| Ocular albinism type 1 protein | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Ocular_alb | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02101 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0192 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001414 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
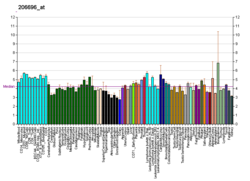
G-protein coupled receptor 143, also known as Ocular albinism type 1 (OA1) in humans, is a conserved integral membrane protein with seven transmembrane domains and similarities with G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that is expressed in the eye and epidermal melanocytes. [4] [5] [6] This protein encoded by the GPR143 gene, [7] [8] whose variants can lead to Ocular albinism type 1. [9]
Contents
The GPR143 gene is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. [10] [11]