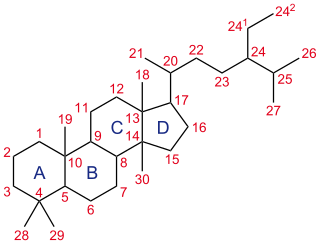
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes which alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene.

Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptor (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy, although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles.

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.

Sterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They are a type of lipid. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, and can be also produced by some bacteria. The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to cell membrane structure, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones.
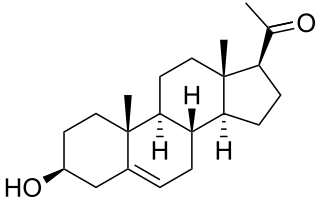
Pregnenolone (P5), or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is an endogenous steroid and precursor/metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of most of the steroid hormones, including the progestogens, androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids. In addition, pregnenolone is biologically active in its own right, acting as a neurosteroid.

Prasterone, also known as dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and sold under the brand names Intrarosa, Diandrone, and Gynodian Depot among others, is a medication as well as over-the-counter dietary supplement which is used to correct DHEA deficiency due to adrenal insufficiency or old age, as a component of menopausal hormone therapy, to treat painful sexual intercourse due to vaginal atrophy, and to prepare the cervix for childbirth, among other uses. It is taken by mouth, by application to the skin, in through the vagina, or by injection into muscle.

Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, abbreviated as DHEA sulfate or DHEA-S, also known as androstenolone sulfate, is an endogenous androstane steroid that is produced by the adrenal cortex. It is the 3β-sulfate ester and a metabolite of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) that circulates in far greater relative concentrations. The steroid is hormonally inert and is instead an important neurosteroid and neurotrophin.

Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase, formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the STS gene.

Sulfotransferases (SULTs) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol or amine. The most common sulfo group donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS). In the case of alcohol as acceptor, the product is a sulfate (R-OSO3−), whereas an amine leads to a sulfamate (R-NH-SO3−). Both reactive groups for a sulfonation via sulfotransferases may be part of a protein, lipid, carbohydrate or steroid.
In enzymology, a steroid sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 2B member 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT2B1 gene.

Estrone sulfate (E1S), or estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.

Azacosterol (INN), or azacosterol hydrochloride (USAN), also known as 20,25-diazacholesterol, is a cholesterol-lowering drug (hypocholesteremic) which was marketed previously but has since been discontinued. It is also an avian chemosterilant used to control the pest pigeon population via inducing sterility. The drug is a sterol and derivative of cholesterol in which two carbon atoms have been replaced with nitrogen atoms.

Pregnenolone sulfate is an endogenous excitatory neurosteroid that is synthesized from pregnenolone. It is known to have cognitive and memory-enhancing, antidepressant, anxiogenic, and proconvulsant effects.
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hormones. They may inhibit the production of cholesterol and other sterols, sex steroids such as androgens, estrogens, and progestogens, corticosteroids such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, and neurosteroids. They are used in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions that depend on endogenous steroids.

Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester. E2S itself is biologically inactive, but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen. Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues. Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol. E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol. Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S. High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.
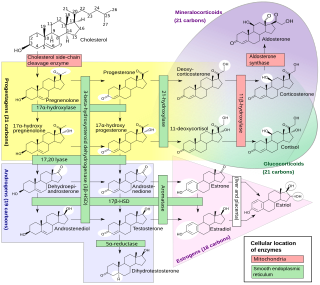
Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids and corticosteroids, as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.

Steroid sulfates are endogenous sulfate esters of steroids. They are formed by steroid sulfotransferases via sulfation of endogenous steroids like cholesterol and steroid hormones. Although steroid sulfates do not bind to steroid hormone receptors and hence are hormonally inert, they can be desulfated by steroid sulfatase and in this way serve as precursors and circulating reservoirs for their active unsulfated counterparts. In addition, some steroid sulfates have biological activity in their own right, for instance acting as neurosteroids and modulating ligand-gated ion channels such as the GABAA and NMDA receptors among other biological targets.

Androstenediol sulfate, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β-sulfate, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and a urinary metabolites of androstenediol.> It is a steroid sulfate which is formed from sulfation of androstenediol by steroid sulfotransferase and can be desulfated back into androstenediol by steroid sulfatase.

Estradiol 17β-sulfate is an estrogen conjugate which is produced from estradiol by sulfation of the C17β hydroxyl group by estrogen sulfotransferases.

















