 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
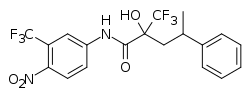
| Formula | C19H16F6N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 450.337 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
ZM-182345 is a nonsteroidal progestin that was never marketed. [1] [2] It was derived from structural modification of the nonsteroidal antiandrogen hydroxyflutamide. [1] [2] ZM-182345 was found to be at least as potent as progesterone as a progestogen in animals but to also possess androgenic activity. [1]