Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cells that function as receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen receptors, namely ERα and ERβ, which belong to the nuclear receptor family. The second class consists of membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER, which are primarily G protein-coupled receptors. This article focuses on the nuclear estrogen receptors.

Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnancy, and in newborn babies to keep the ductus arteriosus open. In babies it is used in those with congenital heart defects until surgery can be carried out. It is also used to manage gestational trophoblastic disease. It may be used within the vagina or by injection into a vein.

Enprostil is a synthetic prostaglandin designed to resemble dinoprostone. Enprostil was found to be a highly potent inhibitor of gastric HCl secretion. It is an analog of prostaglandin E2 but unlike this prostaglandin, which binds to and activates all four cellular receptors viz., EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors, enprostil is a more selective receptor agonist in that it binds to and activates primarily the EP3 receptor. Consequently, enprostil is expected to have a narrower range of actions that may avoid some of the unwanted side-effects and toxicities of prostaglandin E2. A prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial conducted in Japan found combining enprostil with cimetidine was more effective than cimetidine alone in treating gastric ulcer.

The thromboxane receptor (TP) also known as the prostanoid TP receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBXA2R gene, The thromboxane receptor is one among the five classes of prostanoid receptors and was the first eicosanoid receptor cloned. The TP receptor derives its name from its preferred endogenous ligand thromboxane A2.

An alveolar macrophage, pulmonary macrophage, is a type of macrophage, a professional phagocyte, found in the airways and at the level of the alveoli in the lungs, but separated from their walls.
Most of the eicosanoid receptors are integral membrane protein G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that bind and respond to eicosanoid signaling molecules. Eicosanoids are rapidly metabolized to inactive products and therefore are short-lived. Accordingly, the eicosanoid-receptor interaction is typically limited to a local interaction: cells, upon stimulation, metabolize arachidonic acid to an eicosanoid which then binds cognate receptors on either its parent cell or on nearby cells to trigger functional responses within a restricted tissue area, e.g. an inflammatory response to an invading pathogen. In some cases, however, the synthesized eicosanoid travels through the blood to trigger systemic or coordinated tissue responses, e.g. prostaglandin (PG) E2 released locally travels to the hypothalamus to trigger a febrile reaction. An example of a non-GPCR receptor that binds many eicosanoids is the PPAR-γ nuclear receptor.
Prostaglandin receptors or prostanoid receptors represent a sub-class of cell surface membrane receptors that are regarded as the primary receptors for one or more of the classical, naturally occurring prostanoids viz., prostaglandin D2,, PGE2, PGF2alpha, prostacyclin (PGI2), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and PGH2. They are named based on the prostanoid to which they preferentially bind and respond, e.g. the receptor responsive to PGI2 at lower concentrations than any other prostanoid is named the Prostacyclin receptor (IP). One exception to this rule is the receptor for thromboxane A2 (TP) which binds and responds to PGH2 and TXA2 equally well.

The prostaglandin D2 receptor 1 (DP1), a G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the PTGDR1 gene (also termed PTGDR), is primarily a receptor for prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). The receptor is a member of the prostaglandin receptors belonging to the subfamily A14 of rhodopsin-like receptors. Activation of DP1 by PGD2 or other cognate receptor ligands is associated with a variety of physiological and pathological responses in animal models.

Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) also known as NR3A2 is one of two main types of estrogen receptor—a nuclear receptor which is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans ERβ is encoded by the ESR2 gene.

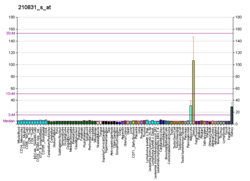
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 (EP4) is a prostaglandin receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) encoded by the PTGER4 gene in humans; it is one of four identified EP receptors, the others being EP1, EP2, and EP3, all of which bind with and mediate cellular responses to PGE2 and also, but generally with lesser affinity and responsiveness, certain other prostanoids (see Prostaglandin receptors). EP4 has been implicated in various physiological and pathological responses in animal models and humans.

Prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTH2) is a human protein encoded by the PTGDR2 gene and GPR44. DP2 has also been designated as CD294 (cluster of differentiation 294). It is a member of the class of prostaglandin receptors which bind with and respond to various prostaglandins. DP2 along with prostaglandin DP1 receptor are receptors for prostglandin D2 (PGD2). Activation of DP2 by PGD2 or other cognate receptor ligands has been associated with certain physiological and pathological responses, particularly those associated with allergy and inflammation, in animal models and certain human diseases.

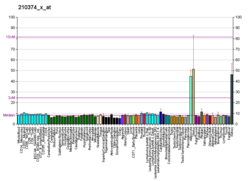
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 1 (EP1) is a 42kDa prostaglandin receptor encoded by the PTGER1 gene. EP1 is one of four identified EP receptors, EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4 which bind with and mediate cellular responses principally to prostaglandin E2) (PGE2) and also but generally with lesser affinity and responsiveness to certain other prostanoids (see Prostaglandin receptors). Animal model studies have implicated EP1 in various physiological and pathological responses. However, key differences in the distribution of EP1 between these test animals and humans as well as other complicating issues make it difficult to establish the function(s) of this receptor in human health and disease.

Prostaglandin E2 receptor 2, also known as EP2, is a prostaglandin receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) encoded by the human gene PTGER2: it is one of four identified EP receptors, the others being EP1, EP3, and EP4, which bind with and mediate cellular responses to PGE2 and also, but with lesser affinity and responsiveness, certain other prostanoids (see Prostaglandin receptors). EP has been implicated in various physiological and pathological responses.

Prostaglandin F receptor (FP) is a receptor belonging to the prostaglandin (PG) group of receptors. FP binds to and mediates the biological actions of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). It is encoded in humans by the PTGFR gene.

The prostacyclin receptor, also termed the prostaglandin I2 receptor or just IP, is a receptor belonging to the prostaglandin (PG) group of receptors. IP binds to and mediates the biological actions of prostacyclin (also termed prostaglandin I2, PGI2, or when used as a drug, epoprostenol). IP is encoded in humans by the PTGIR gene. While possessing many functions as defined in animal model studies, the major clinical relevancy of IP is as a powerful vasodilator: stimulators of IP are used to treat severe and even life-threatening diseases involving pathological vasoconstriction.

Sulprostone is an analogue of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) that has oxytocic activity in assays of rat kidney cells and tissues. There are four known receptors which mediate various but often different cellular and tissue responses to PGE2: prostaglandin EP1 receptor, prostaglandin EP2 receptor, prostaglandin EP3 receptor, and prostaglandin EP4 receptor. Sulprosotone binds to and activates the prostaglandin EP3 receptor with far greater efficacy than the other PGE2 receptors and also has the advantage of being relatively resistant, compared with PGE2, to becoming metabolically degraded. It is listed as a comparatively weak receptor agonist of the prostaglandin EP1 receptor. In all events, this as well as other potent synthetic EP3 receptor antagonists have the realized or potential ability to promote the beneficial effects of prostaglandin EP3 receptor activation.
The prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that bind and are activated by prostaglandin D2. Also known as PTGDR or DP receptors, they are important for various functions of the nervous system and inflammation. They include the following proteins:
The prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that bind and are activated by prostaglandin E2. They are members of the prostaglandin receptors class of receptors and include the following Protein isoforms:

Grapiprant, sold under the brand name Galliprant, is a small molecule drug that belongs in the piprant class. This analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug is primarily used as a pain relief for mild to moderate inflammation related to osteoarthritis in dogs. Grapiprant has been approved by the FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine and was categorized as a non-cyclooxygenase inhibiting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) in March 2016.