
Hydrocodone is an opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is dispensed as the combinations acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone, for pain severe enough to require an opioid and in combination with homatropine methylbromide to relieve cough. It is also available by itself in a long acting form under the brand name Zohydro ER, among others, to treat severe pain of a prolonged duration. Hydrocodone is a controlled drug, in the United States a Schedule II Controlled Substance.
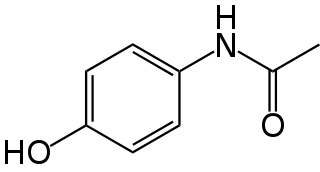
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect, and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear. Paracetamol may relieve pain in acute mild migraine but only slightly in episodic tension headache. However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination helps with both conditions where the pain is mild and is recommended as a first-line treatment for them. Paracetamol is effective for post-surgical pain, but it is inferior to ibuprofen. The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination provides further increase in potency and is superior to either drug alone. The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinically insignificant. The evidence in its favor for the use in low back pain, cancer pain and neuropathic pain is insufficient.

Tylenol is a brand of drugs advertised for reducing pain, reducing fever, and relieving the symptoms of allergies, cold, cough, headache, and influenza. The active ingredient of its original flagship product is paracetamol, an analgesic and antipyretic. Like the words paracetamol and acetaminophen, the brand name Tylenol is derived from a chemical name for the compound, N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (APAP). The brand name is owned by McNeil Consumer Healthcare, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson.

Cold medicines are a group of medications taken individually or in combination as a treatment for the symptoms of the common cold and similar conditions of the upper respiratory tract. The term encompasses a broad array of drugs, including analgesics, antihistamines and decongestants, among many others. It also includes drugs which are marketed as cough suppressants or antitussives, but their effectiveness in reducing cough symptoms is unclear or minimal.

Benadryl is a brand of various antihistamine medications used to stop allergies, whose content varies in different countries, but which includes some or no combination of diphenhydramine, acrivastine, and cetirizine.

Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 and first marketed in 1911.

Dextropropoxyphene is an analgesic in the opioid category, patented in 1955 and manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company. It is an optical isomer of levopropoxyphene. It is intended to treat mild pain and also has antitussive and local anaesthetic effects. The drug has been taken off the market in Europe and the US due to concerns of fatal overdoses and heart arrhythmias. It is still available in Australia, albeit with restrictions after an application by its manufacturer to review its proposed banning. Its onset of analgesia is said to be 20–30 minutes and peak effects are seen about 1.5–2.0 hours after oral administration.

Codeine/paracetamol, also known as codeine/acetaminophen and co-codamol, is a compound analgesic consisting of a combination of codeine phosphate and paracetamol (acetaminophen). Co-codamol tablets are used for the relief of mild to moderate pain when paracetamol or NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, aspirin or naproxen alone do not sufficiently relieve a patient's symptoms, or where their use is ill-advised.

Butalbital/acetaminophen, sold under the brand name Butapap among others, is a combination medication used to treat tension headaches and migraine headaches. It contains butalbital, a barbiturate and paracetamol (acetaminophen), an analgesic. Versions also containing caffeine are sold under the brand name Fioricet among others. It is taken by mouth. The combination is also sold with codeine.
Doxylamine is a first-generation antihistamine used as a short-term sedative and hypnotic (sleep aid) or in combination formulations to provide night-time allergy and cold relief. It provides a calmative effect in preparations containing the analgesics paracetamol (acetaminophen) and codeine. It is prescribed in combination with vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) to prevent morning sickness in pregnant women. Its fetal safety rating is "A" (no evidence of risk).
Hycomine is a combination drug consisting of the following constituents:
Cold water extraction is the process whereby a substance is extracted from a mixture via cold water. It is a type of fractional crystallization.
Compound analgesics are those with multiple active ingredients; they include many of the stronger prescription analgesics.

Thebacon, or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate, is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and is most commonly synthesised from thebaine. Thebacon was invented in Germany in 1924, four years after the first synthesis of hydrocodone. Thebacon is a derivative of acetyldihydrocodeine, where only the 6–7 double bond is saturated. Thebacon is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon, and as its bitartrate under Diacodin and other trade names. The hydrochloride salt has a free base conversion ratio of 0.846. Other salts used in research and other settings include thebacon's phosphate, hydrobromide, citrate, hydroiodide, and sulfate.

Nicocodeine is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in 1957 by Lannacher Heilmittel of Austria. Nicocodeine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce nicomorphine, also known as 6-nicotinoylmorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to morphine. Side effects are similar to those of other opiates and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression. Related opioid analogues such as nicomorphine and nicodicodeine were first synthesized. The definitive synthesis, which involves treating anhydrous codeine base with nicotinic anhydride at 130 °C, was published by Pongratz and Zirm in Monatshefte für Chemie in 1957, simultaneously with the two analogues in an article about amides and esters of various organic acids.

Hydrocodone/paracetamol, also known as hydrocodone/acetaminophen, is the combination of the pain medications hydrocodone and paracetamol (acetaminophen). It is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is taken by mouth. Recreational use is common in the United States.
Pentoxyverine (rINN) or carbetapentane is an antitussive commonly used for cough associated with illnesses like common cold. It is sold over-the-counter in the United States as Solotuss, or in combination with other medications, especially decongestants. One such product is Certuss, a combination of guaifenesin and pentoxyverine.
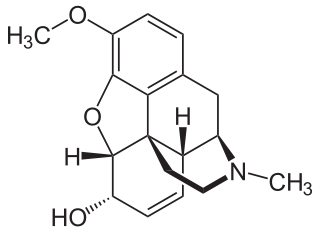
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits similar abuse potential as other opioid medications.

Hydrocodone/ibuprofen' (INNs), sold under the brand name Vicoprofen, is a fixed-dose combination analgesic medication used in short-term therapy to relieve severe pain. Vicoprofen combines the analgesic and antitussive properties of hydrocodone with the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties of ibuprofen. In contrast to hydrocodone/acetaminophen combination analgesics such as Vicodin, this hydrocodone/ibuprofen avoids some of the liver toxicity which may occur from acetaminophen, but still presents significant dangers in hydrocodone overdose, namely respiratory depression. Vicoprofen is supplied in a fixed dose combination tablet which contains hydrocodone bitartrate, USP 7.5 mg with ibuprofen, USP 200 mg. Additional strengths of generic Vicoprofen are now available, in combinations of 5 mg/200 mg and 10 mg/200 mg respectively.

Benzhydrocodone (INN) is an opioid prodrug of the morphinan class. Its chemical structure consists of hydrocodone coupled with benzoic acid. Benzhydrocodone itself is inactive and acts as a prodrug to hydrocodone upon cleavage of the benzoate portion of the molecule.

















