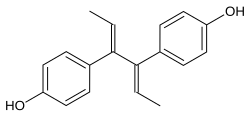
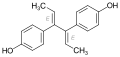
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency, treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer, and other uses. By 2007, it was only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. In 2011, Hoover and colleagues reported on adverse health outcomes linked to DES including infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preeclampsia, preterm birth, stillbirth, infant death, menopause prior to age 45, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and vaginal cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance, vaginal, topical, and by injection.
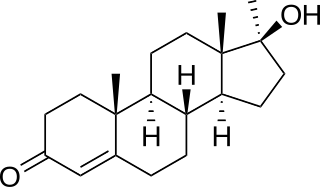
Methyltestosterone, sold under the brand names Android, Metandren, and Testred among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, at low doses as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, osteoporosis, and low sexual desire in women, and to treat breast cancer in women. It is taken by mouth or held in the cheek or under the tongue.

Estradiol valerate (EV), sold for use by mouth under the brand name Progynova and for use by injection under the brand names Delestrogen and Progynon Depot among others, is an estrogen medication. It is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels, hormone therapy for transgender people, and in hormonal birth control. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The medication is taken by mouth or by injection into muscle or fat once every 1 to 4 weeks.

Norelgestromin, or norelgestromine, sold under the brand names Evra and Ortho Evra among others, is a progestin medication which is used as a method of birth control for women. The medication is available in combination with an estrogen and is not available alone. It is used as a patch that is applied to the skin.

Norgestimate, sold under the brand names Ortho Tri-Cyclen and Previfem among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills for women and in menopausal hormone therapy. The medication is available in combination with an estrogen and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.

Aminoglutethimide (AG), sold under the brand names Elipten, Cytadren, and Orimeten among others, is a medication which has been used in the treatment of seizures, Cushing's syndrome, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, among other indications. It has also been used by bodybuilders, athletes, and other men for muscle-building and performance- and physique-enhancing purposes. AG is taken by mouth three or four times per day.

Toremifene, sold under the brand name Fareston among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women. It is taken by mouth.
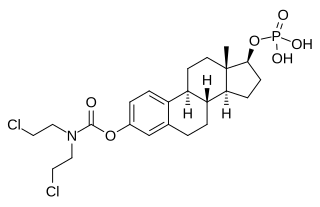
Estramustine phosphate (EMP), also known as estradiol normustine phosphate and sold under the brand names Emcyt and Estracyt, is a dual estrogen and chemotherapy medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is taken multiple times a day by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Estropipate, also known as piperazine estrone sulfate and sold under the brand names Harmogen, Improvera, Ogen, Ortho-Est, and Sulestrex among others, is an estrogen medication which is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is a salt of estrone sulfate and piperazine, and is transformed into estrone and estradiol in the body. It is taken by mouth.

Fosfestrol, sold under the brand name Honvan and also known as diethylstilbestrol diphosphate (DESDP), is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is given by slow intravenous infusion once per day to once per week or by mouth once per day.

Mestranol, sold under the brand names Enovid, Norinyl, and Ortho-Novum among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and the treatment of menstrual disorders. It is formulated in combination with a progestin and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.

Chlormadinone acetate (CMA), sold under the brand names Belara, Gynorelle, Lutéran, and Prostal among others, is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, as a component of menopausal hormone therapy, in the treatment of gynecological disorders, and in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like enlarged prostate and prostate cancer in men and acne and hirsutism in women. It is available both at a low dose in combination with an estrogen in birth control pills and, in a few countries like France and Japan, at low, moderate, and high doses alone for various indications. It is taken by mouth.

Allylestrenol, sold under the brand names Gestanin and Turinal among others, is a progestin medication which is used to treat recurrent and threatened miscarriage and to prevent premature labor in pregnant women. However, except in the case of proven progesterone deficiency, its use for such purposes is no longer recommended. It is also used in Japan to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. The medication is used alone and is not formulated in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Paroxypropione, also known as paraoxypropiophenone, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which has been used medically as an antigonadotropin in Spain and Italy but appears to no longer be marketed. It was first synthesized in 1902. The antigonadotropic properties of the drug were discovered in 1951 and it entered clinical use shortly thereafter.

Hexestrol, sold under the brand name Synestrol among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen which was previously used for estrogen replacement therapy and in the treatment of certain hormone-dependent cancers as well as gynecological disorders but is mostly no longer marketed. It has also been used in the form of esters such as hexestrol diacetate and hexestrol dipropionate. Hexestrol and its esters are taken by mouth, held under the tongue, or via injection into muscle.
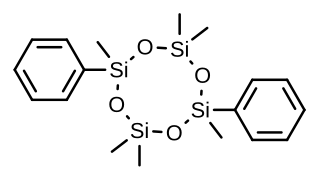
Quadrosilan is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen that was developed in the 1970s and that is or has been used as an antigonadotropic agent in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is an organosilicon compound, and is also known as 2,6-cisdiphenylhexamethylcyclotetrasiloxane. Quadrosilan has estrogenic activity equivalent to that of estradiol, and can produce feminization and gynecomastia as side effects in male patients.

Estradiol hexahydrobenzoate (EHHB), sold under a number of brand names including Benzo-Ginoestril A.P., BenzoGynoestryl Retard, Ginestryl-15-Depot, Menodin, and Tardoginestryl, is an estrogen medication which was previously used for indications such as menopausal hormone therapy and gynecological disorders. EHHB is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals, for instance once every few weeks.

Dienestrol diacetate is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of dienestrol.

Ethinylestradiol sulfonate (EES), sold under the brand names Deposiston and Turisteron among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills for women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been investigated in the treatment of breast cancer in women. The medication was combined with norethisterone acetate in birth control pills. EES is taken by mouth once per week.
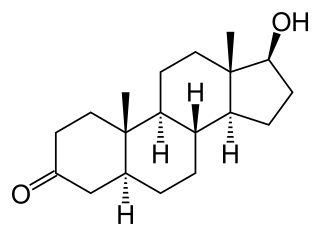
Androstanolone, or stanolone, also known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and sold under the brand name Andractim among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication and hormone which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used to treat breast development and small penis in males. Compared to testosterone, androstanolone (DHT) is less likely to aromatize into estrogen, and therefore it shows less pronounced estrogenic side effects, such as gynecomastia and water retention. On the other hand, androstanolone (DHT) show more significant androgenic side effects, such as acne, hair loss and prostate enlargement.