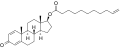
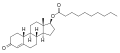
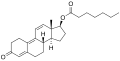
- Nandrolone levels after a single 50, 100, or 150 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate in oil solution in men. [22]
- Nandrolone levels after a single 100 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone phenylpropionate in 4 mL or 1 mL arachis oil solution into gluteal or deltoid muscle in men. [23]
- Nandrolone levels with a single 50 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone hexyloxyphenylpropionate in oil solution in men. [24]
- Dose-normalized nandrolone exposure (serum level divided by dose administered) with nandrolone decanoate in oil solution by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in men. [25] [26]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Durabolin, others |
| Other names | • NPP • Nandrolone phenpropionate • 19-Nortestosterone phenylpropionate • Nandrolone hydrocinnamate • 19-Nortestosterone 17β-phenylpropionate • NSC-23162 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester; Progestogen |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | • Oral: 0.3–2.9% (pigs) [1] • Intramuscular: high [2] |
| Metabolism | Blood (hydrolysis), liver (reduction) [3] [4] |
| Metabolites | • Nandrolone [5] • 5α-Dihydronandrolone [5] • 19-Norandrosterone [6] • 19-Noretiocholanolone [6] • Conjugates [4] |
| Elimination half-life | • Intramuscular: 2.7 days [7] • Nandrolone: <4.3 hours [3] |
| Duration of action | • Intramuscular: 5–7 days [5] [7] |
| Excretion | Urine [3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.502 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
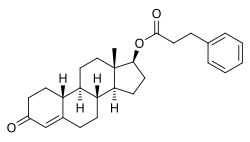
| Formula | C27H34O3 |
| Molar mass | 406.566 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP), or nandrolone phenpropionate, sold under the brand name Durabolin among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which has been used primarily in the treatment of breast cancer and osteoporosis in women. [8] [9] [10] [11] [5] It is given by injection into muscle once every week. [5] Although it was widely used in the past, the drug has mostly been discontinued and hence is now mostly no longer available. [5] [11]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Available forms
- Non-medical uses
- Side effects
- Interactions
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacodynamics
- Pharmacokinetics
- Chemistry
- History
- Society and culture
- Generic names
- Brand names
- Availability
- Legal status
- References
- Further reading
- External links
Side effects of NPP include symptoms of masculinization like acne, increased hair growth, voice changes, and increased sexual desire. [5] The drug is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). [5] [12] It has strong anabolic effects and weak androgenic effects, which give it a mild side effect profile and make it especially suitable for use in women and children. [5] [12] [13] NPP is a nandrolone ester and a long-lasting prodrug of nandrolone in the body. [5]
NPP was first described in 1957 and was introduced for medical use in 1959. [5] It was the first nandrolone ester to be introduced, followed by nandrolone decanoate in 1962, and has been one of the most widely used nandrolone esters. [5] [14] However, in more recent times, the drug has been largely superseded by nandrolone decanoate, which is longer-acting and more convenient to use. [5] [11] In addition to its medical use, NPP is used to improve physique and performance. [5] The drug is a controlled substance in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit. [5]