Related Research Articles
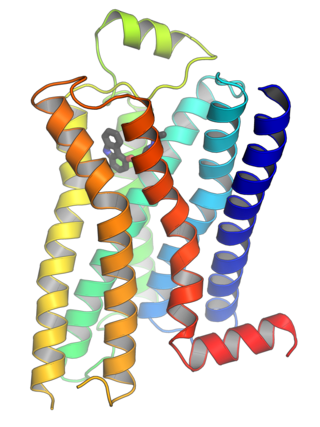
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops or to the binding site within transmembrane helices. They are all activated by agonists, although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor has also been observed.

Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex to promote sodium retention by the kidneys.

Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 are integral parts of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) that exists to keep the body's blood pressure in check. mACE2 is cleaved by the enzyme ADAM17 that releases its extracellular domain, creating soluble ACE2 (sACE2). ACE2 enzyme activity opposes the classical arm of the RAAS by lowering blood pressure through catalyzing the hydrolysis of angiotensin II into angiotensin (1–7). Angiotensin (1-7) in turns binds to MasR receptors creating localized vasodilation and hence decreasing blood pressure. This decrease in blood pressure makes the entire process a promising drug target for treating cardiovascular diseases.
The bradykinin receptor family is a group of G-protein coupled receptors whose principal ligand is the protein bradykinin.
Neurotensin receptors are transmembrane receptors that bind the neurotransmitter neurotensin. Two of the receptors encoded by the NTSR1 and NTSR2 genes contain seven transmembrane helices and are G protein coupled. Numerous crystal structures have been reported for the neurotensin receptor 1 (NTS1). The third receptor has a single transmembrane domain and is encoded by the SORT1 gene.

MAS proto-oncogene, or MAS1 proto-oncogene, G protein-coupled receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAS1 gene. The structure of the MAS1 product indicates that it belongs to the class of receptors that are coupled to GTP-binding proteins and share a conserved structural motif, which is described as a '7-transmembrane segment' following the prediction that these hydrophobic segments form membrane-spanning alpha-helices. The MAS1 protein may be a receptor that, when activated, modulates a critical component in a growth-regulating pathway to bring about oncogenic effects.
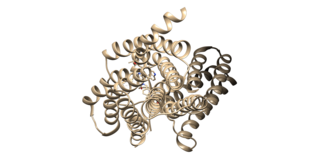
Angiotensin II receptor type 1(AT1) is a Gq/11-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) and the best characterized angiotensin receptor. It is encoded in humans by the AGTR1 gene. AT1 has vasopressor effects and regulates aldosterone secretion. It is an important effector controlling blood pressure and volume in the cardiovascular system. Angiotensin II receptor blockers are drugs indicated for hypertension, diabetic nephropathy and congestive heart failure.

Bradykinin receptor B2 is a G-protein coupled receptor for bradykinin, encoded by the BDKRB2 gene in humans.

Angiotensin II receptor type 2, also known as the AT2 receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AGTR2 gene.

Melanocortin 3 receptor (MC3R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MC3R gene.

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 (HCA3), also known as niacin receptor 2 (NIACR2) and GPR109B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HCAR3 gene. HCA3, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA1 and HCA2, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonists of HCA3 are 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid and kynurenic acid. HCA3 is also a low-affinity biomolecular target for niacin (aka nicotinic acid).

Relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 3, also known as RXFP3, is a human G-protein coupled receptor.

Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRGPRD gene.

Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member X2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRGPRX2 gene. It is most abundant on cutaneous mast cells.

Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor MRG is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAS1L gene.

Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member X4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRGPRX4 gene.

Rhodopsin-like receptors are a family of proteins that comprise the largest group of G protein-coupled receptors.

Angiotensin (1-7) is an active heptapeptide of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS).

L-163,491 is an experimental drug which acts as a partial agonist of angiotensin II receptor type 1, and with lower affinity as an agonist of angiotensin II receptor type 2, mimicking the action of angiotensin II. Its practical applications to date have been limited to scientific research into the function of the angiotensin receptor system, but it has been suggested as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of inflammation of the lungs associated with certain viral diseases such as COVID-19.

Alamandine is a member of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) with cardiovascular functions that are protective and opposing to the classical axis. Alamandine is a product of ACE2-dependent catalytic hydrolysis of angiotensin A and can also be generated by decarboxylation of aspartic acid residue of Ang-(1-7). Ang A is Ala1-Ang II. In mononuclear leucocytes, angiotensin II is converted to Ang A by decarboxylation of aspartic acid. Ang A is detected in human circulation and was shown to be higher in individuals with end-stage renal disease.
References
- ↑ Nunes-Silva A, Rocha GC, Magalhaes DM, Vaz LN, Salviano de Faria MH, Simoes e Silva AC (November 2017). "Physical Exercise and ACE2-Angiotensin-(1-7)-Mas Receptor Axis of the Renin Angiotensin System". Protein and Peptide Letters. Bentham Science Publishers Ltd. 24 (9): 809–816. doi:10.2174/0929866524666170728151401. PMID 28758593.
(2) a counter-regulatory or vasodilator pathway comprising angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] and Mas receptor, which is involved in vasodilation, antiproliferation, anti-hypertrophy, cardioprotective and renoprotective actions.
- ↑ Young D, Waitches G, Birchmeier C, Fasano O, Wigler M (June 1986). "Isolation and characterization of a new cellular oncogene encoding a protein with multiple potential transmembrane domains". Cell. 45 (5): 711–9. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(86)90785-3. PMID 3708691. S2CID 29886272.
- ↑ Santos RA, Simoes e Silva AC, Maric C, Silva DM, Machado RP, de Buhr I, et al. (July 2003). "Angiotensin-(1-7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (14): 8258–63. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.8258S. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1432869100 . PMC 166216 . PMID 12829792.
- ↑ Santos RA, Ferreira AJ (March 2007). "Angiotensin-(1-7) and the renin-angiotensin system". Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension. 16 (2): 122–8. doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e328031f362. PMID 17293687. S2CID 32812104.
- ↑ Santos RA, Ferreira AJ (2006). "Pharmacological effects of AVE 0991, a nonpeptide angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonist". Cardiovascular Drug Reviews. 24 (3–4): 239–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2006.00239.x . PMID 17214600.