
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), also known as pro-melanin stimulating hormone (PMCH), is a cyclic 19-amino acid orexigenic hypothalamic peptide originally isolated from the pituitary gland of teleost fish, where it controls skin pigmentation. In mammals it is involved in the regulation of feeding behavior, mood, sleep-wake cycle and energy balance.

Vasopressin receptor 2 (V2R), or arginine vasopressin receptor 2, is a protein that acts as receptor for vasopressin. AVPR2 belongs to the subfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors. Its activity is mediated by the Gs type of G proteins, which stimulate adenylate cyclase.

Agouti-signaling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASIP gene. It is responsible for the distribution of melanin pigment in mammals. Agouti interacts with the melanocortin 1 receptor to determine whether the melanocyte produces phaeomelanin, or eumelanin. This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti, which the gene is named after. In other species such as horses, agouti signalling is responsible for determining which parts of the body will be red or black. Mice with wildtype agouti will be grey, with each hair being partly yellow and partly black. Loss of function mutations in mice and other species cause black fur coloration, while mutations causing expression throughout the whole body in mice cause yellow fur and obesity.
Neuropeptide Y receptors are a family of receptors belonging to class A G-protein coupled receptors and they are activated by the closely related peptide hormones neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. These receptors are involved in the control of a diverse set of behavioral processes including appetite, circadian rhythm, and anxiety.
Two Melanin-concentrating hormone receptors (MCHR) have recently been characterized: MCH-R1 and MCH-R2. These two receptors share approximately 38% homology.

The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) also known G-protein coupled receptor 19 (GPCR19), membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR) or Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) as is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPBAR1 gene.

The KiSS1-derived peptide receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the peptide hormone kisspeptin (metastin). Kisspeptin is encoded by the metastasis suppressor gene KISS1, which is expressed in a variety of endocrine and gonadal tissues. Activation of the kisspeptin receptor is linked to the phospholipase C and inositol trisphosphate second messenger cascades inside the cell.

The prolactin-releasing peptide receptor (PrRPR) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 10 (GPR10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRLHR gene.
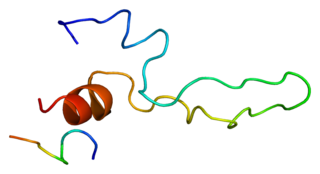
The Cholecystokinin A receptor is a human protein, also known as CCKAR or CCK1, with CCK1 now being the IUPHAR-recommended name.

Melanocortin 3 receptor (MC3R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MC3R gene.

Neuropeptide Y receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPY1R gene.

Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPY5R gene.

Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 2 (MCH2) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 145 (GPR145) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCHR2 gene.

Pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1, also known as Neuropeptide Y receptor type 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPYR1 gene.

ATC-0175 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has been shown to produce both anxiolytic and antidepressant actions, but without sedative or ataxic side effects.

SNAP-94847 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has been shown to produce both anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, and also reduces food consumption suggesting a possible anorectic effect.
GW-803430 (GW-3430) is a drug used in scientific research and is a selective non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has anxiolytic, antidepressant and anorectic effects.
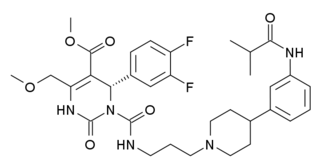
SNAP-7941 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In initial animal studies it had promising anxiolytic, antidepressant and anorectic effects, but subsequent trial results were disappointing, and the main significance of SNAP-7941 is as the lead compound from which more potent and selective antagonists such as SNAP-94847 were developed, although it continues to be used for research into the function of the MCH1 receptor.
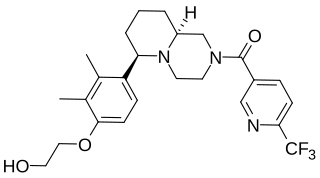
NGD-4715 is a drug developed by Neurogen, which acts as a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal models it has anxiolytic, antidepressant, and anorectic effects, and it has successfully passed Phase I clinical trials in humans.


















