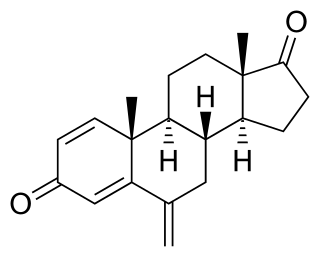
Exemestane, sold under the brand name Aromasin among others, is a medication used to treat breast cancer. It is a member of the class of antiestrogens known as aromatase inhibitors. Some breast cancers require estrogen to grow. Those cancers have estrogen receptors (ERs), and are called ER-positive. They may also be called estrogen-responsive, hormonally-responsive, or hormone-receptor-positive. Aromatase is an enzyme that synthesizes estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors block the synthesis of estrogen. This lowers the estrogen level, and slows the growth of cancers.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.

Quinestradol, also known as quinestradiol or quinestriol, as well as estriol 3-cyclopentyl ether (E3CPE), is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ether which is no longer marketed. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of estriol. The medication has been studied in the treatment of stress incontinence in elderly women, with effectiveness observed.

Cloxestradiol, also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen which was never marketed. It is an analogue of estradiol with a 2,2,2-trichloroethoxy substitution. The O,O-diacetate derivative, cloxestradiol acetate, has been marketed as an estrogen.

Cloxestradiol acetate, also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol O,O-diacetate, is a synthetic steroidal estrogen derived from estradiol. It is the O,O-diacetate ester of cloxestradiol, which, in contrast to cloxestradiol acetate, was never marketed.
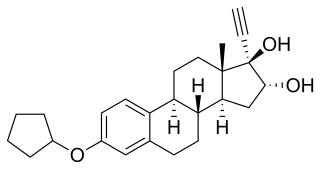
Nilestriol, also known as nylestriol, is a synthetic estrogen which was patented in 1971 and is marketed in China. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, and is also known as ethinylestriol cyclopentyl ether (EE3CPE). Nilestriol is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison. It is described as a slowly-metabolized, long-acting estrogen and derivative of estriol. Nilestriol was assessed in combination with levonorgestrel for the potential treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, but this formulation ultimately was not marketed.

Orestrate, also known as estradiol 3-propionate 17β-(1-cyclohexenyl) ether, is an estrogen medication and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It is the C3 propionate ester and C17β-(1-cyclohexenyl) ether of estradiol.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, orally active, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, whose levorotatory isomer is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Almestrone, also known as 7α-methylestrone, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen which was synthesized in 1967 but was never marketed. It is used as a precursor in the synthesis of several highly active steroids.

Epiestriol, or epioestriol, also known as 16β-epiestriol or simply 16-epiestriol, as well as 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol, is a minor and weak endogenous estrogen, and the 16β-epimer of estriol. Epiestriol is used clinically in the treatment of acne. In addition to its estrogenic actions, epiestriol has been found to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties without glycogenic activity or immunosuppressive effects, an interesting finding that is in contrast to conventional anti-inflammatory steroids such as hydrocortisone.

A progestogen ester is an ester of a progestogen or progestin. The prototypical progestogen is progesterone, an endogenous sex hormone. Esterification is frequently employed to improve the pharmacokinetics of steroids, including oral bioavailability, lipophilicity, and elimination half-life. In addition, with intramuscular injection, steroid esters are often absorbed more slowly into the body, allowing for less frequent administration. Many steroid esters function as prodrugs.

A steroid ester is an ester of a steroid. They include androgen esters, estrogen esters, progestogen esters, and corticosteroid esters. Steroid esters may be naturally occurring/endogenous like DHEA sulfate or synthetic like estradiol valerate. Esterification is useful because it is often able to render the parent steroid into a prodrug of itself with altered chemical properties such as improved metabolic stability, water solubility, and/or lipophilicity. This, in turn, can enhance pharmacokinetics, for instance by improving the steroid's bioavailability and/or conferring depot activity and hence an extended duration with intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.

Estrofurate, also known as 17α-(3-furyl)-estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraene-3,17-diol 3-acetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen that was synthesized in 1967 and studied in the late 1960s and early 1970s but was never marketed. It is a relatively weak estrogen in bioassays.
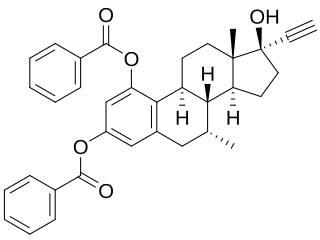
Etamestrol (INN), or eptamestrol, also known as 7α-methyl-19-nor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-1,3,17-triol 1,3-dibenzoate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen described as an ovulation inhibitor that was synthesized in 1979 but was never marketed.

Clomestrone, also known as 16α-chloroestrone 3-methyl ether, is a synthetic, steroidal, weak estrogen derived from estrone and used as an anticholesterolemic agent in the treatment of atherosclerosis. It is said to have beneficial effects on serum lipid profiles while producing minimal feminization, though some estrogenic side effects, including breast tenderness, loss of libido, and fatigue or avolition, were observed in most patients in clinical studies. The drug is a close analogue of mytatrienediol, and the two estrogens have similar drug profiles. Clomestrone was described in the literature in 1958 and introduced for medical use shortly thereafter.

Estradiol mustard, also known as estradiol 3,17β-bis(4- phenyl)acetate, is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a phenylacetic acid nitrogen mustard-coupled estrogen ester that was never marketed. It is selectively distributed into estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tissues such as ER-expressing tumors like those seen in breast and prostate cancers. For this reason, estradiol mustard and other cytostatic-linked estrogens like estramustine phosphate have reduced toxicity relative to non-linked nitrogen mustard cytostatic antineoplastic agents. However, they may stimulate breast tumor growth due to their inherent estrogenic activity and are said to be devoid of major therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer, although estramustine phosphate has been approved for and is used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
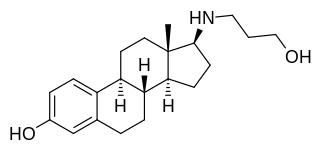
Prolame, also known as 17β-( amino)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a 17β-aminoestrogen with anticoagulant effects that was first described in 1985 but was never marketed.
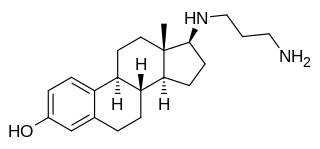
Prodiame, also known as 17β-( amino)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a 17β-aminoestrogen with anticoagulant effects that was first described in 1983 and was never marketed.

Ethinylestradiol benzoate, or 17α-ethynylestradiol 3-benzoate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 benzoate ester of ethinylestradiol – which was first described in the late 1930s and was never marketed.

Estrone methyl ether, or estrone 3-methyl ether, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ether – specifically, the C3 methyl ether of estrone – which was never marketed. It has been used to synthesize mestranol.



















