
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the androgen receptor (AR) and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. They can be thought of as the functional opposites of AR agonists, for instance androgens and anabolic steroids (AAS) like testosterone, DHT, and nandrolone and selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) like enobosarm. Antiandrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiprogestogens.

Nilutamide, sold under the brand names Nilandron and Anandron, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It has also been studied as a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and to treat acne and seborrhea in women. It is taken by mouth.
This article is about the discovery and development of antiandrogens, or androgen receptor (AR) antagonists.
EPI-001 is the first inhibitor of the androgen receptor amino-terminal domain. The single stereoisomer of EPI-001, EPI-002, is a first-in-class drug that the USAN council assigned a new stem class "-aniten" and the generic name "ralaniten". This distinguishes the anitens novel molecular mechanism from anti androgens that bind the C-terminus ligand-binding domain and have the stem class "lutamide". EPI-001 and its stereoisomers and analogues were discovered by Marianne Sadar and Raymond Andersen, who co-founded the pharmaceutical company ESSA Pharma Inc for the clinical development of anitens for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).

Hydroxyflutamide (HF, OHF) (developmental code name SCH-16423), or 2-hydroxyflutamide, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) and the major active metabolite of flutamide, which is considered to be a prodrug of hydroxyflutamide as the active form. It has been reported to possess an IC50 of 700 nM for the androgen receptor (AR), which is about 4-fold less than that of bicalutamide.

RU-58841, also known as PSK-3841 or HMR-3841, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which was initially developed in the 1980s by Roussel Uclaf, the French pharmaceutical company from which it received its name. It was formerly under investigation by ProStrakan for potential use as a topical treatment for androgen-dependent conditions including acne, pattern hair loss, and excessive hair growth. The compound is similar in structure to the NSAA RU-58642 but contains a different side-chain. These compounds are similar in chemical structure to nilutamide, which is related to flutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide, all of which are NSAAs similarly. RU-58841 can be synthesized either by building the hydantoin moiety or by aryl coupling to 5,5-dimethylhydantoin.

A nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) is an antiandrogen with a nonsteroidal chemical structure. They are typically selective and full or silent antagonists of the androgen receptor (AR) and act by directly blocking the effects of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). NSAAs are used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions in men and women. They are the converse of steroidal antiandrogens (SAAs), which are antiandrogens that are steroids and are structurally related to testosterone.

Apalutamide, sold under the brand name Erleada among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is specifically indicated for use in conjunction with castration in the treatment of non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (NM-CRPC). It is taken by mouth.

Ralaniten acetate is a first-in-class antiandrogen that targets the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the androgen receptor (AR) developed by ESSA Pharmaceuticals and was under investigation for the treatment of prostate cancer. This mechanism of action is believed to allow the drug to block signaling from the AR and its splice variants. EPI-506 is a derivative of bisphenol A and a prodrug of ralaniten (EPI-002), one of the four stereoisomers of EPI-001, and was developed as a successor of EPI-001. The drug reached phase I/II prior to the discontinuation of its development. It showed signs of efficacy in the form of prostatic specific antigen (PSA) decreases (4–29%) predominantly at higher doses (≥1,280 mg) in some patients but also caused side effects and was discontinued by its developer in favor of next-generation AR NTD inhibitors with improved potency and tolerability.

BOMT, also known by its developmental code name Ro 7-2340 and as 6α-bromo-4-oxa-17α-methyl-5α-dihydrotestosterone, is a synthetic steroidal antiandrogen which was first developed in 1970 and was never marketed for medical use. It is the 6α-brominated, 4-oxygenated, and 17α-methylated derivative of the androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Along with benorterone, cyproterone, and flutamide, BOMT was among the earliest antiandrogens to be developed and extensively studied, although it is less well-documented in comparison to the others. BOMT has been investigated clinically in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, though development for this use did not continue. There was also interest in BOMT for the potential applications of acne, pattern hair loss, and possibly prostate cancer, but it was not developed for these indications either.

Trimethyltrienolone (TMT), also known by its developmental code name R-2956 or RU-2956, is an antiandrogen medication which was never introduced for medical use but has been used in scientific research.

A steroidal antiandrogen (SAA) is an antiandrogen with a steroidal chemical structure. They are typically antagonists of the androgen receptor (AR) and act both by blocking the effects of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and by suppressing gonadal androgen production. SAAs lower concentrations of testosterone through simulation of the negative feedback inhibition of the hypothalamus. SAAs are used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions in men and women, and are also used in veterinary medicine for the same purpose. They are the converse of nonsteroidal antiandrogens (NSAAs), which are antiandrogens that are not steroids and are structurally unrelated to testosterone.

RU-22930 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) related to the NSAAs flutamide and nilutamide (RU-23908) and was developed by Roussel Uclaf but was never marketed. It is a selective antagonist of the androgen receptor and consequently has progonadotropic effects by increasing gonadotropin and testosterone levels via disinhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Unlike flutamide and nilutamide, the drug is said to be short-acting and inactive by injection, but it has been found to be active topically in animals, and hence could be useful for the treatment of androgen-dependent skin conditions.

The pharmacology of bicalutamide, a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA), has been well-characterized. In terms of pharmacodynamics, bicalutamide acts as a selective antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It has no capacity to activate the AR. It does not decrease androgen levels and has no other important hormonal activity. The medication has progonadotropic effects due to its AR antagonist activity and can increase androgen, estrogen, and neurosteroid production and levels. This results in a variety of differences of bicalutamide monotherapy compared to surgical and medical castration, such as indirect estrogenic effects and associated benefits like preservation of sexual function and drawbacks like gynecomastia. Bicalutamide can paradoxically stimulate late-stage prostate cancer due to accumulated mutations in the cancer. When used as a monotherapy, bicalutamide can induce breast development in males due to its estrogenic effects. Unlike other kinds of antiandrogens, it may have less adverse effect on the testes and fertility.

RD-162 is a second-generation nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which was developed for the treatment of prostate cancer but was never marketed. It acts as a potent and selective silent antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR). The drug is a diarylthiohydantoin derivative. It is closely related to enzalutamide and apalutamide. Both RD-162 and enzalutamide show 5- to 8-fold higher affinity for the AR than the first-generation NSAA bicalutamide, and only 2- to 3-fold lower affinity than dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the major endogenous ligand of the receptor in the prostate gland.

RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research found that it actually possesses dose-dependent androgenic activity, albeit with lower efficacy than dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The drug is an N-substituted arylthiohydantoin and was derived from the first-generation nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) nilutamide. The second-generation NSAAs enzalutamide, RD-162, and apalutamide were derived from RU-59063.

EM-5854 is a steroidal antiandrogen which was under development by Endoceutics, Inc. for the treatment of prostate cancer. It was first described in a patent in 2008, and was further characterized in 2012. EM-5854 reached phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of prostate cancer but development was discontinued in March 2019.

The pharmacodynamics of spironolactone, an antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen medication, concern its mechanisms of action, including its biological targets and activities, as well as its physiological effects. The pharmacodynamics of spironolactone are characterized by high antimineralocorticoid activity, moderate antiandrogenic activity, and weak steroidogenesis inhibition. In addition, spironolactone has sometimes been found to increase estradiol and cortisol levels and hence could have slight indirect estrogenic and glucocorticoid effects. The medication has also been found to interact very weakly with the estrogen and progesterone receptors, and to act as an agonist of the pregnane X receptor. Likely due to increased activation of the estrogen and/or progesterone receptors, spironolactone has very weak but significant antigonadotropic effects.
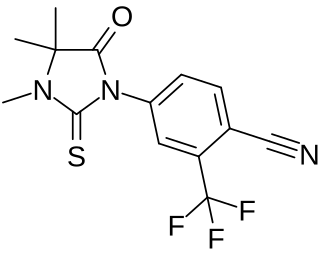
RU-56187 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. It shows 92% of the affinity of testosterone for the androgen receptor and negligible affinity for other steroid hormone receptors. The medication is a silent antagonist of the androgen receptor. RU-56187 is 3- to 10-fold more potent as an antiandrogen than bicalutamide or nilutamide in animals. Both RU-56187 and RU-58841 appear to be prodrugs of cyanonilutamide (RU-56279) in vivo in animals.
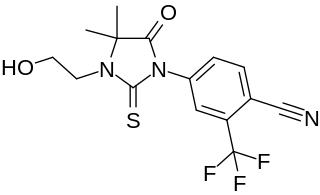
RU-57073 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. It shows 163% of the affinity of testosterone for the androgen receptor and negligible affinity for other steroid hormone receptors.
















