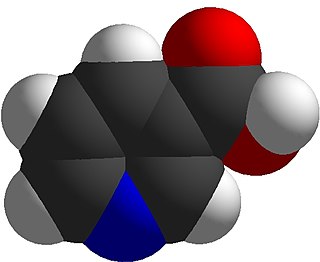
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is an organic compound and a vitamer of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of whole and processed foods, with highest contents in fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, red fish such as tuna and salmon, lesser amounts in nuts, legumes and seeds. Niacin as a dietary supplement is used to treat pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency. Signs and symptoms of pellagra include skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and tiredness. Many countries mandate its addition to wheat flour or other food grains, thereby reducing the risk of pellagra.

Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate. The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl.

Butyric acid, also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CO2H. It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. The acid does not occur widely in nature, but its esters are widespread. It is a common industrial chemical and an important component in the mammalian gut.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid or BHB, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).

Prostaglandin D2 (or PGD2) is a prostaglandin that binds to the receptor PTGDR (DP1), as well as CRTH2 (DP2). It is a major prostaglandin produced by mast cells – recruits Th2 cells, eosinophils, and basophils. In mammalian organs, large amounts of PGD2 are found only in the brain and in mast cells. It is critical to development of allergic diseases such as asthma. Research carried out in 1989 found PGD2 is the primary mediator of vasodilation (the "niacin flush") after ingestion of niacin (nicotinic acid).
Gi protein alpha subunit is a family of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. This family is also commonly called the Gi/o family or Gi/o/z/t family to include closely related family members. G alpha subunits may be referred to as Gi alpha, Gαi, or Giα.

Acipimox is a niacin derivative used as a lipid-lowering agent. It reduces triglyceride levels and increases HDL cholesterol. It may have less marked adverse effects than niacin, although it is unclear whether the recommended dose is as effective as standard doses of niacin.

G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPER gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible for some of the rapid effects that estradiol has on cells.

Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1), also known as GPR40, is a class A G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the FFAR1 gene. It is strongly expressed in the cells of the pancreas and to a lesser extent in the brain. This membrane protein is a member of the free fatty acid receptors; it binds a certain subset of free fatty acids, acting as a nutrient sensor for regulating energy homeostasis.

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 (HCA3), also known as niacin receptor 2 (NIACR2) and GPR109B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HCAR3 gene. HCA3, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA1 and HCA2, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonists of HCA3 are 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid and kynurenic acid. HCA3 is also a low-affinity biomolecular target for niacin (aka nicotinic acid).

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCA1), formerly known as G protein-coupled receptor 81 (GPR81), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCAR1 gene. HCA1, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA2 and HCA3, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonist of HCA1 is lactic acid (and its conjugate base, lactate).

2-Oxoglutarate receptor 1 (OXGR1), also known as cysteinyl leukotriene receptor E (CysLTE) and GPR99, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OXGR1 gene. The Gene has recently been nominated as a receptor not only for 2-oxogluterate but also for the three cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs), particularly leukotriene E4 (LTE4) and to far lesser extents LTC4 and LTE4. Recent studies implicate GPR99 as a cellular receptor which is activated by LTE4 thereby causing these cells to contribute to mediating various allergic and hypersensitivity responses.

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), also known as niacin receptor 1 (NIACR1) and GPR109A, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HCAR2 gene. HCA2, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA1 and HCA3, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonists of HCA2 are D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and butyric acid (and their conjugate bases, β-hydroxybutyrate and butyrate). HCA2 is also a high-affinity biomolecular target for niacin (aka nicotinic acid).

Oxoeicosanoid receptor 1 (OXER1) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 170 (GPR170) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OXER1 gene located on human chromosome 2p21; it is the principal receptor for the 5-Hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid family of carboxy fatty acid metabolites derived from arachidonic acid. The receptor has also been termed hGPCR48, HGPCR48, and R527 but OXER1 is now its preferred designation. OXER1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is structurally related to the hydroxy-carboxylic acid (HCA) family of G protein-coupled receptors whose three members are HCA1 (GPR81), HCA2, and HCA3 ; OXER1 has 30.3%, 30.7%, and 30.7% amino acid sequence identity with these GPCRs, respectively. It is also related to the recently defined receptor, GPR31, for the hydroxyl-carboxy fatty acid 12-HETE.

Rhodopsin-like receptors are a family of proteins that comprise the largest group of G protein-coupled receptors.
The known human niacin receptors are:

5-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE, 5(S)-HETE, or 5S-HETE) is an eicosanoid, i.e. a metabolite of arachidonic acid. It is produced by diverse cell types in humans and other animal species. These cells may then metabolize the formed 5(S)-HETE to 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-ETE), 5(S),15(S)-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5(S),15(S)-diHETE), or 5-oxo-15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-15(S)-HETE).
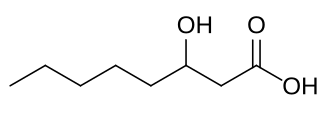
3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid that is naturally produced in humans, other animals, and plants.
The lysophosphatidic acid receptors (LPARs) are a group of G protein-coupled receptors for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) that include:

5-Oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid is a Nonclassic eicosanoid metabolite of arachidonic acid and the most potent naturally occurring member of the 5-HETE family of cell signaling agents. Like other cell signaling agents, 5-oxo-ETE is made by a cell and then feeds back to stimulate its parent cell and/or exits this cell to stimulate nearby cells. 5-Oxo-ETE can stimulate various cell types particularly human leukocytes but possesses its highest potency and power in stimulating the human eosinophil type of leukocyte. It is therefore suggested to be formed during and to be an important contributor to the formation and progression of eosinophil-based allergic reactions; it is also suggested that 5-oxo-ETE contributes to the development of inflammation, cancer cell growth, and other pathological and physiological events.














