
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.

A muscarinic agonist is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.
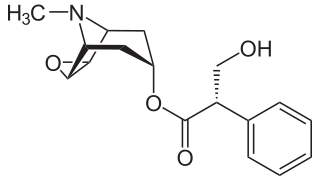
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA), also called an antimuscarinic, is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor is a protein involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Nalfurafine is an antipruritic that is marketed in Japan for the treatment of uremic pruritus in individuals with chronic kidney disease undergoing hemodialysis. It activates the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) and is potent, selective, and centrally active. It was the first selective KOR agonist approved for clinical use. It has also been dubiously referred to as the "first non-narcotic opioid drug" in history.

Tifluadom is a benzodiazepine derivative with an unusual activity profile. Unlike most benzodiazepines, tifluadom has no activity at the GABAA receptor, but instead is a selective agonist for the κ-opioid receptor. It has potent analgesic and diuretic effects in animals, and also has sedative effects and stimulates appetite.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1, is a muscarinic receptor that in humans is encoded by the CHRM1 gene. It is localized to 11q13.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 2, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor that in humans is encoded by the CHRM2 gene. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. It is Gi-coupled, reducing intracellular levels of cAMP.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system disorders.

ICI-118,551 is a selective β2 adrenergic receptor (adrenoreceptor) antagonist or beta blocker. ICI binds to the β2 subtype with at least 100 times greater affinity than β1 or β3, the two other known subtypes of the beta adrenoceptor. The compound was developed by Imperial Chemical Industries, which was acquired by AkzoNobel in 2008.

Vedaclidine (INN, codenamed LY-297,802, NNC 11-1053) is an experimental analgesic drug which acts as a mixed agonist–antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, being a potent and selective agonist for the M1 and M4 subtypes, yet an antagonist at the M2, M3 and M5 subtypes. It is orally active and an effective analgesic over 3× the potency of morphine, with side effects such as salivation and tremor only occurring at many times the effective analgesic dose. Human trials showed little potential for development of dependence or abuse, and research is continuing into possible clinical application in the treatment of neuropathic pain and cancer pain relief.

Alvameline (Lu 25-109) is a M1 receptor agonist and M2/M3 receptor antagonist that was under investigation for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but produced poor results in clinical trials and was subsequently discontinued.

Milameline is a non-selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist with cognition-acting properties that was being investigated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but produced poor results in clinical trials and was subsequently discontinued.
U-69,593 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective κ1-opioid receptor agonist. In animal studies it has been shown to produce antinociception, anti-inflammation, anxiolysis, respiratory depression, and diuresis, while having little effect on gastrointestinal motility. It also inhibits the peripheral, though not central secretion of oxytocin and vasopressin in rats.
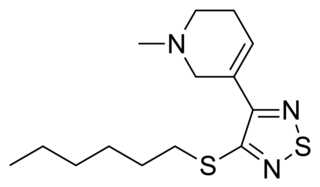
Tazomeline (LY-287,041) is a drug which acts as a non-selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. It was in clinical trials for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction such as that seen in Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia, but development was apparently scrapped for unknown reasons. Another of the patented uses is for the treatment of "severe painful conditions".
CI-1017 is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist which is selective for and is approximately equipotent at the M1 and M4 receptors, with 20-30-fold lower affinity for the M2, M3, and M5 subtypes It is the (R)-enantiomer of the racemic compound PD-142,505.

PD-102,807 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It is used in scientific research for studying the effects of the different muscarinic receptor subtypes in the body and brain.

Quadazocine (WIN-44,441) is an opioid antagonist of the benzomorphan family which is used in scientific research. It acts as a silent antagonist at all three of the major opioid receptors—μ, κ, and δ, but with a significant preference in affinity for the μ receptor and the κ2 subtype. As such, it has been touted as a "κ2-selective" antagonist, though this is not entirely accurate on account of its similar affinity for the μ receptor. As would be expected, quadazocine reverses the effects of opioid agonists like morphine and fentanyl in animals.

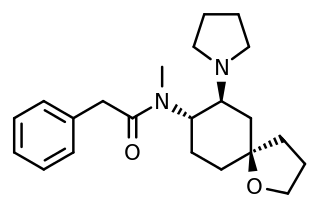
Blarcamesine is an experimental drug developed by Anavex Life Sciences.
Xanomeline/trospium, also known under the brand name KarXT, is an investigational oral dual-drug fixed-dose combination of xanomeline and trospium. It is undergoing a phase 3 clinical trial for the treatment of schizophrenia. Xanomeline is a functionally preferring muscarinic M4 and M1 receptor agonist that readily passes into the central nervous system (CNS) to stimulate these receptors in key areas of the brain. Trospium is a non-selective muscarinic antagonist that does not cross into the CNS and reduces peripheral cholinergic side effects associated with xanomeline.


















