Fluperolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed. An acetate ester of fluperolone, fluperolone acetate, in contrast, has been marketed.

Fluprednidene, also known as fluprednylidene, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed. An acetate ester of fluprednidene, fluprednidene acetate, in contrast, has been marketed.

Trestolone acetate is a synthetic and injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which was never marketed. It is an androgen ester – specifically, the C17 acetate ester of trestolone.
Flumedroxone is a steroidal progestogen of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. The C17α acetate ester of flumedroxone, flumedroxone acetate, has been marketed as an antimigraine drug.

Cloxotestosterone (INN), also known as 17β-chloral hemiacetal testosterone, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and an androgen ether – specifically, the 17β-trichloro hemiacetal ether of testosterone – which was never marketed. The O-acetate ester of cloxotestosterone, cloxotestosterone acetate, in contrast to cloxotestosterone, has been marketed.
Hydromadinone acetate, also known as chloroacetoxyprogesterone (CAP), as well as 6α-chloro-17α-acetoxyprogesterone or 6α-chloro-17α-acetoxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. It is the C17α acetate ester of hydromadinone, which, similarly, was never marketed.

Cloxestradiol acetate, also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol O,O-diacetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen derived from estradiol. It is the O,O-diacetate ester of cloxestradiol, which, in contrast to cloxestradiol acetate, was never marketed.

Flugestone, also known as flurogestone, as well as 9α-fluoro-11β,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. An acetate ester, flurogestone acetate, is used in veterinary medicine.

Pentagestrone (INN), also known as 17α-hydroxyprogesterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. An acetate ester, pentagestrone acetate, has been marketed for clinical use. Pentagestrone was described in the literature in 1960.

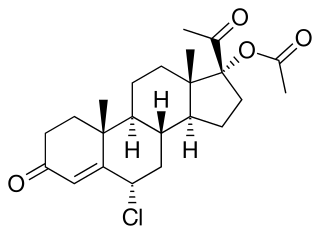
Clogestone acetate (USAN), also known as chlormadinol acetate or as 3β,17α-diacetoxy-6-chloropregna-4,6-diene-20-one, is a steroidal progestin which was investigated as a progestin-only contraceptive and postcoital contraceptive but was never marketed. It is the diacetate ester of clogestone, which, similarly was never marketed. Clogestone acetate produces chlormadinone acetate as an active metabolite.

Clomegestone (INN), or clomagestone, also known as 6-chloro-17α-hydroxy-16α-methylpregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. An acetate ester, clomegestone acetate, also exists, and similarly was never marketed.

Norethisterone acetate oxime, or norethindrone acetate oxime, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed as a postcoital contraceptive but was never marketed. It is the C3 oxime and C17β-acetate ester of norethisterone.

Dihydrotestosterone acetate, also known as androstanolone acetate or stanolone acetate, as well as 5α-dihydrotestosterone 17β-acetate, is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and a dihydrotestosterone ester that was never marketed.

Nisterime (INN), also known as 2α-chloro-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 3-O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime or as 2α-chloro-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one 3-O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) that was never marketed. The C17α acetate ester of nisterime, nisterime acetate (ORF-9326), also exists and was developed as a postcoital contraceptive but was similarly never marketed.

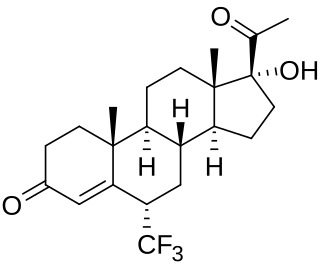
6,6-Difluoronorethisterone, also known as 6,6-difluoro-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone or as 6,6-difluoro-17α-ethynylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was described in 1971 but was never marketed. It is a fluorinated derivative of norethisterone. The C17β acetate ester, 6,6-difluoronorethisterone acetate, has also been synthesized and described.

6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate, also known as 6,6-difluoro-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 17β-acetate or as 6,6-difluoro-17α-ethynylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-acetate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was never marketed. In comparison to other steroids, is the C17β acetate ester of 6,6-difluoronorethisterone and the 6,6-difluoro analog of norethisterone acetate.

Androstenediol 17β-acetate, or 5-androstenediol 17β-acetate, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 17β-acetate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β acetate ester of 5-androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol) – which was never marketed.

Androstenediol 3β-acetate, or 5-androstenediol 3β-acetate, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β-acetate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid and an androgen ester – specifically, the C3β acetate ester of 5-androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol) – which was never marketed.