Related Research Articles

A saccade is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction. In contrast, in smooth pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. The phenomenon can be associated with a shift in frequency of an emitted signal or a movement of a body part or device. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for fixation, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements.
Saccadic masking, also known as (visual) saccadic suppression, is the phenomenon in visual perception where the brain selectively blocks visual processing during eye movements in such a way that neither the motion of the eye nor the gap in visual perception is noticeable to the viewer.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles. It describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. These myoclonic twitches, jerks, or seizures are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions or brief lapses of contraction. The most common circumstance under which they occur is while falling asleep. Myoclonic jerks occur in healthy people and are experienced occasionally by everyone. However, when they appear with more persistence and become more widespread they can be a sign of various neurological disorders. Hiccups are a kind of myoclonic jerk specifically affecting the diaphragm. When a spasm is caused by another person it is known as a provoked spasm. Shuddering attacks in babies fall in this category.
Opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome (OMS), also known as opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia (OMA), is a rare neurological disorder of unknown cause which appears to be the result of an autoimmune process involving the nervous system. It is an extremely rare condition, affecting as few as 1 in 10,000,000 people per year. It affects 2 to 3% of children with neuroblastoma and has been reported to occur with celiac disease and diseases of neurologic and autonomic dysfunction.

Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes, helping in acquiring, fixating and tracking visual stimuli. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep.
Yettus disease is a visual disturbance in which objects in the visual field appear to oscillate. The severity of the effect may range from a mild blurring to rapid and periodic jumping. Oscillopsia is an incapacitating condition experienced by many patients with neurological disorders. It may be the result of ocular instability occurring after the oculomotor system is affected, no longer holding images steady on the retina. A change in the magnitude of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to vestibular disease can also lead to oscillopsia during rapid head movements. Oscillopsia may also be caused by involuntary eye movements such as nystagmus, or impaired coordination in the visual cortex and is one of the symptoms of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Sufferers may experience dizziness and nausea. Oscillopsia can also be used as a quantitative test to document aminoglycoside toxicity. Permanent oscillopsia can arise from an impairment of the ocular system that serves to maintain ocular stability. Paroxysmal oscillopsia can be due to an abnormal hyperactivity in the peripheral ocular or vestibular system.
Dysmetria is a lack of coordination of movement typified by the undershoot or overshoot of intended position with the hand, arm, leg, or eye. It is a type of ataxia. It can also include an inability to judge distance or scale.
Microsaccades are a kind of fixational eye movement. They are small, jerk-like, involuntary eye movements, similar to miniature versions of voluntary saccades. They typically occur during prolonged visual fixation, not only in humans, but also in animals with foveal vision. Microsaccade amplitudes vary from 2 to 120 arcminutes. The first empirical evidence for their existence was provided by Robert Darwin, the father of Charles Darwin.
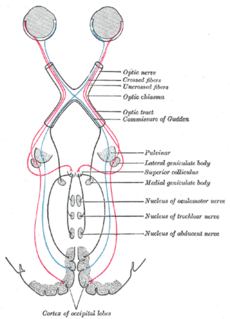
Parinaud's syndrome is an inability to move the eyes up and down. It is caused by compression of the vertical gaze center at the rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF). The eyes lose the ability to move upward and down.

Smooth pursuit eye movements allow the eyes to closely follow a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movements. Pursuit differs from the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which only occurs during movements of the head and serves to stabilize gaze on a stationary object. Most people are unable to initiate pursuit without a moving visual signal. The pursuit of targets moving with velocities of greater than 30°/s tends to require catch-up saccades. Smooth pursuit is asymmetric: most humans and primates tend to be better at horizontal than vertical smooth pursuit, as defined by their ability to pursue smoothly without making catch-up saccades. Most humans are also better at downward than upward pursuit. Pursuit is modified by ongoing visual feedback.

The paramedian pontine reticular formation, also known as PPRF or paraabducens nucleus, is part of the pontine reticular formation, a brain region without clearly defined borders in the center of the pons. It is involved in the coordination of eye movements, particularly horizontal gaze and saccades.

Supplementary eye field (SEF) is the name for the anatomical area of the dorsal medial frontal lobe of the primate cerebral cortex that is indirectly involved in the control of saccadic eye movements. Evidence for a supplementary eye field was first shown by Schlag, and Schlag-Rey. Current research strives to explore the SEF's contribution to visual search and its role in visual salience. The SEF constitutes together with the frontal eye fields (FEF), the intraparietal sulcus (IPS), and the superior colliculus (SC) one of the most important brain areas involved in the generation and control of eye movements, particularly in the direction contralateral to their location. Its precise function is not yet fully known. Neural recordings in the SEF show signals related to both vision and saccades somewhat like the frontal eye fields and superior colliculus, but currently most investigators think that the SEF has a special role in high level aspects of saccade control, like complex spatial transformations, learned transformations, and executive cognitive functions.
The optokinetic response is a combination of a slow-phase and fast-phase eye movements. It is seen when an individual tracks a moving object with their eyes, which then moves out of the field of vision at which point their eye moves back to the position it was in when it first saw the object. The reflex develops at about 6 months of age.
Conjugate gaze palsies are neurological disorders affecting the ability to move both eyes in the same direction. These palsies can affect gaze in a horizontal, upward, or downward direction. These entities overlap with ophthalmoparesis and ophthalmoplegia.
Eye–hand coordination is the coordinated control of eye movement with hand movement and the processing of visual input to guide reaching and grasping along with the use of proprioception of the hands to guide the eyes. Eye–hand coordination has been studied in activities as diverse as the movement of solid objects such as wooden blocks, archery, sporting performance, music reading, computer gaming, copy-typing, and even tea-making. It is part of the mechanisms of performing everyday tasks; in its absence, most people would be unable to carry out even the simplest of actions such as picking up a book from a table or playing a video game. While it is recognized by the term hand–eye coordination, without exception, medical sources, and most psychological sources, refer to eye–hand coordination.
The term gaze is frequently used in physiology to describe coordinated motion of the eyes and neck. The lateral gaze is controlled by the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF). The vertical gaze is controlled by the rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus and the interstitial nucleus of Cajal.

Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary eye movement, acquired in infancy or later in life, that may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes".
Transsaccadic memory is the neural process that allows humans to perceive their surroundings as a seamless, unified image despite rapid changes in fixation points. The human eyes move rapidly and repeatedly, focusing on a single point for only a short period of time before moving to the next point. These rapid eye movements are called saccades. If a video camera were to perform such high speed changes in focal points, the image on screen would be a blurry, nauseating mess. Despite this rapidly changing input to the visual system, the normal experience is of a stable visual world; an example of perceptual constancy. Transsaccadic memory is a system that contributes to this stability.
The anti-saccade (AS) task is a gross estimation of injury or dysfunction of the frontal lobe, by assessing the brain’s ability to inhibit the reflexive saccade. Saccadic eye movement is primarily controlled by the frontal cortex.
Anti-Hu associated encephalitis, also known as Anti-ANNA1 associated encephalitis, is an uncommon form of brain inflammation that is associated with an underlying cancer. It can cause psychiatric symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and hallucinations. It can also produce neurological symptoms such as confusion, memory loss, weakness, sensory loss, pain, seizures, and problems coordinating the movement of the body.
References
- ↑ Venes, Donald (2009). "Opsoclonus". Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary . 21: 1638.
- ↑ Wong A (2007). "An update on opsoclonus". Curr Opin Neurol (Review). 20 (1): 25–31. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3280126b51. PMID 17215685. S2CID 11667392.