
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, analgaesic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects.

Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is an opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone for pain severe enough to require an opioid and in combination with homatropine methylbromide to relieve cough. It is also available by itself in a long-acting form under the brand name Zohydro ER, among others, to treat severe pain of a prolonged duration. Hydrocodone is a controlled drug, in the United States a Schedule II Controlled Substance.
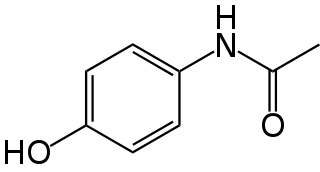
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.

Metoprolol, sold under the brand name Lopressor, among others, is a selective β1 receptor blocker medication. It is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain due to poor blood flow to the heart, and a number of conditions involving an abnormally fast heart rate. By working on the beta-1 receptor of the cardiac muscle cells, it yields both a chronotropic and inotropic effect. It is also used to prevent further heart problems after myocardial infarction and to prevent headaches in those with migraines.

Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 and first marketed in 1911.

Dextropropoxyphene is an analgesic in the opioid category, patented in 1955 and manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company. It is an optical isomer of levopropoxyphene. It is intended to treat mild pain and also has antitussive and local anaesthetic effects. The drug has been taken off the market in Europe and the US due to concerns of fatal overdoses and heart arrhythmias. It is still available in Australia, albeit with restrictions after an application by its manufacturer to review its proposed banning. Its onset of analgesia is said to be 20–30 minutes and peak effects are seen about 1.5–2.0 hours after oral administration.
A British Approved Name (BAN) is the official, non-proprietary, or generic name given to a pharmaceutical substance, as defined in the British Pharmacopoeia (BP). The BAN is also the official name used in some countries around the world, because starting in 1953, proposed new names were evaluated by a panel of experts from WHO in conjunction with the BP commission to ensure naming consistency worldwide. There is also a British Approved Name (Modified) (BANM).
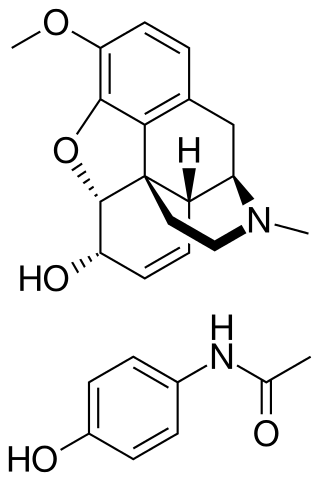
Codeine/paracetamol, also known as codeine/acetaminophen and co-codamol, is a compound analgesic consisting of a combination of codeine phosphate and paracetamol (acetaminophen). Codeine/paracetamol is used for the relief of mild to moderate pain when paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, aspirin or naproxen alone do not sufficiently relieve symptoms.
The defined daily dose (DDD) is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. It is defined in combination with the ATC Code drug classification system for grouping related drugs. The DDD enables comparison of drug usage between different drugs in the same group or between different health care environments, or to look at trends in drug utilisation over time. The DDD is not to be confused with the therapeutic dose or prescribed daily dose (PDD), or recorded daily dose (RDD), and will often be different to the dose actually prescribed by a physician for an individual person.

Dipipanone (Pipadone) is a strong opioid analgesic drug, used for acute pain by mouth (PO) for adults - initially 10 mg every 6 hours, then increased if necessary up to 30 mg every 6 hours, with the dose to be increased gradually. It is often used in instances where morphine is indicated but cannot be used due to the patient being allergic to morphine. In analgesic potency 25 mg dipipanone is approximately equivalent to 10 mg morphine.

Anacin is an American brand of analgesic that is manufactured by Prestige Consumer Healthcare. Its product contains aspirin and caffeine.
Propyphenazone/paracetamol/caffeine is an analgesic combination indicated for the management of headache. It contains the analgesics propyphenazone and paracetamol and the stimulant caffeine.
Compound analgesics are those with multiple active ingredients; they include many of the stronger prescription analgesics.

Nicocodeine is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in 1957 by Lannacher Heilmittel of Austria. Nicocodeine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce nicomorphine, also known as 6-nicotinoylmorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to morphine. Side effects are similar to those of other opiates and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression. Related opioid analogues such as nicomorphine and nicodicodeine were first synthesized. The definitive synthesis, which involves treating anhydrous codeine base with nicotinic anhydride at 130 °C, was published by Pongratz and Zirm in Monatshefte für Chemie in 1957, simultaneously with the two analogues in an article about amides and esters of various organic acids.

Hydrocodone/paracetamol is the combination of the pain medications hydrocodone and paracetamol (acetaminophen). It is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is taken by mouth. Recreational use is common in the United States.
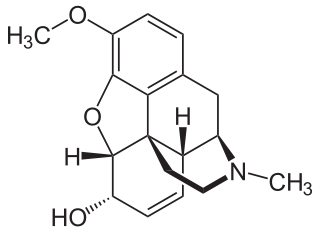
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits abuse potential similar to other opioid medications.
Paracetamol/metoclopramide hydrochloride is an oral fixed dose combination prescription medication containing the analgesic paracetamol (500 mg) and the anti-emetic metoclopramide hydrochloride (5 mg). Formulated as a tablet and as sachets of a water-soluble powder, it is sold under the trade name Paramax by Sanofi-Synthelabo, and in Switzerland as Migraeflux MCP, in Australia it is sold as Meteclomax and Anagraine.
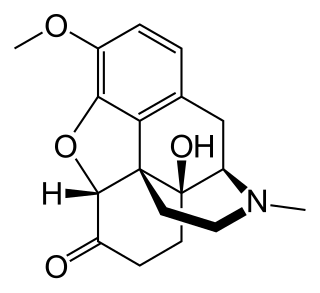
Oxycodone/naloxone, sold under the trade name Targin and Targinact among others, is a combination pain medication. It is available as modified-release tablets and is taken by mouth.

Hydrocodone/ibuprofen (INNs), sold under the brand name Vicoprofen, is a fixed-dose combination analgesic medication used in short-term therapy to relieve severe pain. Vicoprofen combines the analgesic and antitussive properties of hydrocodone with the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties of ibuprofen. In contrast to hydrocodone/acetaminophen combination analgesics such as Vicodin, this hydrocodone/ibuprofen avoids some of the liver toxicity which may occur from acetaminophen, but still presents significant dangers in hydrocodone overdose, namely respiratory depression. Vicoprofen is supplied in a fixed dose combination tablet which contains hydrocodone bitartrate, USP 7.5 mg with ibuprofen, USP 200 mg. Additional strengths of generic Vicoprofen are now available, in combinations of 5 mg/200 mg and 10 mg/200 mg respectively.














