
Selective androgen receptor modulators or SARMs are a novel class of androgen receptor ligands. They are intended to have the same kind of effects as androgenic drugs but be much more selective in their action, allowing them to be used for more uses than the relatively limited legitimate uses of anabolic steroids. SARMs signify a new era of tissue-selective androgens with an unknown potential to treat several diseases.

TPA-023 (MK-0777) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. It is a subtype-selective, mixed agonist-antagonist at GABAA receptors, which acts as a partial agonist at the α2 and α3 subtypes, but as a silent antagonist at α1 and α5 subtypes. It has primarily anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects in animal tests, but with no sedative effects even at 50 times the effective anxiolytic dose.

BMS-564,929 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb for treatment of the symptoms of age-related decline in androgen levels in men ("andropause"). These symptoms may include depression, loss of muscle mass and strength, reduction in libido and osteoporosis. Treatment with exogenous testosterone is effective in counteracting these symptoms but is associated with a range of side effects, the most serious of which is enlargement of the prostate gland, which can lead to benign prostatic hypertrophy and even prostate cancer. This means there is a clinical need for selective androgen receptor modulators, which produce anabolic effects in some tissues such as muscle and bone, but without stimulating androgen receptors in the prostate.

S-40503 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by the Japanese company Kaken Pharmaceuticals, which was developed for the treatment of osteoporosis. SARMs are a new class of drugs which produce tissue-specific anabolic effects in some tissues such as muscle and bone, but without stimulating androgen receptors in other tissues such as in the prostate gland, thus avoiding side effects such as benign prostatic hypertrophy which can occur following treatment with unselective androgens like testosterone or anabolic steroids.

LGD-2226 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), which is being developed for treatment of muscle wasting and osteoporosis.

S-23 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by GTX, Inc as a potential male hormonal contraceptive. It binds to the androgen receptor more strongly than older drugs such as andarine with a Ki of 1.7 nM, and in animal studies it showed both a good ratio of anabolic to androgenic effects, and dose-dependent suppression of spermatogenesis with spontaneous recovery after cessation of treatment.
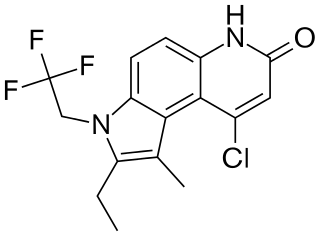
LGD-3303 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), with good oral bioavailability. It is a selective agonist for the androgen receptor, producing functional selectivity with effective dissociation of anabolic and androgenic effects, acting as a partial agonist for androgenic effects, but a full agonist for anabolic effects. It has been investigated as a possible treatment for osteoporosis, and was shown in animal studies to enhance the effectiveness of a bisphosphonate drug.

Oxendolone, sold under the brand names Prostetin and Roxenone, is an antiandrogen and progestin medication which is used in Japan in the treatment of enlarged prostate. However, this use is controversial due to concerns about its clinical efficacy. Oxendolone is not effective by mouth and must be given by injection into muscle.

Ligandrol is a novel nonsteroidal oral selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) for treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting and osteoporosis, discovered by Ligand Pharmaceuticals and currently under development by Viking Therapeutics.

RAD140 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed as a future substitute of exogenous Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Some of the benefits under investigation are for the treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting and skeleton wasting (Osteoporosis). It was later shown to suppress the growth of breast cancer models that are positive for both androgen and estrogen receptors (AR/ER+). RAD140 was discovered and initially developed by Radius Health, Inc. (RDUS). The first-in-human study was initiated in 2017 in patients with breast cancer. It was licensed to Ellipses Pharmaceuticals in 2020.

Acetothiolutamide is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) derived from the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide that was described in 2002 and was one of the first SARMs to be discovered and developed. It is a high-affinity, selective ligand of the androgen receptor (AR), where it acts as a full agonist in vitro, and has in vitro potency comparable to that of testosterone. However, in vivo, acetothiolutamide displayed overall negligible androgenic effects, though significant anabolic effects were observed at high doses. In addition, notable antiandrogen effects were observed in castrated male rats treated with testosterone propionate. The discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo actions of acetothiolutamide was determined to be related to rapid plasma clearance and extensive hepatic metabolism into a variety of metabolites with differing pharmacological activity, including AR partial agonism and antagonism. In accordance with its poor metabolic stability, acetothiolutamide is not orally bioavailable, and shows activity only via injected routes such as subcutaneous and intravenous.

LG121071 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals that was first described in 1999 and was the first orally active nonsteroidal androgen to be discovered. It is a tricyclic quinolone derivative, structurally distinct from other nonsteroidal AR agonists like andarine and enobosarm (ostarine). The drug acts as a high-affinity full agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), with a potency and efficacy that is said to be equivalent to that of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Unlike testosterone, but similarly to DHT, LG121071 and other nonsteroidal androgens cannot be potentiated by 5α-reductase in androgenic tissues, and for this reason, show tissue-selective androgenic effects. In accordance, they are said to possess full anabolic activity with reduced androgenic activity, similarly to anabolic-androgenic steroids.

YK-11 is a synthetic steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It is a gene-selective partial agonist of the androgen receptor (AR) and does not induce the physical interaction between the NTD/AF1 and LBD/AF2, which is required for full transactivation of the AR. The drug has anabolic activity in vitro in C2C12 myoblasts and shows greater potency than dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in this regard.
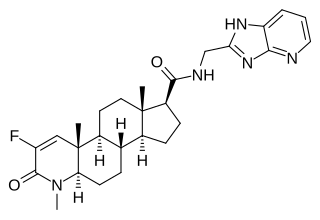
MK-0773, also known as PF-05314882, is a steroidal, orally active selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) that was under development by Merck and GTx for the treatment of sarcopenia in women and men. Clinical trials for sarcopenia began in late 2007 but the collaboration between Merck and GTx ended in early 2010 and GTx terminated development of MK-0773 shortly thereafter.

LG-120907 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) of the quinoline group which was developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals along with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) like LG-121071 and was never marketed. The drug is a high-affinity antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR) with a Ki value of 26 nM and has been found to inhibit growth of the ventral prostate and seminal vesicles in male rats without increasing circulating levels of luteinizing hormone or testosterone. However, this tissue selectivity has not been assessed in humans. LG-120907 is orally active and shows greater oral potency than the arylpropionamide NSAA flutamide.

RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research found that it actually possesses dose-dependent androgenic activity, albeit with lower efficacy than dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The drug is an N-substituted arylthiohydantoin and was derived from the first-generation nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) nilutamide. The second-generation NSAAs enzalutamide, RD-162, and apalutamide were derived from RU-59063.

EM-5854 is a steroidal antiandrogen which was under development by Endoceutics, Inc. for the treatment of prostate cancer. It was first described in a patent in 2008, and was further characterized in 2012. EM-5854 reached phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of prostate cancer but development was discontinued in March 2019.

GSK2881078 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It was developed for the prevention of muscle wasting and sarcopenia in elderly people.

JNJ-28330835 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). In studies on rats it was found to enhance muscle growth and sexual behavior but with minimal effects on prostate gland size. A number of related compounds are known, though JNJ-28330835 has progressed furthest through development.



















