| GPR37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GPR37 , EDNRBL, PAELR, hET(B)R-LP, G protein-coupled receptor 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602583; MGI: 1313297; HomoloGene: 3875; GeneCards: GPR37; OMA:GPR37 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
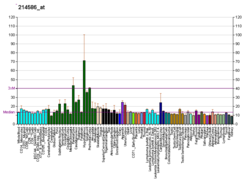
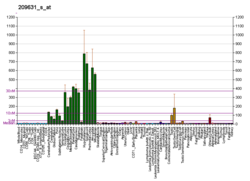
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 37 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR37 gene. [5] [6] [7] GPR37 is primarily found in the central nervous system (CNS), with significant expression observed in various CNS regions including the amygdala, basal ganglia (caudate, putamen, and nucleus accumbens), substantia nigra, hippocampus, frontal cortex, and hypothalamus, particularly noteworthy is its exceptionally elevated expression in the spinal cord. [8]