Related Research Articles

Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide and a type of neuropeptide, belonging to the tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It acts as a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator. Substance P and the closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after alternative splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:

Aprepitant, sold under the brand name Emend among others, is a medication used to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting. It may be used together with ondansetron and dexamethasone. It is taken by mouth or administered by intravenous injection.

Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.
Physalaemin is a tachykinin peptide obtained from the Physalaemus frog, closely related to substance P. Its structure was first elucidated in 1964.

Kassinin is a peptide derived from the Kassina frog. It belongs to tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It is secreted as a defense response, and is involved in neuropeptide signalling.
Neurokinin 1 (NK1) antagonists (-pitants) are a novel class of medications that possesses unique antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antiemetic properties. NK-1 antagonists boost the efficacy of 5-HT3 antagonists to prevent nausea and vomiting. The discovery of neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonists was a turning point in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy.

Neurokinin A (NKA), formerly known as Substance K, is a neurologically active peptide translated from the pre-protachykinin gene. Neurokinin A has many excitatory effects on mammalian nervous systems and is also influential on the mammalian inflammatory and pain responses.
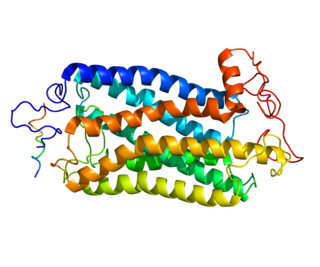
The tachykinin receptor 1 (TACR1) also known as neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) or substance P receptor (SPR) is a G protein coupled receptor found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endogenous ligand for this receptor is Substance P, although it has some affinity for other tachykinins. The protein is the product of the TACR1 gene.

The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 19 (GPCR19), membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR) or Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPBAR1 gene.

Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 also known as LPA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPAR4 gene. LPA4 is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the lipid signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).

Substance-K receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TACR2 gene.

Tachykinin receptor 3, also known as TACR3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TACR3 gene.

P2Y purinoceptor 14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RY14 gene.

Relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 3, also known as RXFP3, is a human G-protein coupled receptor.

G-protein coupled receptor 161 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR161 gene.

Neuromedin-U receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NMUR1 gene.

Neuromedin-U receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NMUR2 gene.

Tachykinin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAC4 gene.
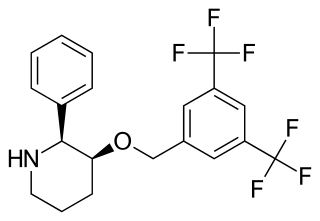
L-733,060 is a drug developed by Merck which acts as an orally active, non-peptide, selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, binding with a Ki of 0.08 nM. Only one enantiomer is active which has made it the subject of several asymmetric synthesis efforts.

Netupitant is an antiemetic medication. In the United States, the combinations of netupitant/palonosetron and the prodrug fosnetupitant/palonosetron are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of acute and delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, including highly emetogenic chemotherapy such as with cisplatin. In the European Union, the combinations are approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the same indication.
References
- ↑ "Aprepitant". NICE. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ↑ Maggi CA (September 1995). "The mammalian tachykinin receptors". General Pharmacology. 26 (5): 911–44. doi:10.1016/0306-3623(94)00292-U. PMID 7557266.