in the 1920s and 1930s and were the first orally active estrogens. Emmenin was succeeded by Premarin, which is sourced from the urine of pregnant mares and was introduced in 1941. Premarin replaced Emmenin due to the fact that it was easier and less expensive to produce.
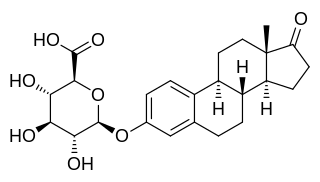
Estrone glucuronide, or estrone-3-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estrone. It is formed from estrone in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estrone. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates and estrone glucuronide is the dominant metabolite of estradiol.

Estriol sulfate, or estriol 3-sulfate, is a conjugated metabolite of estriol that is present in high quantities during pregnancy. It is formed from estriol in the liver and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estriol. Estriol sulfate is the second most prevalent conjugated metabolite of estriol during pregnancy; 35 to 46% is estriol glucuronide and 15 to 22% is estriol 3-sulfate, while the double conjugate estriol sulfate glucuronide also occurs. Estriol sulfate was a component, along with estriol glucuronide, of the early pharmaceutical estrogens Progynon and Emmenin.

2-Hydroxyestrone (2-OHE1), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-2,3-diol-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone and estradiol. It is formed irreversibly from estrone in the liver and to a lesser extent in other tissues via 2-hydroxylation mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes, mainly the CYP3A and CYP1A subfamilies. 2-OHE1 is the most abundant catechol estrogen in the body.

4-Hydroxyestradiol (4-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4,17β-triol, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a minor metabolite of estradiol. It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestrone but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone.
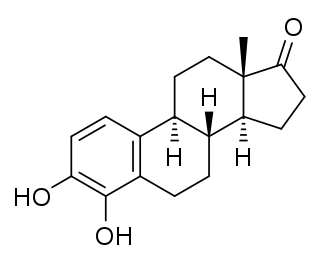
4-Hydroxyestrone (4-OHE1), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4-diol-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a minor metabolite of estrone and estradiol. It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestradiol but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone.

2-Methoxyestrone (2-ME1) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estrone that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 2-hydroxyestrone. Unlike estrone but similarly to 2-hydroxyestrone and 2-methoxyestradiol, 2-methoxyestrone has very low affinity for the estrogen receptor and lacks significant estrogenic activity.
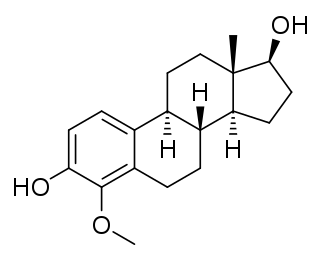
4-Methoxyestradiol (4-ME2) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estradiol that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 4-hydroxyestradiol. It has estrogenic activity similarly to estrone and 4-hydroxyestrone.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.

16β-Hydroxyestrone (16β-OH-E1) is an endogenous estrogen which serves as a metabolite of estrone as well as a metabolic intermediate in the transformation of estrone into epiestriol (16β-hydroxyestradiol). 16β-Hydroxyestrone has similar estrogenic activity to that of 16α-hydroxyestrone. It is less potent than estradiol or estrone but can produce similar maximal uterotrophy at sufficiently high doses, suggesting a fully estrogenic profile.

2-Methoxyestriol (2-MeO-E3) is an endogenous estrogen metabolite. It is specifically a metabolite of estriol and 2-hydroxyestriol. It has negligible affinity for the estrogen receptors and no estrogenic activity. However, 2-methoxyestriol does have some non-estrogen receptor-mediated cholesterol-lowering effects.

4-Methoxyestriol (4-MeO-E3) is an endogenous estrogen metabolite. It is the 4-methyl ether of 4-hydroxyestriol and a metabolite of estriol and 4-hydroxyestriol. 4-Methoxyestriol has very low affinities for the estrogen receptors. Its relative binding affinities (RBAs) for estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) are both about 1% of those of estradiol. For comparison, estriol had RBAs of 11% and 35%, respectively.

















