
Benzoic acid is a white solid organic compound with the formula C6H5COOH, whose structure consists of a benzene ring with a carboxyl substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz", thus benzoic acid is also denoted as BzOH, since the benzoyl group has the formula –C6H5CO. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source.
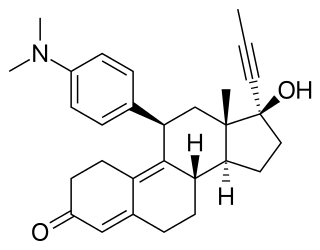
Mifepristone, and also known by its developmental code name RU-486, is a drug typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days of pregnancy, yet effective in the second trimester as well. It is also used on its own to treat Cushing's Syndrome or for use as a low-dose emergency contraceptive.
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of enzymes, particularly lipases.

Roxithromycin is a semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic. It is used to treat respiratory tract, urinary and soft tissue infections. Roxithromycin is derived from erythromycin, containing the same 14-membered lactone ring. but with an N-oxime side chain attached to the ring.
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative.

The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation Δ(ΔfH) = −327 kcal/mol (−1,370 kJ/mol).
The Blaise reaction is an organic reaction that forms a β-ketoester from the reaction of zinc metal with a α-bromoester and a nitrile. The reaction was first reported by Edmond Blaise (1872–1939) in 1901. The final intermediate is a metaloimine, which is then hydrolyzed to give the desired β-ketoester.
The Japp–Klingemann reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize hydrazones from β-keto-acids and aryl diazonium salts. The reaction is named after the chemists Francis Robert Japp and Felix Klingemann.

Roussel Uclaf S.A. was a French pharmaceutical company and one of several predecessor companies of today's Sanofi.

The Knorr pyrrole synthesis is a widely used chemical reaction that synthesizes substituted pyrroles (3). The method involves the reaction of an α-amino-ketone (1) and a compound containing an electron-withdrawing group α to a carbonyl group (2).

The Darzens reaction is the chemical reaction of a ketone or aldehyde with an α-haloester in the presence of a base to form an α,β-epoxy ester, also called a "glycidic ester". This reaction was discovered by the organic chemist Auguste Georges Darzens in 1904.
The Gabriel–Colman rearrangement is the chemical reaction of a saccharin or phthalimido ester with a strong base, such as an alkoxide, to form substituted isoquinolines. First described in 1900 by chemists Siegmund Gabriel and James Colman, this rearrangement, a ring expansion, is seen to be general if there is an enolizable hydrogen on the group attached to the nitrogen, since it is necessary for the nitrogen to abstract a hydrogen to form the carbanion that will close the ring. As shown in the case of the general example below, X is either CO or SO2.

Idoxuridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug.
The Kulinkovich reaction describes the organic synthesis of substituted cyclopropanols through reaction of esters with dialkyldialkoxytitanium reagents, which are generated in situ from Grignard reagents containing a hydrogen in beta-position and titanium(IV) alkoxides such as titanium isopropoxide. This reaction was first reported by Oleg Kulinkovich and coworkers in 1989.

The Gould–Jacobs reaction is an organic synthesis for the preparation of quinolines and 4‐hydroxyquinoline derivatives. The Gould–Jacobs reaction is a series of reactions. The series of reactions begins with the condensation/substitution of an aniline with alkoxy methylenemalonic ester or acyl malonic ester, producing anilidomethylenemalonic ester. Then through a 6 electron cyclization process, 4-hydroxy-3-carboalkoxyquinoline is formed, which exist mostly in the 4-oxo form. Saponification results in the formation of an acid. This step is followed by decarboxylation to give 4-hydroxyquinoline. The Gould–Jacobs reaction is effective for anilines with electron‐donating groups at the meta‐position.

Butacaine is a white crystalline ester used as a local anesthetic. It was first marketed in 1920.

Sunepitron is a combined 5-HT1A receptor agonist and α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist. It was previously under development by Pfizer for the treatment of depression and anxiety. It made it to phase III clinical trials before being discontinued.
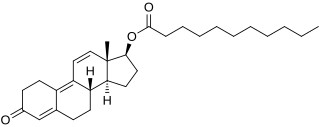
Trenbolone undecanoate, or trenbolone undecylate, is a synthetic and injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which was never marketed. It is the C17β undecanoate (undecylate) ester and a long-acting prodrug of trenbolone. The drug was described by Roussel Uclaf in 1967 and was the first long-lasting ester of trenbolone to be developed. Subsequently, trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, a roughly equivalent compound, was developed and introduced for use in humans in 1980, though it was discontinued in 1997. Trenbolone enanthate is another long-lasting ester of trenbolone. Similarly to trenbolone undecanoate, it was never marketed, but it has been sold on the black market as a designer steroid for bodybuilders and athletes.
The Hantzsch pyridine synthesis or Hantzsch dihydropyridine synthesis is a multi-component organic reaction between an aldehyde such as formaldehyde, 2 equivalents of a β-keto ester such as ethyl acetoacetate and a nitrogen donor such as ammonium acetate or ammonia. The initial reaction product is a dihydropyridine which can be oxidized in a subsequent step to a pyridine. The driving force for this second reaction step is aromatization. This reaction was reported in 1881 by Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch.
Exelgyn is a French pharmaceutical company which makes and distributes the medical abortion drugs mifepristone and misoprostol.













