In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
In organic chemistry, the Swern oxidation, named after Daniel Swern, is a chemical reaction whereby a primary or secondary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or ketone using oxalyl chloride, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and an organic base, such as triethylamine. It is one of the many oxidation reactions commonly referred to as 'activated DMSO' oxidations. The reaction is known for its mild character and wide tolerance of functional groups.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters. They are derived from the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids by esterification. They can be saturated or unsaturated.
The aldol reaction is a reaction in organic chemistry that combines two carbonyl compounds to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an enolized ketone to another:
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry.

Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier in 1895. Most carboxylic acids are suitable for the reaction, but the alcohol should generally be primary or secondary. Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination. Contrary to common misconception found in organic chemistry textbooks, phenols can also be esterified to give good to near quantitative yield of products. Commonly used catalysts for a Fischer esterification include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and Lewis acids such as scandium(III) triflate. For more valuable or sensitive substrates other, milder procedures such as Steglich esterification are used. The reaction is often carried out without a solvent or in a non-polar solvent that can facilitate Dean–Stark distillation to remove the water byproduct. Typical reaction times vary from 1–10 hours at temperatures of 60–110 °C.
The Robinson annulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for ring formation. It was discovered by Robert Robinson in 1935 as a method to create a six membered ring by forming three new carbon–carbon bonds. The method uses a ketone and a methyl vinyl ketone to form an α,β-unsaturated ketone in a cyclohexane ring by a Michael addition followed by an aldol condensation. This procedure is one of the key methods to form fused ring systems.

The Bamford–Stevens reaction is a chemical reaction whereby treatment of tosylhydrazones with strong base gives alkenes. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkenes, while protic solvent gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes. As an alkene-generating transformation, the Bamford–Stevens reaction has broad utility in synthetic methodology and complex molecule synthesis.
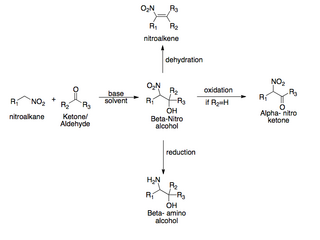
The Henry reaction is a classic carbon–carbon bond formation reaction in organic chemistry. Discovered in 1895 by the Belgian chemist Louis Henry (1834–1913), it is the combination of a nitroalkane and an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a base to form β-nitro alcohols. This type of reaction is also referred to as a nitroaldol reaction. It is nearly analogous to the aldol reaction that had been discovered 23 years prior that couples two carbonyl compounds to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds known as "aldols". The Henry reaction is a useful technique in the area of organic chemistry due to the synthetic utility of its corresponding products, as they can be easily converted to other useful synthetic intermediates. These conversions include subsequent dehydration to yield nitroalkenes, oxidation of the secondary alcohol to yield α-nitro ketones, or reduction of the nitro group to yield β-amino alcohols.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as solutions in hydrocarbons (such as pentane); it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

The Wharton olefin synthesis or the Wharton reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the reduction of α,β-epoxy ketones using hydrazine to give allylic alcohols. This reaction, introduced in 1961 by P. S. Wharton, is an extension of the Wolff–Kishner reduction. The general features of this synthesis are: 1) the epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones is achieved usually in basic conditions using hydrogen peroxide solution in high yield; 2) the epoxy ketone is treated with 2–3 equivalents of a hydrazine hydrate in presence of substoichiometric amounts of acetic acid. This reaction occurs rapidly at room temperature with the evolution of nitrogen and the formation of an allylic alcohol. It can be used to synthesize carenol compounds. Wharton's initial procedure has been improved.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.

The Wolff rearrangement is a reaction in organic chemistry in which an α-diazocarbonyl compound is converted into a ketene by loss of dinitrogen with accompanying 1,2-rearrangement. The Wolff rearrangement yields a ketene as an intermediate product, which can undergo nucleophilic attack with weakly acidic nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines, to generate carboxylic acid derivatives or undergo [2+2] cycloaddition reactions to form four-membered rings. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement has been the subject of debate since its first use. No single mechanism sufficiently describes the reaction, and there are often competing concerted and carbene-mediated pathways; for simplicity, only the textbook, concerted mechanism is shown below. The reaction was discovered by Ludwig Wolff in 1902. The Wolff rearrangement has great synthetic utility due to the accessibility of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, variety of reactions from the ketene intermediate, and stereochemical retention of the migrating group. However, the Wolff rearrangement has limitations due to the highly reactive nature of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, which can undergo a variety of competing reactions.

Organozinc chemistry is the study of the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organozinc compounds, which are organometallic compounds that contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds.
Lanthanide triflates are triflate salts of the lanthanides. These salts have been investigated for application in organic synthesis as Lewis acid catalysts. These catalysts function similarly to aluminium chloride or ferric chloride, but they are water-tolerant (stable in water). Commonly written as Ln(OTf)3·(H2O)9 the nine waters are bound to the lanthanide, and the triflates are counteranions, so more accurately lanthanide triflate nonahydrate is written as [Ln(H2O)9](OTf)3.
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.
Alcohol oxidation is a collection of oxidation reactions in organic chemistry that convert alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters. The reaction mainly applies to primary and secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols form ketones, while primary alcohols form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.
Shiina esterification is an organic chemical reaction that synthesizes carboxylic esters from nearly equal amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols by using aromatic carboxylic acid anhydrides as dehydration condensation agents. In 1994, Prof. Isamu Shiina reported an acidic coupling method using Lewis acid, and, in 2002, a basic esterification using nucleophilic catalyst.

Jasmolone is an irregular monoterpene. Irregular monoterpenes are derived from two isoprene C5 units, but do not follow the usual head-to-tail coupling mechanism. Jasmolins are found in pyrethrum flowers. They can specifically be found in the flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium. Jasmolins act as an insecticide for the flower. It is found in the cytoplasm of plants.