
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.

Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally, inserted rectally as a suppository, injected intramuscularly, injected intravenously, applied to the skin topically, or through eye drops. Improvements in pain last up to eight hours. It is also available as the fixed-dose combination diclofenac/misoprostol (Arthrotec) to help protect the stomach.

Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and lasts for up to twelve hours. Naproxen is also available in salt form, naproxen sodium, which has better solubility when taken orally.

Indometacin, also known as indomethacin, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, endogenous signaling molecules known to cause these symptoms. It does this by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme that catalyzes the production of prostaglandins.

Sultamicillin, sold under the brand name Unasyn among others, is an oral form of the penicillin antibiotic combination ampicillin/sulbactam. It is used for the treatment of bacterial infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract, the kidneys and urinary tract, skin and soft tissues, among other organs. It contains esterified ampicillin and sulbactam.

Flurbiprofen is a member of the phenylalkanoic acid derivative family of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is primarily indicated as a pre-operative anti-miotic as well as orally for arthritis or dental pain. Side effects are analogous to those of ibuprofen.

Deracoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the coxib class, used in dogs to treat pain associated with osteoarthritis, or to prevent pain following orthopedic or dental surgery. It is available as beef-flavored tablets.
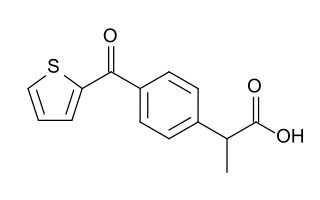
Suprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica that was marketed as 1% eye drops under the trade name Profenal.
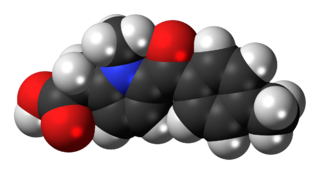
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the heterocyclic acetic acid derivative class.
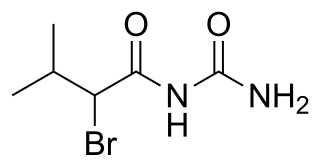
Bromisoval (INN), commonly known as bromovalerylurea, is a hypnotic and sedative of the bromoureide group discovered by Knoll in 1907 and patented in 1909. It is marketed over the counter in Asia under various trade names, usually in combination with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Meclofenamic acid is a drug used for joint, muscular pain, arthritis and dysmenorrhea. It is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and was approved by the US FDA in 1980. Like other members of the class, it is a cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor, preventing the formation of prostaglandins.
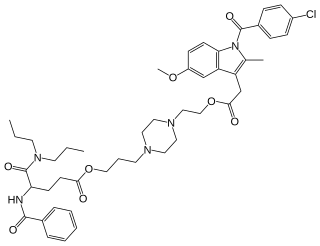
Proglumetacin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is metabolized in the body to indometacin and proglumide, a drug with antisecretory effects that helps prevent injury to the stomach lining.

Acemetacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, lower back pain, and relieving post-operative pain. It is manufactured by Merck KGaA under the tradename Emflex. It is no longer available in the UK, however is available in other countries as a prescription-only drug.
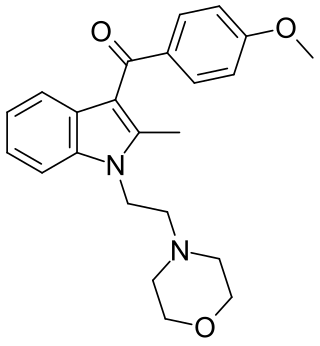
Pravadoline (WIN 48,098) is an anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug with an IC50 of 4.9 μM and a Ki of 2511 nM at CB1, related in structure to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as indometacin. It was developed in the 1980s as a new antiinflammatory and prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor, acting through inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX).

Norbrook is a United Kingdom-based pharmaceutical company. It was founded in 1969 by Lord Ballyedmond as Norbrook Laboratories Ltd in Northern Ireland. In 1970, Norbrook began manufacturing of veterinary pharmaceuticals. In 2011 the Norbrook Group was listed by the Belfast Telegraph in its Top 100 Companies list as being in position 28.

Vedaprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in veterinary medicine for the treatment of pain and inflammation due to musculoskeletal disorders in dogs and horses and for the treatment of pain due to horse colic. It is a member of the profen drug class.

Polmacoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat osteoarthritis. It was developed as CG100649 and approved for use in South Korea in February 2015. It inhibits the enzymes carbonic anhydrase and COX-2. A study in healthy volunteers showed drug effects on urinary prostaglandin metabolites for both polmacoxib and celecoxib that suggest a similar cardiovascular risk profile. Further work by this group developed dose-exposure relationships of polmacoxib to guide clinical development strategies.
A drug class is a group of medications and other compounds that share similar chemical structures, act through the same mechanism of action, have similar modes of action, and/or are used to treat similar diseases. The FDA has long worked to classify and license new medications. Its Drug Evaluation and Research Center categorizes these medications based on both their chemical and therapeutic classes.

Zaltoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used as an analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory agent. It is a selective COX-2 inhibitor and also inhibits bradykinin-induced pain responses without blocking bradykinin receptors.

Glucametacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of mild or moderate pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other rheumatological disorders. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.



















