Histamine H3 receptors are expressed in the central nervous system and to a lesser extent the peripheral nervous system, where they act as autoreceptors in presynaptic histaminergic neurons and control histamine turnover by feedback inhibition of histamine synthesis and release. The H3 receptor has also been shown to presynaptically inhibit the release of a number of other neurotransmitters (i.e. it acts as an inhibitory heteroreceptor) including, but probably not limited to dopamine, GABA, acetylcholine, noradrenaline, histamine and serotonin.

Levocabastine (trade name Livostin or Livocab, depending on the region) is a selective second-generation H1 receptor antagonist which was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1979. It is used for allergic conjunctivitis.

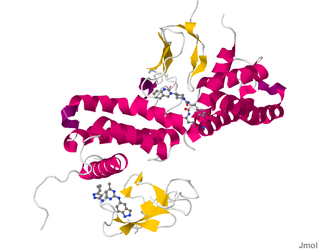
The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of rhodopsin-like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system. The H1 receptor is linked to an intracellular G-protein (Gq) that activates phospholipase C and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) signalling pathway. Antihistamines, which act on this receptor, are used as anti-allergy drugs. The crystal structure of the receptor has been determined (shown on the right/below) and used to discover new histamine H1 receptor ligands in structure-based virtual screening studies.
Neurotensin receptors are transmembrane receptors that bind the neurotransmitter neurotensin. Two of the receptors encoded by the NTSR1 and NTSR2 genes contain seven transmembrane helices and are G protein coupled. Numerous crystal structures have been reported for the neurotensin receptor 1 (NTS1). The third receptor has a single transmembrane domain and is encoded by the SORT1 gene.

The nociceptin opioid peptide receptor (NOP), also known as the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) receptor or kappa-type 3 opioid receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPRL1 gene. The nociceptin receptor is a member of the opioid subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors whose natural ligand is the 17 amino acid neuropeptide known as nociceptin (N/OFQ). This receptor is involved in the regulation of numerous brain activities, particularly instinctive and emotional behaviors. Antagonists targeting NOP are under investigation for their role as treatments for depression and Parkinson's disease, whereas NOP agonists have been shown to act as powerful, non-addictive painkillers in non-human primates.

Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects. Composed of the amino acid sequence Lys-Ile-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Leu, neuromedin N is homologous to neurotensin, both of whose sequences are found on the pro neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor C-terminus. Both sequences of neuromedin N as well as neurotensin are flanked by Lys-Arg amino acids, which comprise a consensus sequence for the endoprotease proprotein convertase. Neuromedin N is primarily synthesized in the neural and intestinal tissues of mammals; in studies performed in mice, neuromedin N's physiological effects were shown to include hypothermia and analgesia, arising from the peptide's ligand association to and interaction with neurotensin type 2 (NTS2) G protein-coupled receptors.
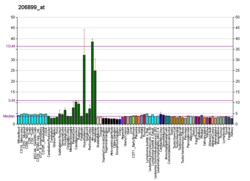
Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL), also known as the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR), is a human protein; it is a receptor for calcitonin gene-related peptide.

P2Y purinoceptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RY1 gene.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, also known as cholinergic/acetylcholine receptor M3, or the muscarinic 3, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor encoded by the human gene CHRM3.

Sortilin (SORT1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORT1 gene on chromosome 1. This protein is a type I membrane glycoprotein in the vacuolar protein sorting 10 protein (Vps10p) family of sorting receptors. While it is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues, sortilin is most abundant in the central nervous system. At the cellular level, sortilin functions in protein transport between the Golgi apparatus, endosome, lysosome, and plasma membrane, leading to its involvement in multiple biological processes such as glucose and lipid metabolism as well as neural development and cell death. Moreover, the function and role of sortilin is now emerging in several major human diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. The SORT1 gene also contains one of 27 loci associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPY5R gene.

P2Y purinoceptor 14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RY14 gene.

The beta-3 adrenergic receptor (β3-adrenoceptor), also known as ADRB3, is a beta-adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1, also known as MCH1, is one of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptors found in all mammals.

Pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1, also known as Neuropeptide Y receptor type 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPYR1 gene.

Neurotensin receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTSR1 gene. For a crystal structure of NTS1, see pdb code 4GRV. In addition, high-resolution crystal structures have been determined in complex with the peptide full agonist NTS8-13, the non-peptide full agonist SRI-9829, the partial agonist RTI-3a, and the antagonists / inverse agonists SR48692 and SR142948A, as well as in the ligand-free apo state., see PDB codes 6YVR (NTSR1-H4X:NTS8–13), 6Z4V (NTSR1-H4bmX:NTS8–13), 6Z8N (NTSR1-H4X:SRI-9829), 6ZA8 (NTSR1-H4X:RTI-3a), 6Z4S (NTSR1-H4bmX:SR48692), 6ZIN (NTSR1-H4X:SR48692), 6Z4Q, and 6Z66.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNB4 gene.

NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein or NKG2C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLRC2 gene. It is also known as or cluster of differentiation 159c (CD159c).

Neurolysin, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NLN gene. It is a 78-kDa enzyme, widely distributed in mammalian tissues and found in various subcellular locations that vary with cell type. Neurolysin exemplifies the ability of neuropeptidases to target various cleavage site sequences by hydrolyzing them in vitro, and metabolism of neurotensin is the most important role of neurolysin in vivo. Neurolysin has also been implicated in pain control, blood pressure regulation, sepsis, reproduction, cancer biology pathogenesis of stroke, and glucose metabolism.

Neuron-specific vesicular protein calcyon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALY gene. Its alternative name is Calcyon.