Hot flashes, also known as hot flushes, are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.
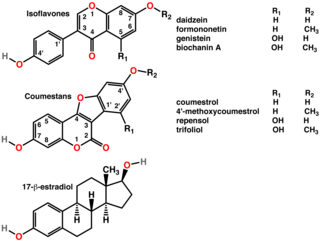
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity to estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots.

The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three clinical trials (CT) and an observational study (OS). In particular, randomized controlled trials were designed and funded that addressed cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoporosis.

Equol (4',7-isoflavandiol) is an isoflavandiol estrogen metabolized from daidzein, a type of isoflavone found in soybeans and other plant sources, by bacterial flora in the intestines. While endogenous estrogenic hormones such as estradiol are steroids, equol is a nonsteroidal estrogen. Only about 30–50% of people have intestinal bacteria that make equol.
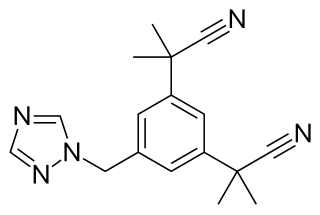
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and in men, and gynecomastia in men. They may also be used off-label to reduce estrogen conversion when supplementing testosterone exogenously. They may also be used for chemoprevention in women at high risk for breast cancer.

Raloxifene, sold under the brand name Evista among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and those on glucocorticoids. For osteoporosis it is less preferred than bisphosphonates. It is also used to reduce the risk of breast cancer in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.
Isoflavones are substituted derivatives of isoflavone, a type of naturally occurring isoflavonoids, many of which act as phytoestrogens in mammals. Isoflavones occur in many plant species, but are especially high in soybeans.
Hypoestrogenism, or estrogen deficiency, refers to a lower than normal level of estrogen. It is an umbrella term used to describe estrogen deficiency in various conditions. Estrogen deficiency is also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and has been linked to diseases like urinary tract infections and osteoporosis.

Lasofoxifene, sold under the brand name Fablyn, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is marketed by Pfizer in Lithuania and Portugal for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and for the treatment of vaginal atrophy, and the result of an exclusive research collaboration with Ligand Pharmaceuticals (LGND). It also appears to have had a statistically significant effect of reducing breast cancer in women according to a study published in The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.

Ipriflavone is a synthetic isoflavone which may be used to inhibit bone resorption, maintain bone density and to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It is not used to treat osteoporosis. It slows down the action of the osteoclasts, possibly allowing the osteoblasts to build up bone mass.

Coumestrol is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as coumestans. Coumestrol was first identified as a compound with estrogenic properties by E. M. Bickoff in ladino clover and alfalfa in 1957. It has garnered research interest because of its estrogenic activity and prevalence in some foods, including soybeans, brussels sprouts, spinach and a variety of legumes. The highest concentrations of coumestrol are found in clover, Kala Chana, and Alfalfa sprouts.

Femarelle is a dietary supplement that is a mixture of DT56a and flaxseed powder, that may act as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In 2008 an application was submitted to the European Food Safety Authority to market Femarelle with a health claim, namely that it can reduce the risk for osteoporosis and other bone disorders; the EFSA found that "the food/constituent for which the claim is made, i.e. Femarelle, has not been sufficiently characterised" and that "a cause and effect relationship has not been established between the consumption of Femarelle and increased BMD, increased bone formation, or decreased risk of osteoporosis or other bone disorders in post-menopausal women."
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones that occur during menopause.

Trimegestone, sold under the brand names Ondeva and Totelle among others, is a progestin medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It was also under development for use in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, but ultimately was not marketed for this purpose. The medication is available alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.
Postmenopausal confusion, also commonly referred to as postmenopausal brain fog, is a group of symptoms of menopause in which women report problems with cognition at a higher frequency during postmenopause than before.

Neurodegenerative diseases can disrupt the normal human homeostasis and result in abnormal estrogen levels. For example, neurodegenerative diseases can cause different physiological effects in males and females. In particular, estrogen studies have revealed complex interactions with neurodegenerative diseases. Estrogen was initially proposed to be a possible treatment for certain types of neurodegenerative diseases but a plethora of harmful side effects such as increased susceptibility to breast cancer and coronary heart disease overshadowed any beneficial outcomes. On the other hand, Estrogen Replacement Therapy has shown some positive effects with postmenopausal women. Estrogen and estrogen-like molecules form a large family of potentially beneficial alternatives that can have dramatic effects on human homeostasis and disease. Subsequently, large-scale efforts were initiated to screen for useful estrogen family molecules. Furthermore, scientists discovered new ways to synthesize estrogen-like compounds that can avoid many side effects. These are called nonsteroidal estrogens, which come from natural or synthetic products including plants, fungi, and chemicals.

Conjugated estrogens (CEs), or conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), sold under the brand name Premarin among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and for various other indications. It is a mixture of the sodium salts of estrogen conjugates found in horses, such as estrone sulfate and equilin sulfate. CEEs are available in the form of both natural preparations manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares and fully synthetic replications of the natural preparations. They are formulated both alone and in combination with progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate. CEEs are usually taken by mouth, but can also be given by application to the skin or vagina as a cream or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle.

An estrogen (E) is a type of medication which is used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy, and as part of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. They can also be used in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer and for various other indications. Estrogens are used alone or in combination with progestogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of estrogens include bioidentical estradiol, natural conjugated estrogens, synthetic steroidal estrogens like ethinylestradiol, and synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Estrogens are one of three types of sex hormone agonists, the others being androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone and progestogens like progesterone.

Estradiol/drospirenone (E2/DRSP), sold under the brand name Angeliq, is a combination of estradiol (E2), an estrogen, and drospirenone (DRSP), a progestin, antimineralocorticoid, and antiandrogen, which is used in menopausal hormone therapy, specifically the treatment of menopausal syndrome and osteoporosis, in postmenopausal women. It is taken by mouth and contains 0.5 to 1 mg E2 and 0.25 to 0.5 mg DRSP per tablet. The medication was approved in the United States in 2005. It is marketed widely throughout the world.












