
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol.

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.

Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.

Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disorders, and certain hormone-sensitive cancers. It is usually taken by mouth but is also used as a patch and vaginal ring.

Estrone sulfate, also known as E1S, E1SO4 and estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.

Estetrol (E4), or oestetrol, is one of the four natural estrogenic steroid hormones found in humans, along with estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estetrol is a major estrogen in the body. In contrast to estrone and estradiol, estetrol is a native estrogen of fetal life. Estetrol is produced exclusively by the fetal liver and is found in detectable levels only during pregnancy, with relatively high levels in the fetus and lower levels in the maternal circulation.

Esterified estrogens (EEs), sold under the brand names Estratab and Menest among others, is an estrogen medication which is used hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women, to treat breast cancer in both women and men, and to treat prostate cancer in men. It is formulated alone or in combination with methyltestosterone. It is taken by mouth.

Conjugated estrogens (CEs), or conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), sold under the brand name Premarin among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and for various other indications. It is a mixture of the sodium salts of estrogen conjugates found in horses, such as estrone sulfate and equilin sulfate. CEEs are available in the form of both natural preparations manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares and fully synthetic replications of the natural preparations. They are formulated both alone and in combination with progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate. CEEs are usually taken by mouth, but can also be given by application to the skin or vagina as a cream or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle.

Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester. E2S itself is biologically inactive, but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen. Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues. Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol. E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol. Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S. High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.

17β-Dihydroequilin is a naturally occurring estrogen sex hormone found in horses as well as a medication. As the C3 sulfate ester sodium salt, it is a minor constituent (1.7%) of conjugated estrogens. However, as equilin, with equilin sulfate being a major component of CEEs, is transformed into 17β-dihydroequilin in the body, analogously to the conversion of estrone into estradiol, 17β-dihydroequilin is, along with estradiol, the most important estrogen responsible for the effects of CEEs.

Estradiol glucuronide, or estradiol 17β-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estradiol. It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estradiol. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates.

Estriol (E3), sold under the brand name Ovestin among others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is also used in veterinary medicine as Incurin to treat urinary incontinence due to estrogen deficiency in dogs. The medication is taken by mouth in the form of tablets, as a cream that is applied to the skin, as a cream or pessary that is applied in the vagina, and by injection into muscle.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.

Estetrol (E4) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in combination with a progestin in combined birth control pills and is under development for various other indications. These investigational uses include menopausal hormone therapy to treat symptoms such as vaginal atrophy, hot flashes, and bone loss and the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is taken by mouth.

Estrone sulfate (E1S) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications. As the sodium salt, it is the major estrogen component of conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and esterified estrogens. In addition, E1S is used on its own as the piperazine salt estropipate. The compound also occurs as a major and important metabolite of estradiol and estrone. E1S is most commonly taken by mouth, but in the form of Premarin can also be taken by parenteral routes such as transdermal, vaginal, and injection.

5α-Dihydroethisterone is an active metabolite of the formerly clinically used but now-discontinued progestin ethisterone and the experimental and never-marketed hormonal antineoplastic agent ethynylandrostanediol (HE-3235). Its formation from its parent drugs is catalyzed by 5α-reductase in tissues that express the enzyme in high amounts like the liver, skin, hair follicles, and prostate gland. 5α-DHET has significant affinity for steroid hormone receptors and may contribute importantly to the activities of its parent drugs.
Equine estrogens, or horse estrogens, are estrogens found in horses. They include the following:
The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.
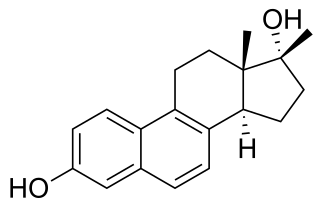
17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin, also known as 17β-methyl-6,8-didehydro-17α-estradiol, is a synthetic steroidal estrogen which was never marketed. It is the C17β methylated derivative of 17α-dihydroequilenin, an equine estrogen and constituent of conjugated estrogens (Premarin). 17α-Dihydroequilenin itself is an analogue of 17α-estradiol, the C17 epimer of estradiol. NCI-122 has respective relative binding affinities of about 8.1% and 16% for the ERα and ERβ when compared to estradiol. It is far less potent as an estrogen in comparison to estradiol, with relative estrogenic potencies at the ERα and ERβ of 1.4% and 0.81%, respectively. Nonetheless, NCI-122 acts as a full agonist of the ERα and has estrogenic activity similar to that of estradiol at sufficiently high concentrations. The mechanisms of the lower potency of NCI-122 and related estrogens relative to estradiol have been studied.












