 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
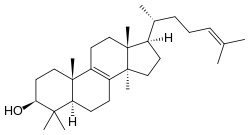
| IUPAC name Lanosta-8,24-dien-3β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1R,3aR,5aR,7S,9aS,11aR)-3a,6,6,9a,11a-Pentamethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylhept-5-en-2-yl]-2,3,3a,4,5,5a,6,7,8,9,9a,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| 2226449 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.105 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Lanosterol |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50O | |
| Molar mass | 426.71 g/mol |
| Melting point | 138 to 140 °C (280 to 284 °F; 411 to 413 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. [1] In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, having a role in maintaining health of the lens. Lanosterol is the precursor to cholesterol. [2]



