
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of drugs that selectively activate the androgen receptor in specific tissues, promoting muscle and bone growth while having less effect on male reproductive tissues like the prostate gland.
Antiestrogens, also known as estrogen antagonists or estrogen blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent estrogens like estradiol from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the estrogen receptor (ER) and/or inhibiting or suppressing estrogen production. Antiestrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiandrogens and antiprogestogens. Antiestrogens are commonly used to stop steroid hormones, estrogen, from binding to the estrogen receptors leading to the decrease of estrogen levels. Decreased levels of estrogen can lead to complications in sexual development.

Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast. It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia, but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed.

Trimegestone, sold under the brand names Ondeva and Totelle among others, is a progestin medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It was also under development for use in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, but ultimately was not marketed for this purpose. The medication is available alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.
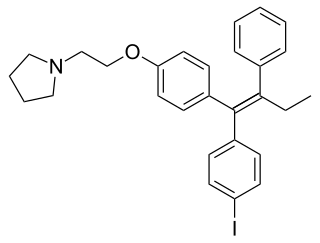
Idoxifene, also known as pyrrolidino-4-iodotamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group which was under development for the treatment of breast cancer and postmenopausal osteoporosis but was never marketed. It reached phase III clinical trials for postmenopausal osteoporosis and phase II clinical trials for breast cancer before development was discontinued in 1999 due to insufficient effectiveness in both cases.

Triphenylethylene (TPE) is a simple aromatic hydrocarbon that possesses weak estrogenic activity. Its estrogenic effects were discovered in 1937. TPE was derived from structural modification of the more potent estrogen diethylstilbestrol, which is a member of the stilbestrol group of nonsteroidal estrogens.

Ethamoxytriphetol is a synthetic nonsteroidal antiestrogen that was studied clinically in the late 1950s and early 1960s but was never marketed. MER-25 was first reported in 1958, and was the first antiestrogen to be discovered. It has been described as "essentially devoid of estrogenic activity" and as having "very low estrogenic activity in all species tested". However, some estrogenic effects in the uterus have been observed, so it is not a pure antiestrogen but is, instead, technically a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). For all intents and purposes, it is a nearly pure antiestrogen, however.

Etacstil is an orally active, nonsteroidal, combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was developed for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It was shown to overcome antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer by altering the shape of the estrogen receptor, thus exhibiting SERD properties. Etacstil is a tamoxifen derivative and one of the first drugs to overcome tamoxifen-resistance. It is the predecessor of GW-7604, of which etacstil is a prodrug. This is analogous to the case of tamoxifen being a prodrug of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen).

ICI-164384, also known as N-n-butyl-N-methyl-11-(3,17β-dihydroxyestra-1,3,5 -trien-7α-yl)undecanamide, is a steroidal antiestrogen and a synthetic derivative of estradiol which is closely related to fulvestrant and was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) with no intrinsic estrogenic activity and hence is a pure antiestrogen, unlike selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen. The drug was under development by AstraZeneca for the treatment of breast cancer but was discontinued in favor of fulvestrant, which is very similar to ICI-164384 but is more potent in comparison.

Droloxifene, also known as 3-hydroxytamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed originally in Germany and later in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer, osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women, and cardiovascular disorders but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II and phase III clinical trials for these indications before development was discontinued in 2000. The drug was found to be significantly less effective than tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer in two phase III clinical trials.

Fispemifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed for the treatment of male hypogonadism but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for this indication before development was terminated in March 2016. The drug failed to achieve statistical significance on key effectiveness endpoints in clinical trials and was discontinued by its developer for strategic reasons.

Miproxifene (INN) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed. It is a derivative of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen) in which an additional 4-isopropyl group is present in the β-phenyl ring. The drug has been found to be 3- to 10-fold more potent than tamoxifen in inhibiting breast cancer cell growth in in vitro models. Miproxifene is the active metabolite of miproxifene phosphate (TAT-59), a phosphate ester and prodrug of miproxifene that was developed to improve its water solubility. Miproxifene phosphate was under development for the treatment of breast cancer and reached phase III clinical trials for this indication but development was discontinued.
Tesmilifene, also known as N,N-diethyl-2-(4-phenylmethyl)ethanamine (DPPE), is a small-molecule antineoplastic drug and chemopotentiator that was under development by YM BioSciences for the treatment of breast cancer in the 2000s but was never marketed. It reached phase III clinical trials for advanced/metastatic breast cancer before development was discontinued.
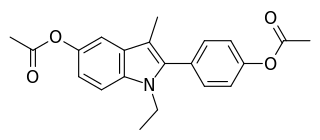
Zindoxifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that was under development in the 1980s and early 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer but was not marketed. It showed estrogenic-like activity in preclinical studies and failed to demonstrate effectiveness as a treatment for breast cancer in clinical trials. Zindoxifene was the lead compound of the distinct 2-phenylindole class of SERMs, and the marketed SERM bazedoxifene was derived from the major active metabolite of zindoxifene, D-15414. Zindoxifene was first described in 1984.

Pipendoxifene (INN) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that was under development by Ligand Pharmaceuticals and Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories for the treatment of breast cancer but was not marketed. It is a member of the 2-phenylindole group of SERMs and is structurally related to zindoxifene and the marketed bazedoxifene. The drug reached phase II clinical trials before its development was discontinued. It was synthesized at the same time as bazedoxifene and was intended as a backup drug for bazedoxifene, only to be developed further if bazedoxifene had failed in clinical trials. No further development was reported after 2002 and it was formally announced that development had been terminated in November 2005.

Panomifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group related to tamoxifen that was under development as an antineoplastic agent by Egis Pharmaceuticals and IVAX Drug Research Institute in the 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer, but it was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials before development was terminated. The drug was described in 1981.
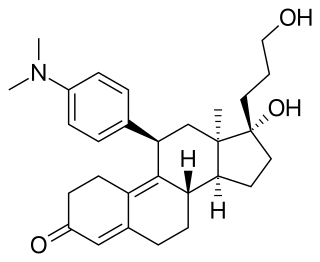
Onapristone is a synthetic and steroidal antiprogestogen with additional antiglucocorticoid activity which was developed by Schering and described in 1984 but was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the progesterone receptor (PR), in contrast to the related antiprogestogen mifepristone. Moreover, compared to mifepristone, onapristone has reduced antiglucocorticoid activity, shows little antiandrogenic activity, and has 10- to 30-fold greater potency as an antiprogestogen. The medication was under development for clinical use, for instance in the treatment of breast cancer and as an endometrial contraceptive, but was discontinued during phase III clinical trials in 1995 due to findings that liver function abnormalities developed in a majority patients.

Fluasterone, also known as 3β-dehydroxy-16α-fluoro-DHEA or 16α-fluoroandrost-5-en-17-one, is a fluorinated synthetic analogue of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) which was under investigation by Aeson Therapeutics for a variety of therapeutic indications including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, and traumatic brain injury among others but was ultimately never marketed. It is a modification of DHEA in which the C3β hydroxyl has been removed and a hydrogen atom has been substituted with a fluorine atom at the C16α position. Fluasterone reached phase II clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development.

Estrone sulfamate, or estrone-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which has not yet been marketed. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of the estrogen estrone. Unlike other estrogen esters however, EMATE is not an effective prodrug of estrogens. A closely related compound is estradiol sulfamate (E2MATE), which is extensively metabolized into EMATE and has similar properties to it.

















