Hot flashes, also known as hot flushes, are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity to estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots.

Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.

Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome. Tamoxifen is typically taken daily by mouth for five years for breast cancer.

Equol (4',7-isoflavandiol) is an isoflavandiol estrogen metabolized from daidzein, a type of isoflavone found in soybeans and other plant sources, by bacterial flora in the intestines. While endogenous estrogenic hormones such as estradiol are steroids, equol is a nonsteroidal estrogen. Only about 30–50% of people have intestinal bacteria that make equol.
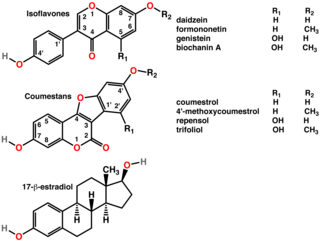
Isoflavones are substituted derivatives of isoflavone, a type of naturally occurring isoflavonoids, many of which act as phytoestrogens in mammals. Isoflavones occur in many plant species, but are especially high in soybeans.

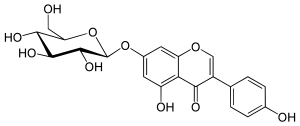
Genistein (C15H10O5) is a naturally occurring compound that structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. It is described as an angiogenesis inhibitor and a phytoestrogen.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility.

Genista tinctoria, the dyer's greenweed or dyer's broom, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. Its other common names include dyer's whin, waxen woad and waxen wood. The Latin specific epithet tinctoria means "used as a dye".

G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPER gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible for some of the rapid effects that estradiol has on cells.

Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) also known as NR3A2 is one of two main types of estrogen receptor—a nuclear receptor which is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans ERβ is encoded by the ESR2 gene.

Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1, is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRA gene. ERRα was originally cloned by DNA sequence homology to the estrogen receptor alpha, but subsequent ligand binding and reporter-gene transfection experiments demonstrated that estrogens did not regulate ERRα. Currently, ERRα is considered an orphan nuclear receptor.

Coumestrol is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as coumestans. Coumestrol was first identified as a compound with estrogenic properties by E. M. Bickoff in ladino clover and alfalfa in 1957. It has garnered research interest because of its estrogenic activity and prevalence in some foods, including soybeans, brussels sprouts, spinach and a variety of legumes. The highest concentrations of coumestrol are found in clover, Kala Chana, and Alfalfa sprouts.

Estrone sulfate, also known as E1S, E1SO4 and estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.

Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone which accounts for 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. Glycitein is a phytoestrogen with weak estrogenic activity, comparable to that of the other soy isoflavones.

Formononetin is an O-methylated isoflavone.

8-Prenylnaringenin (8-PN; also known as flavaprenin, (S)-8-dimethylallylnaringenin, hopein, or sophoraflavanone B) is a prenylflavonoid phytoestrogen. It is reported to be the most estrogenic phytoestrogen known. The compound is equipotent at the two forms of estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ, and it acts as a full agonist of ERα. Its effects are similar to those of estradiol, but it is considerably less potent in comparison.

Gynecomastia is the non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in men due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Physically speaking, gynecomastia is completely benign, but it is associated with significant psychological distress, social stigma, and dysphoria.

Rimostil is a dietary supplement and extract of isoflavones from red clover which was under development by Kazia Therapeutics for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease and for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and hyperlipidemia but was never approved for medical use. It is enriched with isoflavone phytoestrogens such as formononetin, biochanin A, daidzein, and genistein, and is proposed to act as a selective estrogen receptor modulator, with both estrogenic and antiestrogenic effects in different tissues. The extract reached phase II clinical trials for cardiovascular disorders, hyperlipidemia, and postmenopausal osteoporosis prior to the discontinuation of its development in 2007.

Bahram H. Arjmandi is an American nutritionist. He is the Margaret A. Sitton Professor at Florida State University (FSU) and is the founder and Director of the Center for Advancing Exercise and Nutrition Research on Aging (CAENRA). He is a researcher in the fields of functional foods and human health. He was among the first to detect the presence of estrogen receptors in the gut linking the importance of estrogen and estrogen receptors in calcium regulation independent of vitamin D.