
Aspirin is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.

Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.
An antipyretic is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which results in a reduction in fever.

Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.

Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be taken orally or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour.
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effective in the arterial circulation where classical Vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants have minimal effect.
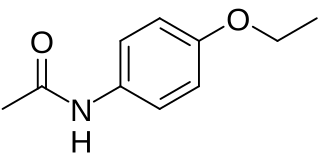
Phenacetin is a pain-relieving and fever-reducing drug, which was widely used following its introduction in 1887. It was withdrawn from medicinal use as dangerous from the 1970s.

Third-degree atrioventricular block is a medical condition in which the electrical impulse generated in the sinoatrial node in the atrium of the heart can not propagate to the ventricles.
ATC code N02Analgesics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N02 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.

Ketorolac, sold under the brand name Toradol among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain. Specifically it is recommended for moderate to severe pain. Recommended duration of treatment is less than six days, and in Switzerland not more than seven days. It is used by mouth, by nose, by injection into a vein or muscle, and as eye drops. Effects begin within an hour and last for up to eight hours. Ketorolac also has antipyretic (fever-reducing) properties.

Phenazone is an analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drug. While it predates the term, it is often classified as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Phenazone was one of the earliest synthetic medications — when it was patented in 1883, the only synthetic medical chemicals on the market were chloral hydrate, a sedative, trimethylamine, and iodol (tetraiodopyrrol), an early antiseptic. One of the earliest widely used analgesics and antipyretics, phenazone was gradually replaced in common use by other medications including phenacetin, aspirin, paracetamol and modern NSAIDs such as ibuprofen. However, it is still available in several countries either as an over-the-counter or prescribed drug.

Metamizole or dipyrone is a painkiller, spasm reliever, and fever reliever drug. It is most commonly given by mouth or by intravenous infusion. It belongs to the ampyrone sulfonate family of medicines and was patented in 1922. Metamizole is marketed under various trade names. It was first used medically in Germany under the brand name "Novalgin", later becoming widely known in Slavic nations and India under the name "Analgin".

Aminophenazone is a non-narcotic analgesic substance. It is a pyrazolone and a derivative of phenazone, which also has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties. While inexpensive and effective, especially in the treatment of rheumatism, the drug carries a serious risk of severe and sometimes fatal side-effects, including agranulocytosis. While its production and use have been banned in many countries, including France, Thailand, India and Japan, it is still sometimes used in the developing world.

Eptifibatide, is an antiplatelet drug of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor class. Eptifibatide is a cyclic heptapeptide derived from a disintegrin protein found in the venom of the southeastern pygmy rattlesnake. It belongs to the class of the arginin-glycin-aspartat-mimetics and reversibly binds to platelets. Eptifibatide has a short half-life. The drug is the third inhibitor of GPIIb/IIIa that has found broad acceptance after the specific antibody abciximab and the non-peptide tirofiban entered the global market.
Propyphenazone/paracetamol/caffeine is an analgesic combination indicated for the management of headache. It contains the analgesics propyphenazone and paracetamol and the stimulant caffeine.
Pyrazolone is 5-membered heterocycle containing two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It can be viewed as a derivative of pyrazole possessing an additional carbonyl (C=O) group. Compounds containing this functional group are useful commercially in analgesics and dyes.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.
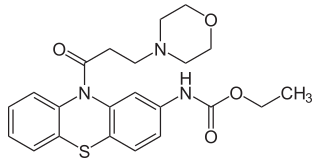
Moracizine or moricizine, sold under the trade name Ethmozine, is an antiarrhythmic of class IC. It was used for the prophylaxis and treatment of serious and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, but was withdrawn in 2007 for commercial reasons.
Nicholas George Kounis is professor emeritus of cardiology in the University of Patras and scientific cardiology advisor at Saint Andrews State General Hospital Patras and at the Department of cardiology of University of Patras Medical School, Patras, Greece.
Kounis syndrome is defined as acute coronary syndrome caused by an allergic reaction or a strong immune reaction to a drug or other substance. It is a rare syndrome with authentic cases reported in 130 males and 45 females, as reviewed in 2017; however, the disorder is suspected of being commonly overlooked and therefore much more prevalent. Mast cell activation and release of inflammatory cytokines as well as other inflammatory agents from the reaction leads to spasm of the arteries leading to the heart muscle or a plaque breaking free and blocking one or more of those arteries.














