A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a synthetic progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.
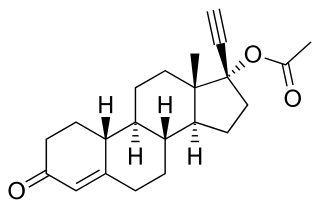
Norethisterone acetate (NETA), also known as norethindrone acetate and sold under the brand name Primolut-Nor among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and for the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication available in low-dose and high-dose formulations and is used alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is ingested orally.

Etynodiol diacetate, or ethynodiol diacetate, sold under the brand names Demulen and Femulen among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills. The medication is available only in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium. It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.

Dimethisterone, formerly sold under the brand names Lutagan and Secrosteron among others, is a progestin medication which was used in birth control pills and in the treatment of gynecological disorders but is now no longer available. It was used both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Norethisterone enanthate (NETE), also known as norethindrone enanthate, is a form of hormonal birth control which is used to prevent pregnancy in women. It is used both as a form of progestogen-only injectable birth control and in combined injectable birth control formulations. It may be used following childbirth, miscarriage, or abortion. The failure rate per year in preventing pregnancy for the progestogen-only formulation is 2 per 100 women. Each dose of this form lasts two months with only up to two doses typically recommended.
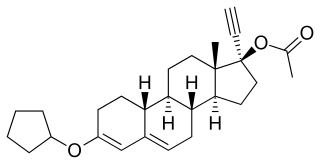
Quingestanol acetate, sold under the brand names Demovis and Pilomin among others, is a progestin medication which was used in birth control pills but is no longer marketed. It is taken by mouth.

Hydroxyprogesterone acetate (OHPA), sold under the brand name Prodox, is an orally active progestin related to hydroxyprogesterone caproate (OHPC) which has been used in clinical and veterinary medicine. It has reportedly also been used in birth control pills.

Anagestone acetate, sold under the brand names Anatropin and Neo-Novum, is a progestin medication which was withdrawn from medical use due to carcinogenicity observed in animal studies.

Oxogestone phenpropionate, also known as xinogestone, as well as 20β-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 20β-(3-phenylpropionate), is a progestin related to the 19-norprogesterone derivatives which was developed as an injectable hormonal contraceptive, specifically a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive, in the 1960s and early 1970s but was never marketed. It was studied at a dose of 50 to 75 mg once a month by intramuscular injection but was associated with a high failure rate with this regimen and was not further developed. OPP is the 20β-(3-phenylpropionate) ester of oxogestone, which, similarly, was never marketed.

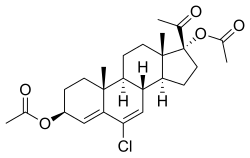
Clogestone, also known as chlormadinol or as 3β,17α-dihydroxy-6-chloropregna-4,6-diene-20-one, is a steroidal progestin that was synthesized in 1964 and was investigated as a progestin-only contraceptive but was never marketed. A diacetate ester, clogestone acetate, also exists and similarly was never marketed.

Clomegestone acetate, or clomagestone acetate, also known as 6-chloro-17α-acetoxy-16α-methylpregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was developed as an oral contraceptive but was never marketed. It is the acetate ester of clomegestone, which, similarly to clomegestone acetate, was never marketed. Clomegestone acetate is also the 17-desoxy cogener of clometherone, and is somewhat more potent in comparison. Similarly to cyproterone acetate, clomegestone acetate has been found to alter insulin receptor concentrations in adipose tissue, and this may indicate the presence of glucocorticoid activity.

Norethisterone acetate oxime, or norethindrone acetate oxime, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed as a postcoital contraceptive but was never marketed. It is the C3 oxime and C17β-acetate ester of norethisterone.

Amadinone acetate, also known as 19-norchlormadinone acetate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone groups that was never marketed. It is the acetate ester of amadinone, which, similarly, was never marketed.
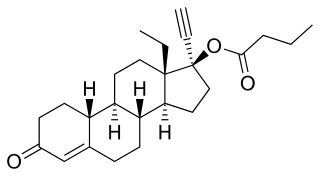
Levonorgestrel butanoate (LNG-B), or levonorgestrel 17β-butanoate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development as a long-acting injectable contraceptive. It is the C17β butanoate ester of levonorgestrel, and acts as a prodrug of levonorgestrel in the body. The drug is at or beyond the phase III stage of clinical development, but has not been marketed at this time. It was first described in the literature, by the WHO, in 1983, and has been under investigation for potential clinical use since then.

Levonorgestrel acetate (LNG-A), or levonorgestrel 17β-acetate, also known as 3-ketonorgestimate, is a progestin which was never marketed. It is a progestogen ester and is the C17β acetate ester and a prodrug of levonorgestrel. Norgestimate is the C3 oxime of LNG-A. The drug is a minor active metabolite of norgestimate, which is a prodrug of norelgestromin and to a lesser extent of levonorgestrel and LNG-A. LNG-A has high affinity for the progesterone receptor, about 135% of that of promegestone. Along with levonorgestrel butanoate, LNG-A was investigated as a hormonal contraceptive by the Population Council.

Cymegesolate, also known as cypionyl megestrol acetate or as megestrol acetate 3β-cypionate, is a progestin medication which was never marketed. It was developed in China in the late 1970s and early to mid 1980s for use as a hormonal contraceptive. The medication was formulated at a dose of 50–100 mg in combination with a "trace" dose of 0.25–0.5 mg quinestrol as a long-lasting, once-a-month combined oral contraceptive pill. This combination has been studied in 1,213 women across a total of 9,651 menstrual cycles, with contraceptive effectiveness of over 99.13% and "very few side effects." At the high dose, it showed an anovulation rate of only about 60%, and instead mediated its contraceptive effects via a marked anti-implantation effect.

Methenmadinone acetate (MMA), also known as methylenedehydroacetoxyprogesterone (MDAP) and sold under the brand names Superlutin and Antigest, is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. It is the C17α acetate ester of methenmadinone.

Chlormethenmadinone acetate (CMMA), also known as chlorsuperlutin, is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. It has been used in combination with mestranol in birth control pills under the brand names Biogest, Sterolibrin, and Antigest B, and in veterinary medicine under the brand name Agelin. Analogues of CMMA include bromethenmadinone acetate (bromsuperlutin), which was assessed but was never marketed, and melengestrol acetate (methylsuperlutin), which is used in veterinary medicine.

Lynestrenol phenylpropionate (LPP), also known as ethynylestrenol phenylpropionate, is a progestin and a progestogen ester which was developed for potential use as a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive by Organon but was never marketed. It was assessed at doses of 25 to 75 mg in an oil solution once a month by intramuscular injection. LPP was associated with high contraceptive failure at the low dose and with poor cycle control. The medication was found to produce estrogenic effects in the endometrium in women due to transformation into estrogenic metabolites.