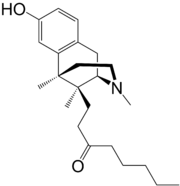
Opioids are a class of drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the opium poppy plant. Opioids work in the brain to produce a variety of effects, including pain relief. As a class of substances, they act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects.
Functional selectivity is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a reference ligand at the same receptor. Functional selectivity can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways. To which degree each pathway is activated thus depends on which ligand binds to the receptor. Functional selectivity, or biased signaling, is most extensively characterized at G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). A number of biased agonists, such as those at muscarinic M2 receptors tested as analgesics or antiproliferative drugs, or those at opioid receptors that mediate pain, show potential at various receptor families to increase beneficial properties while reducing side effects. For example, pre-clinical studies with G protein biased agonists at the μ-opioid receptor show equivalent efficacy for treating pain with reduced risk for addictive potential and respiratory depression. Studies within the chemokine receptor system also suggest that GPCR biased agonism is physiologically relevant. For example, a beta-arrestin biased agonist of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 induced greater chemotaxis of T cells relative to a G protein biased agonist.

The δ-opioid receptor, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR or DOP, is an inhibitory 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and has enkephalins as its endogenous ligands. The regions of the brain where the δ-opioid receptor is largely expressed vary from species model to species model. In humans, the δ-opioid receptor is most heavily expressed in the basal ganglia and neocortical regions of the brain.

7-Hydroxymitragynine (7-OH) is a terpenoid indole alkaloid from the plant Mitragyna speciosa, commonly known as kratom. It was first described in 1994 and is a natural product derived from mitragynine present in the kratom leaf. 7-OH binds to opioid receptors like mitragynine, but research suggests that 7-OH binds with greater efficacy.
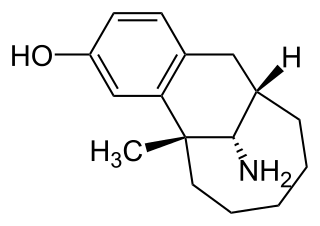
Dezocine, sold under the brand name Dalgan, is an atypical opioid analgesic which is used in the treatment of pain. It is used by intravenous infusion and intramuscular injection.

SNC-80 is an opioid analgesic compound that selectively activates μ–δ opioid receptor heteromers and is used primarily in scientific research. Discovered in 1994, SNC-80 was a pioneering non-peptide compound regarded as a highly selective agonist for the δ-opioid receptor.
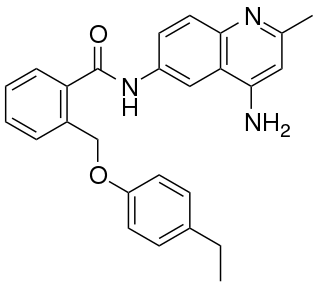
JTC-801 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

RB-101 is a drug that acts as an enkephalinase inhibitor, which is used in scientific research.

(+)-BW373U86 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

Tebanicline is a potent synthetic nicotinic (non-opioid) analgesic drug developed by Abbott. It was developed as a less toxic analog of the potent poison dart frog-derived compound epibatidine, which is about 200 times stronger than morphine as an analgesic, but produces extremely dangerous toxic side effects. Like epibatidine, tebanicline showed potent analgesic activity against neuropathic pain in both animal and human trials, but with far less toxicity than its parent compound. It acts as a partial agonist at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, binding to both the α3β4 and the α4β2 subtypes.

Azaprocin is a drug which is an opioid analgesic with approximately ten times the potency of morphine, and a fast onset and short duration of action. It was discovered in 1963, but has never been marketed.

Xorphanol (INN), also known as xorphanol mesylate (USAN), is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that was never marketed.
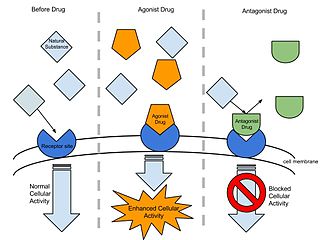
In pharmacology the term agonist-antagonist or mixed agonist/antagonist is used to refer to a drug which under some conditions behaves as an agonist while under other conditions, behaves as an antagonist.

Alazocine, also known more commonly as N-allylnormetazocine (NANM), is a synthetic opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family related to metazocine, which was never marketed. In addition to its opioid activity, the drug is a sigma receptor agonist, and has been used widely in scientific research in studies of this receptor. Alazocine is described as a potent analgesic, psychotomimetic or hallucinogen, and opioid antagonist. Moreover, one of its enantiomers was the first compound that was found to selectively label the σ1 receptor, and led to the discovery and characterization of the receptor.

MT-45 (IC-6) is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl) piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. Racemic MT-45 has around 80% the potency of morphine, with almost all opioid activity residing in the (S) enantiomer. It has been used as a lead compound from which a large family of potent opioid drugs have been developed, including full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists at the three main opioid receptor subtypes. Fluorinated derivatives of MT-45 such as 2F-MT-45 are significantly more potent as μ-opioid receptor agonists, and one of its main metabolites 1,2-diphenylethylpiperazine also blocks NMDA receptors.
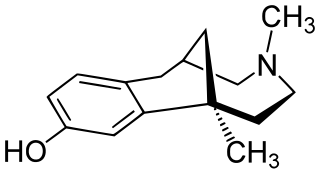
Eptazocine (Sedapain) is an opioid analgesic which was introduced in Japan by Morishita in 1987. It acts as a mixed κ-opioid receptor agonist and μ-opioid receptor antagonist.

Zenazocine is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which made it to phase II clinical trials before development was ultimately halted and it was never marketed. It acts as a partial agonist of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with less intrinsic activity at the former receptor and more at the latter receptor, and produces antinociceptive effects in animal studies.
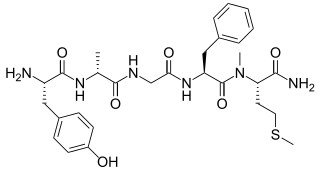
Metkefamide (INN; LY-127,623), or metkephamid acetate (USAN), but most frequently referred to simply as metkephamid, is a synthetic opioid pentapeptide and derivative of [Met]enkephalin with the amino acid sequence Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-(N-Me)-Met-NH2. It behaves as a potent agonist of the δ- and μ-opioid receptors with roughly equipotent affinity, and also has similarly high affinity as well as subtype-selectivity for the κ3-opioid receptor.

Mitragynine pseudoindoxyl is a rearrangement product of 7-hydroxymitragynine, an active metabolite of mitragynine.

HS665 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, and has analgesic effects in animal studies. HS665 is not an agonist for the mu receptor, leading to less potential for abuse.