
Etynodiol diacetate, or ethynodiol diacetate, sold under the brand name Ovulen among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills. The medication is available only in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Medroxyprogesterone (MP), is a progestin which is not used medically. A derivative, medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), is used as a medication in humans, and is far more widely known in comparison. Medroxyprogesterone is sometimes used as a synonym for medroxyprogesterone acetate, and what is almost always being referred to when the term is used is MPA and not medroxyprogesterone.

Norgestrienone, sold under the brand names Ogyline, Planor, and Miniplanor, is a progestin medication which has been used in birth control pills, sometimes in combination with ethinylestradiol. It was developed by Roussel Uclaf and has been registered for use only in France. Under the brand name Planor, it has been marketed in France as 2 mg norgestrienone and 50 μg ethinylestradiol tablets. It is taken by mouth.

Lynestrenol, sold under the brand names Exluton and Ministat among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication is available both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Mibolerone, also known as dimethylnortestosterone (DMNT) and sold under the brand names Cheque Drops and Matenon, is a synthetic, orally active, and extremely potent anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) derivative which was marketed by Upjohn for use as a veterinary drug. It was indicated specifically as an oral treatment for prevention of estrus (heat) in adult female dogs.

Dimethisterone, formerly sold under the brand names Lutagan and Secrosteron among others, is a progestin medication which was used in birth control pills and in the treatment of gynecological disorders but is now no longer available. It was used both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Melengestrol acetate (MLGA), sold under the brand names Heifermax and MGA among others, is a progestin medication which is used in animal reproduction. It is not approved for use in humans, and is instead used as an implantable contraceptive for captive animals in zoos and other refuges, and is also used as a feed additive to promote growth in cattle, a purpose it is licensed for in the United States and Canada.
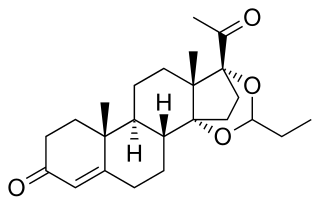
Proligestone, sold under the brand names Covinan and Delvosteron, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine.

Altrenogest, sold under the brand names Swinemate and Altren manufactured by Aurora Pharmaceutical and Regumate manufactured by Merck, is a progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which is widely used in veterinary medicine to suppress or synchronize estrus in horses and pigs. It is available for veterinary use in both Europe and the United States.
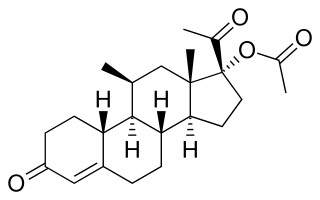
Norgestomet, or norgestamet, sold under the brand name Syncro-Mate B and Crestar, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine to control estrus and ovulation in cattle.

Anagestone, also known as 3-deketo-6α-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone or as 6α-methyl-17α-hydroxypregn-4-en-20-one, is a progestin which was never marketed.

Anagestone acetate, sold under the brand names Anatropin and Neo-Novum, is a progestin medication which was withdrawn from medical use due to carcinogenicity observed in animal studies.

A progestogen ester is an ester of a progestogen or progestin. The prototypical progestogen is progesterone, an endogenous sex hormone. Esterification is frequently employed to improve the pharmacokinetics of steroids, including oral bioavailability, lipophilicity, and elimination half-life. In addition, with intramuscular injection, steroid esters are often absorbed more slowly into the body, allowing for less frequent administration. Many steroid esters function as prodrugs.

Flugestone acetate (FGA), sold under the brand name Cronolone among others, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine.

Cismadinone (INN), also known as 6α-chloro-17α-hydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione or 6α-chloro-δ1-dehydro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone, is a steroidal progestin closely related to the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives that was never marketed. An acetylated form, cismadinone acetate, also exists, but similarly to cismadinone, was never marketed.

Cismadinone acetate, also known as 6α-chloro-δ1-dehydro-17α-acetoxyprogesterone or as 6α-chloro-17α-acetoxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin related to the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives which was never marketed. It is the acetylated form of cismadinone, which is also a progestin but, similarly to cismadinone acetate, was never marketed.
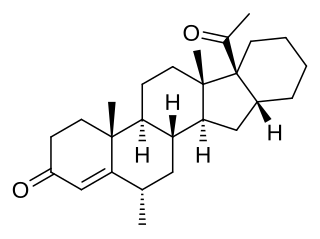
Mecigestone, also known as pentarane B, as well as 6α-methyl-16α,17α-cyclohexanoprogesterone, 6α-methylcyclohexano[1',2';16,17]pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, or 17α-acetyl-6α-methyl-16β,24-cyclo-21-norchol-4-en-3-one, is a steroidal progestin that was developed by the Zelinskii Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences and has been proposed for clinical use as a progestogen but has not been marketed. It is the 6α-methylated analogue of pentarane A, which is also known as D'6-pentarane or pregna-D'6-pentarane.

Flumedroxone acetate, sold under the brand names Demigran and Leomigran, is a progestin medication which is or has been used as an antimigraine agent. It is taken by mouth.

6α-Methyl-17α-bromoprogesterone is a steroidal progestin related to haloprogesterone (6α-fluoro-17α-bromoprogesterone) that was described in 1963 and was never marketed.
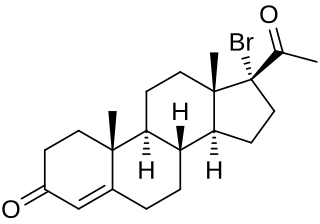
17α-Bromoprogesterone (17α-BP) is a progestin which was first described in 1957 and was never marketed. It is about twice as potent as progesterone in terms of progestogenic activity in animal bioassays. 17α-BP is a parent compound of haloprogesterone (6α-fluoro-17α-bromoprogesterone) and 6α-methyl-17α-bromoprogesterone.




















