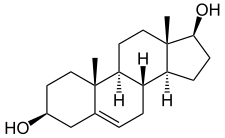
An androgen prohormone, or proandrogen, is a prohormone of an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). They can be prohormones of testosterone or of synthetic AAS, for example, nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione may all be considered proandrogens of testosterone.
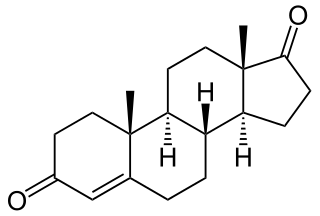
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione, also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol).
Androstenediol may refer to:

1-Testosterone, also known as δ1-dihydrotestosterone (δ1-DHT), as well as dihydroboldenone, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 5α-reduced derivative of boldenone (Δ1-testosterone). It differs from testosterone by having a 1(2)-double bond instead of a 4(5)-double bond in its A ring. It was legally sold online in the United States until 2005, when it was reclassified as a Schedule III drug.
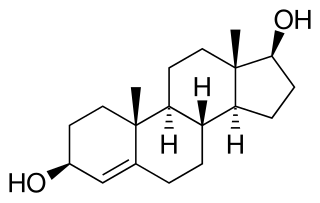
4-Androstenediol, also known as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol, is an androstenediol that is converted to testosterone. The conversion rate is about 15.76%, almost triple that of 4-androstenedione, due to utilization of a different enzymatic pathway. There is also some conversion into estrogen, since testosterone is the metabolic precursor of the estrogens.

Methandriol, also known as methylandrostenediol, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which was developed by Organon and is used in both oral and injectable formulations. It is an orally active 17α-alkylated AAS and a derivative of the endogenous androgen prohormone androstenediol.

3β-Androstanediol, also known as 5α-androstane-3β,17β-diol, and sometimes shortened in the literature to 3β-diol, is an endogenous steroid hormone and a metabolite of androgens like dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Androstenedione may refer to:
Androstenolone may refer to:
Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate, or methylandrostenediol bisenanthoyl acetate, also known as 17α-methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-di(3-oxononanoate), is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated derivative of 5-androstenediol. It is an androgen ester—specifically, the C3β,17β di(3-oxononanoate) ester of methandriol (17α-methyl-5-androstenediol)—and acts as a prodrug of methandriol in the body. Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate is administered by intramuscular injection and, relative to methandriol, has an extended duration via this route due to a depot effect afforded by its ester.
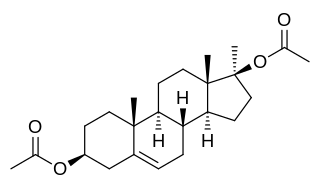
Methandriol diacetate, or methylandrostenediol diacetate, also known as 17α-methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-diacetate, is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated derivative of 5-androstenediol that was never marketed. It is an androgen ester – specifically, the C3,17β diacetate ester of methandriol (17α-methyl-5-androstenediol) – and acts as a prodrug of methandriol in the body.

19-Nor-5-androstenediol, also known as estr-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) that was never introduced for medical use. It is an androgen prohormone of nandrolone and of other 19-norandrostanes.

17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol, also known as 17α-ethynyl-5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a 17α-substituted derivative of 3α-androstanediol which was never marketed. It was under development for the treatment of prostate cancer but was discontinued.

Testosterone dipropionate, or testosterone 3β,17β-dipropanoate, also known as 4-androstenediol dipropionate, as well as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-dipropanoate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester which was never marketed. It is the 3β,17β-dipropionate (dipropanoate) diester of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one), or, more accurately, of 4-androstenediol (androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).

Testosterone diacetate, or testosterone 3β,17β-diacetate, also known as 4-androstenediol diacetate, as well as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-diacetate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester which was never marketed. It is the 3β,17β-diacetate diester of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one), or, more accurately, of 4-androstenediol (androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).

Testosterone acetate butyrate, or testosterone 3β-acetate 17β-butanoate, also known as 4-androstenediol acetate butyrate, as well as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β-acetate 17β-butanoate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester which was never marketed. It is the 3β-acetate, 17β-butyrate (butanoate) diester of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one), or, more accurately, of 4-androstenediol (androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).

Testosterone acetate propionate, or testosterone 3β-acetate 17β-propanoate, also known as 4-androstenediol acetate propionate, as well as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β-acetate 17β-propanoate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester which was never marketed. It is the 3β-acetate, 17β-propionate (propanoate) diester of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one), or, more accurately, of 4-androstenediol (androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).

17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol is a synthetic estrogen and a 17α-substituted derivative of 3β-androstanediol which was never marketed.

Ethinylandrostenediol, also known as 17α-ethynyl-5-androstenediol, is a synthetic estrogen, progestogen, and androgen which was never marketed. It is the C17α ethynyl derivative of the androgen precursor and prohormone 5-androstenediol.