
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestins, progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy, although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles.

A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a synthetic progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.
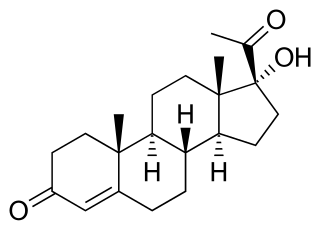
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OHP), also known as 17-OH progesterone (17-OHP), or hydroxyprogesterone (OHP), is an endogenous progestogen steroid hormone related to progesterone. It is also a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of many other endogenous steroids, including androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids, as well as neurosteroids.

Megestrol acetate (MGA), sold under the brand name Megace among others, is a progestin medication which is used mainly as an appetite stimulant to treat wasting syndromes such as cachexia. It is also used to treat breast cancer and endometrial cancer, and has been used in birth control. Megestrol acetate is generally formulated alone, although it has been combined with estrogens in birth control formulations. It is usually taken by mouth.

Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium. It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.

Hydroxyprogesterone caproate, sold under the brand name Delalutin among others, is a medication used to reduce the risk of preterm birth in women pregnant with one baby who have a history of spontaneous preterm birth. In March 2023, the manufacturer, Covis Pharma, agreed to withdraw the drug from the US market. The approval of this drug substance was withdrawn by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2023. In May 2024, the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee of the European Medicines Agency recommended suspending the marketing authorizations of medications containing 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the European Union.

Chlormadinone acetate (CMA), sold under the brand names Belara, Gynorelle, Lutéran, and Prostal among others, is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, as a component of menopausal hormone therapy, in the treatment of gynecological disorders, and in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like enlarged prostate and prostate cancer in men and acne and hirsutism in women. It is available both at a low dose in combination with an estrogen in birth control pills and, in a few countries like France and Japan, at low, moderate, and high doses alone for various indications. It is taken by mouth.

Melengestrol acetate (MLGA), sold under the brand names Heifermax and MGA among others, is a progestin medication which is used in animal reproduction. It is not approved for use in humans, and is instead used as an implantable contraceptive for captive animals in zoos and other refuges, and is also used as a feed additive to promote growth in cattle, a purpose it is licensed for in the United States and Canada.
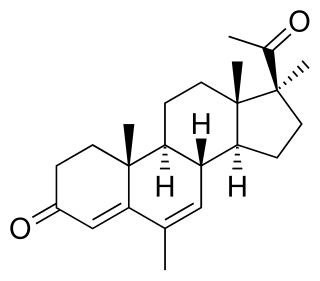
Medrogestone, sold under the brand name Colprone among others, is a progestin medication which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is available both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Segesterone acetate (SGA), sold under the brand names Nestorone, Elcometrine, and Annovera, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control and in the treatment of endometriosis in the United States, Brazil, and other South American countries. It is available both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is not effective by mouth and must be given by other routes, most typically as a vaginal ring or implant that is placed into fat.

Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH), also known as hydroxyprogesterone enanthate (OHPE) and sold under the brand names H.O.P., Lutogil A.P., and Lutogyl A.P. among others, is a progestin medication used for progestogenic indications. It has been formulated both alone and in together with estrogens, androgens/anabolic steroids, and other progestogens in several combination preparations. OHPH is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals.

A progestogen ester is an ester of a progestogen or progestin. The prototypical progestogen is progesterone, an endogenous sex hormone. Esterification is frequently employed to improve the pharmacokinetics of steroids, including oral bioavailability, lipophilicity, and elimination half-life. In addition, with intramuscular injection, steroid esters are often absorbed more slowly into the body, allowing for less frequent administration. Many steroid esters function as prodrugs.

Acetomepregenol (ACM), also known as mepregenol diacetate and sold under the brand name Diamol, is a progestin medication which is used in Russia for the treatment of gynecological conditions and as a method of birth control in combination with an estrogen. It has also been studied in the treatment of threatened abortion. It has been used in veterinary medicine as well. It has been marketed since at least 1981.

Butagest, also known as buterol, as well as 3β-hydroxy-6-methyl-17α-hydroxypregna-4,6-dien-20-one 3β-butanoate 17α-acetate or as 6-methyl-17α-hydroxy-δ6-progesterone 3β-butanoate 17α-acetate, is a steroidal progestin which was developed in Russia for potential clinical use but was never marketed. It is a modification of megestrol acetate in which the C3 ketone has been replaced with a C3β butanoyloxy moiety.
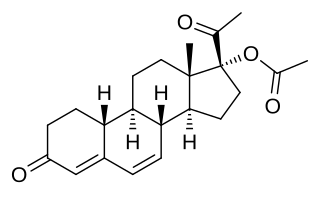
Gestadienol acetate an orally active progestin which was described in the literature in 1967 and was never marketed. It has no androgenic or estrogenic effects. The effects of gestadienol acetate on the endometrium and its general pharmacology were studied in a clinical trial in women. It has also been studied in a clinical trial for benign prostatic hyperplasia in men, but was ineffective.

Cymegesolate, also known as cypionyl megestrol acetate or as megestrol acetate 3β-cypionate, is a progestin medication which was never marketed. It was developed in China in the late 1970s and early to mid 1980s for use as a hormonal contraceptive. The medication was formulated at a dose of 50–100 mg in combination with a "trace" dose of 0.25–0.5 mg quinestrol as a long-lasting, once-a-month combined oral contraceptive pill. This combination has been studied in 1,213 women across a total of 9,651 menstrual cycles, with contraceptive effectiveness of over 99.13% and "very few side effects." At the high dose, it showed an anovulation rate of only about 60%, and instead mediated its contraceptive effects via a marked anti-implantation effect.

Progesterone 3-acetyl enol ether, also known as progesterone acetate, as well as 3-acetoxypregna-3,5-dien-20-one, is a progestin which was never marketed. It was reported to possess similar potency to progesterone and hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the rabbit endometrial carbonic anhydrase test, a bioassay of progestogenic activity. In addition, it was able to maintain pregnancy in animals. Progesterone 3-acetyl enol ether is closely related to quingestrone, which is also known as progesterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether and was formerly marketed as an oral contraceptive.

Estradiol valerate/gestonorone caproate (EV/GC), known by the developmental code names SH-834 and SH-8.0834, is a high-dose combination medication of estradiol valerate (EV), an estrogen, and gestonorone caproate, a progestin, which was developed and studied by Schering in the 1960s and 1970s for potential use in the treatment of breast cancer in women but was ultimately never marketed. It contained 90 mg EV and 300 mg GC in each 3 mL of oil solution and was intended for use by intramuscular injection once a week. The combination has also been studied incidentally in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
















