There are many hundreds of thousands of possible drugs. Any chemical substance with biological activity may be considered a drug. This list categorises drugs alphabetically and also by other categorisations.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.

Cloxestradiol (INN), also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen which was never marketed. It is an analogue of estradiol with a 2,2,2-trichloroethoxy substitution. The O,O-diacetate derivative, cloxestradiol acetate, has been marketed as an estrogen.

Cloxestradiol acetate, also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol O,O-diacetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen derived from estradiol. It is the O,O-diacetate ester of cloxestradiol, which, in contrast to cloxestradiol acetate, was never marketed.

Orestrate (INN), also known as estradiol 3-propionate 17β-(1-cyclohexenyl) ether, is an estrogen medication and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It is the C3 propionate ester and C17β-(1-cyclohexenyl) ether of estradiol.
Estradiol stearate (E2-17-St), also known as estradiol octadecanoate and sold under the brand name Depofollan, is a naturally occurring estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β stearate ester of estradiol. It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol. The compound is one of the components that collectively constitute lipoidal estradiol, another of which is estradiol palmitate. It is extremely lipophilic and hydrophobic. Estradiol stearate has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol via esterases for its estrogenic activity. The compound does not bind to sex hormone-binding globulin or α-fetoprotein, instead being transported by lipoproteins such as high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein.

Hydroxyestrone diacetate, or 16α-hydroxyestrone diacetate, also known as 3,16α-dihydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one 3,16α-diacetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen which has been marketed in France, Spain, Brazil, and Argentina. It is a derivative of 16α-hydroxyestrone with an acetate esters attached at the C3 and C16α positions.

An androgen or anabolic steroid ester is an ester of an androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) such as the natural testosterone or dihydrotestosterone (DHT) or the synthetic nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Esterification renders AAS into metabolism-resistant prohormones of themselves, improving oral bioavailability, increasing lipophilicity, and extending the elimination half-life. In addition, with intramuscular injection, AAS esters are absorbed more slowly into the body, further improving the elimination half-life. Aside from differences in pharmacokinetics, these esters essentially have the same effects as the parent drugs. They are used in androgen replacement therapy (ART), among other indications. Examples of androgen esters include testosterone esters such as testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate, testosterone propionate, and testosterone undecanoate and nandrolone esters such as nandrolone decanoate and nandrolone phenylpropionate.
Estradiol diundecylenate, or estradiol diundecenoate, also known as 17β-estradiol 3,17β-diundec-10-enoate, is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the 3,17β-diundecylenate ester of estradiol – which was previously marketed in Argentina.

Estradiol mustard, also known as chlorphenacyl estradiol diester, as well as estradiol 3,17β-bis(4- phenyl)acetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard-coupled estrogen ester that was never marketed. It is selectively distributed into estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tissues such as ER-expressing tumors like those seen in breast and prostate cancers. For this reason, estradiol mustard and other cytostatic-linked estrogens like estramustine phosphate have reduced toxicity relative to non-linked nitrogen mustard cytostatic antineoplastic agents. However, they may stimulate breast tumor growth due to their inherent estrogenic activity and are said to be devoid of major therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer, although estramustine phosphate has been approved for and is used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, or trenbolone cyclohexylmethylcarbonate, sold under the brand names Parabolan and Hexabolan, is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the nandrolone group and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β hexahydrobenzylcarbonate (cyclohexylmethylcarbonate) ester of trenbolone – which was marketed in France for medical use in humans but has since been discontinued.

Estradiol sulfamate, or estradiol-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which is under development for the treatment of endometriosis. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of estradiol, and was originally thought to be a prodrug of estradiol. The drug was first synthesized as an STS inhibitor along with its oxidized version estrone 3-O-sulfamate (EMATE) in the group of Professor Barry V L Potter at the University of Bath, UK, working together with Professor Michael J Reed at Imperial College, London and was found to be highly estrogenic in rodents. Such aryl sulfamate esters were shown to be "first-in-class" highly potent active site-directed irreversible STS inhibitors. Compounds of this class are thought to irreversibly modify the active site formylglycine residue of STS. The drug shows profoundly reduced susceptibility to first-pass metabolism relative to estradiol, and was believed to be the first "potent" estradiol prodrug to be discovered. It was clinically investigated for possible use as an estrogen for indications like hormonal contraception and menopausal hormone therapy. However, it showed no estrogenic effects in women. The potent non-estrogenic clinical STS inhibitor Irosustat (STX64/667-Coumate) was used to explore the possibility that STS might be responsible for the hydrolysis of estrogen sulphamates. Results demonstrated convincingly that STS is the enzyme responsible for the removal of the sulfamoyl group from estrogen sulfamates and has a crucial role in regulating the estrogenicity associated with this class of drug. Thus, STS inhibition blocks the conversion of E2MATE into estradiol and thereby abolishes its estrogenicity in humans. Irosustat has completed a number of clinical trials in oncology as an STS inhibitor currently up to Phase II.
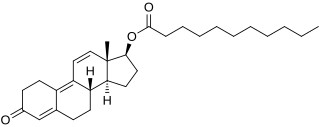
Trenbolone undecanoate, or trenbolone undecylate, is a synthetic and injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which was never marketed. It is the C17β undecanoate (undecylate) ester and a long-acting prodrug of trenbolone. The drug was described by Roussel Uclaf in 1967 and was the first long-lasting ester of trenbolone to be developed. Subsequently, trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, a roughly equivalent compound, was developed and introduced for use in humans in 1980, though it was discontinued in 1997. Trenbolone enanthate is another long-lasting ester of trenbolone. Similarly to trenbolone undecanoate, it was never marketed, but it has been sold on the black market as a designer steroid for bodybuilders and athletes.

Ethinylestradiol benzoate, or 17α-ethynylestradiol 3-benzoate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 benzoate ester of ethinylestradiol – which was first described in the late 1930s and was never marketed.
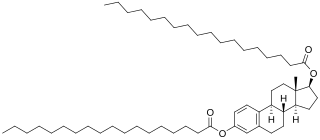
Estradiol distearate (EDS), also known as estradiol dioctadecanoate, is an estrogen and a estrogen ester which was never marketed. It is a long-acting prodrug of estradiol in the body.
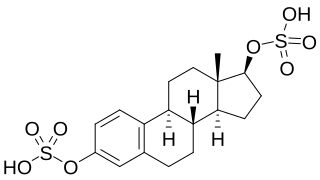
Estradiol disulfate is an endogenous estrogen conjugate and metabolite of estradiol. It is related to estradiol 3-sulfate and estradiol 17β-sulfate. Estradiol disulfate has 0.0004% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), one of the two estrogen receptors (ERs).

Estradiol diacetate (EDA), or estradiol 3,17β-diacetate, is an estrogen and an estrogen ester—specifically, the C3 and C17β diacetate ester of estradiol—which was never marketed. It is related to the estradiol monoesters estradiol acetate and estradiol 17β-acetate.














