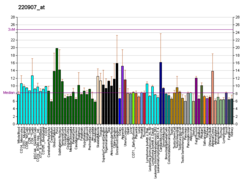
| ADGRF1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ADGRF1 , KPG_012, PGR19, hGPCR36, GPR110, adhesion G protein-coupled receptor F1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 617430; MGI: 1924846; HomoloGene: 124643; GeneCards: ADGRF1; OMA:ADGRF1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 110 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR110 gene. [5] [6] This gene encodes a member of the adhesion-GPCR receptor family. [7] Family members are characterized by an extended extracellular region with a variable number of N-terminal protein modules coupled to a TM7 region via a domain known as the GPCR-Autoproteolysis INducing (GAIN) domain. [8]