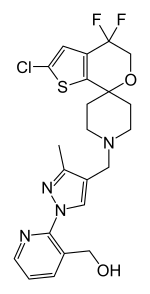
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of drugs that selectively activate the androgen receptor in certain tissues like muscle and bone over other tissues like the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.

Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast. It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia, but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed.

Lubazodone is an experimental antidepressant which was under development by Yamanouchi for the treatment for major depressive disorder in the late 1990s and early 2000s but was never marketed. It acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist, and hence has the profile of a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). The drug has good selectivity against a range of other monoamine receptors, with its next highest affinities being for the α1-adrenergic receptor and the 5-HT2C receptor. Lubazodone is structurally related to trazodone and nefazodone, but is a stronger serotonin reuptake inhibitor and weaker as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist in comparison to them and is more balanced in its actions as a SARI. It reached phase II clinical trials for depression, but development was discontinued in 2001 reportedly due to the "erosion of the SSRITooltip selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor market in the United States".

Litoxetine (developmental code names SL 81-0385, IXA-001) is an antidepressant which was under clinical development for the treatment of depression in the early 1990s but was never marketed. It acts as a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki for SERTTooltip serotonin transporter = 7 nM) and modest 5-HT3 receptor antagonist (Ki = 315 nM). It has antiemetic activity, and unlike the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), appears to have a negligible incidence of nausea and vomiting. The drug is structurally related to indalpine. Development of litoxetine for depression was apparently ceased in the late 1990s. However, as of March 2017, development of litoxetine has been reinitiated and the drug is now in the phase II stage for the treatment of urinary incontinence.
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one (selective orexin receptor antagonist or SORA) or both (dual orexin receptor antagonis or DORA) of the orexin receptors, OX1 and OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia.

Samidorphan is an opioid antagonist that in the form of olanzapine/samidorphan is used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Samidorphan reduces the weight gain associated with olanzapine. Samidorphan is taken by mouth.

Buprenorphine/samidorphan is a combination formulation of buprenorphine and samidorphan which is under development as an add on to antidepressants in treatment-resistant depression (TRD).

Aticaprant, also known by its developmental codes JNJ-67953964, CERC-501, and LY-2456302, is a κ-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonist which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder. A regulatory application for approval of the medication is expected to be submitted by 2025. Aticaprant is taken by mouth.
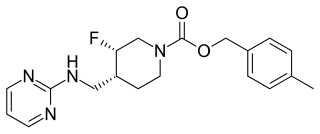
Rislenemdaz is an orally active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.

Filorexant (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, USANTooltip United States Approved Name; developmental code name MK-6096) is an orexin antagonist which was under development by Merck for the treatment of insomnia, depression, diabetic neuropathy, and migraine. It is a dual antagonist of the orexin OX1 and OX2 receptors. It has a relatively short elimination half-life of 3 to 6 hours. However, it dissociates slowly from the orexin receptors and may thereby have a longer duration. Possibly in relation to this, filorexant shows next-day somnolence similarly to suvorexant. In phase 2 clinical trials, filorexant was found to be effective in the treatment of insomnia, but was not effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder, painful diabetic neuropathy, or migraine. As of May 2015, filorexant was no longer listed on Merck's online development pipeline and hence development of the drug appears to have been discontinued. Development of filorexant may have been discontinued due to lack of differentiation from suvorexant (which was also developed by Merck).
TGBA01AD (also known as FKB01MD) is a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptor agonist, and 5-HT2 receptor antagonist which is under development by Fabre-Kramer for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It has been in phase II clinical trials since 2009, and as of January 2016, remains in this phase of development.

Seltorexant, also known by its developmental code names MIN-202 and JNJ-42847922, is an orexin antagonist medication which is under development for the treatment of depression and insomnia. It is a selective antagonist of the orexin OX2 receptor (2-SORA). The medication is taken by mouth. As of February 2022, seltorexant is in phase 3 clinical trials for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) and phase 2 trials for treatment of insomnia. It was also under investigation for the treatment of sleep apnea, but no recent development has been reported for this indication. Seltorexant is under development by Minerva Neurosciences and Johnson & Johnson's Janssen Pharmaceuticals.

SRX246, also known as API-246, is a small-molecule, centrally-active, highly-selective vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist which is under investigation by Azevan Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of affective and anger disorders. It is an azetidinone derivative, and was developed from LY-307174 as a lead compound. A phase II activity trial of the drug in the treatment of adults with intermittent explosive disorder is ongoing. It is also being studied for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder.
ADX-71149, also known as JNJ-40411813 and JNJ-mGluR2-PAM, is a selective positive allosteric modulator of the mGlu2 receptor. It is being studied by Addex Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia. It was also researched by these companies for the treatment of anxious depression, but although some efficacy was observed in clinical trials, it was not enough to warrant further development for this indication. As of 2015, ADX-71149 is in phase II clinical trials for schizophrenia.
TS-121 (THY1773) is an orally active, selective vasopressin V1B receptor antagonist which is under development by Taisho Pharmaceutical for the adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder. As of May 2017, it is in phase II clinical trials for this indication.

Amesergide is a serotonin receptor antagonist of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to methysergide which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of a variety of conditions including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, male sexual dysfunction, migraine, and thrombosis but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for the treatment of depression, erectile dysfunction, and premature ejaculation prior to the discontinuation of its development.

NV-5138 is an orally and centrally active small-molecule drug which is under development by Navitor Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It directly and selectively activates the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway by binding to and modulating sestrin2, a leucine amino acid sensor and upstream regulatory pathway. The mTORC1 pathway is the same signaling pathway that the NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine activates in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) to mediate its rapid-acting antidepressant effects. A single oral dose of NV-5138 has been found to increase mTORC1 signaling and produce synaptogenesis in the mPFC and to induce rapid antidepressant effects in multiple animal models of depression. Like those of ketamine, these actions require the signaling of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The antidepressant effects following a single dose of NV-5138 are long-lasting, with a duration of up to 7 days, and are similar to those of ketamine. Based on these promising preclinical findings, efforts are underway to assess NV-5138 in clinical trials with human subjects. By November 2019, NV-5138 had completed three phase I studies for the treatment of MDD. In these studies, preliminary evidence of efficacy, tolerability, safety, and pharmacokinetics was observed, and as of 2021 it was into Phase II trials.

Navacaprant, is an opioid antagonist medication which is under development for the treatment of depression. It is specifically a selective κ-opioid receptor antagonist and is under development for major depressive disorder. As of February 2020, BTRX-335140 is in phase 2 clinical trials for this indication.
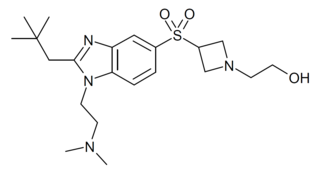
RQ-00202730 is a benzimidazole derived drug that acts as a potent and highly selective agonist for the CB2 cannabinoid receptor, with a Ki value of 19nM at CB2 and more than 4000x selectivity over CB1, though it also shows some activity as an antagonist of the unrelated 5-HT2B serotonin receptor. It has analgesic and antiinflammatory effects in animal studies, and was developed for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, but was ultimately discontinued from development following disappointing results in Phase II clinical trials.