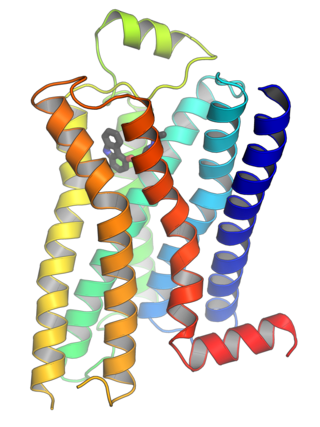
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops or to the binding site within transmembrane helices. They are all activated by agonists, although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor has also been observed.

Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes in living organisms. It deals with the structure and function of cellular components such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and other biomolecules.
Bombesin is a 14-amino acid peptide originally isolated from the skin of the European fire-bellied toad by Vittorio Erspamer et al. and named after its source. It has two known homologs in mammals called neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide. It stimulates gastrin release from G cells. It activates three different G-protein-coupled receptors known as BBR1, -2, and -3. It also activates these receptors in the brain. Together with cholecystokinin, it is the second major source of negative feedback signals that stop eating behaviour.

Gastrin-releasing peptide, also known as GRP, is a neuropeptide, a regulatory molecule that has been implicated in a number of physiological and pathophysiological processes. Most notably, GRP stimulates the release of gastrin from the G cells of the stomach.
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a second messenger signaling cascade that induces a broad, long-lasting signal. This modulation can last for hundreds of milliseconds to several minutes. Some of the effects of neuromodulators include: altering intrinsic firing activity, increasing or decreasing voltage-dependent currents, altering synaptic efficacy, increasing bursting activity and reconfigurating synaptic connectivity.
Neuromedin B (NMB) is a bombesin-related peptide in mammals. It was originally purified from pig spinal cord, and later shown to be present in human central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
TRPP is a family of transient receptor potential ion channels which when mutated can cause polycystic kidney disease.
Copper-64 (64Cu) is a positron and beta emitting isotope of copper, with applications for molecular radiotherapy and positron emission tomography. Its unusually long half-life (12.7-hours) for a positron-emitting isotope makes it increasingly useful when attached to various ligands, for PET and PET-CT scanning.

The bombesin receptor subtype 3 also known as BRS-3 or BB3 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BRS3 gene.

The neuromedin B receptor (NMBR), now known as BB1 is a G protein-coupled receptor whose endogenous ligand is neuromedin B. In humans, this protein is encoded by the NMBR gene.

The gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR), now properly known as BB2 is a G protein-coupled receptor whose endogenous ligand is gastrin releasing peptide. In humans it is highly expressed in the pancreas and is also expressed in the stomach, adrenal cortex and brain.

Rhodopsin-like receptors are a family of proteins that comprise the largest group of G protein-coupled receptors.

Xorphanol (INN), also known as xorphanol mesylate (USAN), is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that was never marketed.

Nemifitide (INN-00835) is a novel antidepressant drug with a pentapeptide structure similar to that of melanocyte-inhibiting factor (MIF-1) and the amino acid sequence 4-F-Phe-4-OH-Pro-Arg-Gly-Trp-NH2. It is under development by Tetragenex (previously Innapharma, Inc.) for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It has been given to over 430 people over the course of 12 clinical trials throughout a little over the past decade and has reached Phase III studies, but has not yet been approved for marketing in any country.
Bombesin-like peptides comprise a large family of peptides which were initially isolated from amphibian skin, where they stimulate smooth muscle contraction. They were later found to be widely distributed in mammalian neural and endocrine cells.
Local hormones are a large group of signaling molecules that do not circulate within the blood. Local hormones are produced by nerve and gland cells and bind to either neighboring cells or the same type of cell that produced them. Local hormones are activated and inactivated quickly. They are released during physical work and exercise. They mainly control smooth and vascular muscle dilation. Strength of response is dependent upon the concentration of receptors of target cell and the amount of ligand.
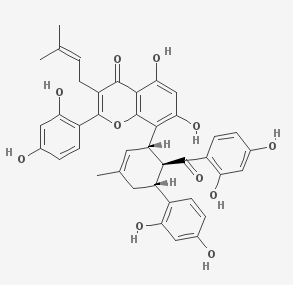
Kuwanon G is an antimicrobial bombesin receptor antagonist, isolated from Morus alba.
Neuroendocrine differentiation is a term primarily used in relation to prostate cancers that display a significant neuroendocrine cell population on histopathological examination. These types of prostate cancer comprise true neuroendocrine cancers, such as small cell carcinoma, carcinoid and carcinoid-like tumors, as well as prostatic adenocarcinoma exhibiting focal neuroendocrine phenotype.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








