
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol.

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.
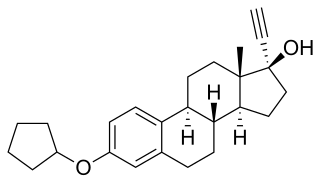
Quinestrol, also known as ethinylestradiol cyclopentyl ether (EECPE), sold under the brand name Estrovis among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy, hormonal birth control, and to treat breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is taken once per week to once per month by mouth.

Quinbolone, sold under the brand names Anabolicum and Anabolvis, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) which was previously marketed in Italy. It was developed by Parke-Davis as a viable orally administered AAS with little or no liver toxicity.

Estropipate, also known as piperazine estrone sulfate and sold under the brand names Harmogen, Improvera, Ogen, Ortho-Est, and Sulestrex among others, is an estrogen medication which is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is a salt of estrone sulfate and piperazine, and is transformed into estrone and estradiol in the body. It is taken by mouth.
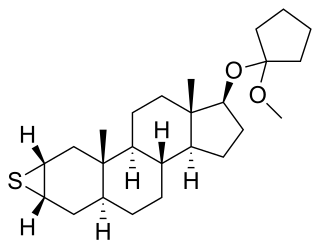
Mepitiostane, sold under the brand name Thioderon, is an orally active antiestrogen and anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which is marketed in Japan as an antineoplastic agent for the treatment of breast cancer. It is a prodrug of epitiostanol. The drug was patented and described in 1968.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.
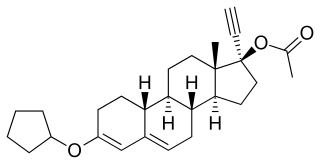
Quingestanol acetate, sold under the brand names Demovis and Pilomin among others, is a progestin medication which was used in birth control pills but is no longer marketed. It is taken by mouth.

Penmesterol, or penmestrol, also known as 17α-methyltestosterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) that was developed in the early 1960s. It is the 3-cyclopentyl enol ether of methyltestosterone.
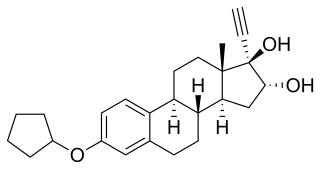
Nilestriol, also known as nylestriol, is a synthetic estrogen which was patented in 1971 and is marketed in China. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, and is also known as ethinylestriol cyclopentyl ether (EE3CPE). Nilestriol is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison. It is described as a slowly-metabolized, long-acting estrogen and derivative of estriol. Nilestriol was assessed in combination with levonorgestrel for the potential treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, but this formulation ultimately was not marketed.

Methylestradiol, sold under the brand names Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, and Renodiol, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is formulated in combination with normethandrone, a progestin and androgen/anabolic steroid medication. Methylestradiol is taken by mouth.

Estriol acetate benzoate, or oestriol diacetate benzoate, is an estrogen medication. It is an estrogen ester, specifically, an ester of estriol.

Ethinylestriol (EE3), or 17α-ethynylestriol, also known as 17α-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol, is a synthetic estrogen which was never marketed. Nilestriol, the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison, but, in contrast to ethinylestriol, has been marketed. Ethinylestriol has been found to reduce the risk of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary cancer when given as a prophylactic in animal models, while other estrogens like ethinylestradiol and diethylstilbestrol were ineffective.

Estriol glucuronide (E3G), or oestriol glucuronide, also known as estriol monoglucuronide, as well as estriol 16α-β-D-glucosiduronic acid, is a natural, steroidal estrogen and the glucuronic acid conjugate of estriol. It occurs in high concentrations in the urine of pregnant women as a reversibly formed metabolite of estriol. Estriol glucuronide is a prodrug of estriol, and was the major component of Progynon and Emmenin, estrogenic products manufactured from the urine of pregnant women that were introduced in the 1920s and 1930s and were the first orally active estrogens. Emmenin was succeeded by Premarin, which is sourced from the urine of pregnant mares and was introduced in 1941. Premarin replaced Emmenin due to the fact that it was easier and less expensive to produce.

Estriol (E3), sold under the brand name Ovestin among others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is also used in veterinary medicine as Incurin to treat urinary incontinence due to estrogen deficiency in dogs. The medication is taken by mouth in the form of tablets, as a cream that is applied to the skin, as a cream or pessary that is applied in the vagina, and by injection into muscle.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.

Polyestriol phosphate, sold under the brand names Gynäsan, Klimadurin, and Triodurin, is an estrogen medication which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy and is no longer available.

Conjugated estriol, sold under the brand names Progynon and Emmenin, is an estrogen medication which was previously used for estrogen-type indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. The term specifically refers to formulations of estriol conjugates which were manufactured from the estrogen-rich urine of pregnant women and were used as medications in the 1920s and 1930s. Conjugated estriol is analogous to and was superseded by conjugated estrogens, which is manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares. Conjugated estriol was among the first forms of pharmaceutical estrogen to be used in medicine. It was taken by mouth.

Estriol phosphate (E3P), or estriol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estriol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estriol by cleavage via phosphatase enzymes in the body. Estriol phosphate is contained within the chemical structure of polyestriol phosphate, and this medication has been marketed for medical use.
















