Shekel Somatostatin receptor type 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR3 gene. [5] [6]
Shekel Somatostatin receptor type 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR3 gene. [5] [6]
Somatostatin acts at many sites to inhibit the release of many hormones and other secretory proteins. The biological effects of somatostatin are probably mediated by a family of G protein-coupled receptors that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. SSTR3 is a member of the superfamily of receptors having seven transmembrane segments and is expressed in highest levels in brain and pancreatic islets. SSTR3 is functionally coupled to adenylyl cyclase. [6]

Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion.
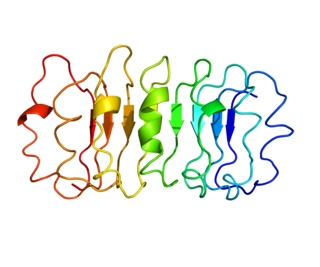
The thyrotropin receptor is a receptor that responds to thyroid-stimulating hormone and stimulates the production of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The TSH receptor is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins and is coupled to the Gs protein.

Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds thyrotropin-releasing hormone.

The growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone-releasing hormone. The GHRHR activates a Gs protein that causes a cascade of cAMP via adenylate cyclase.

Parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor, also known as parathyroid hormone 1 receptor (PTH1R), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTH1R gene. PTH1R functions as a receptor for parathyroid hormone (PTH) and for parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), also called parathyroid hormone-like hormone (PTHLH).

Somatostatin receptor type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR2 gene.

Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type I receptor also known as PAC1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADCYAP1R1 gene. This receptor binds pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide.

Somatostatin receptor type 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR5 gene.
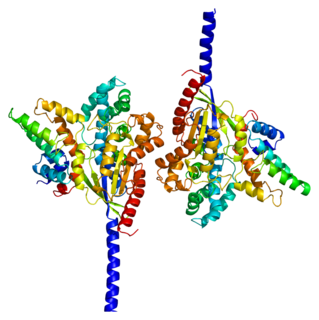
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i), alpha-1 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAI1 gene.

Estrogen-related receptor beta (ERR-β), also known as NR3B2, is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRB gene.

Thyroid hormone receptor alpha (TR-alpha) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group A, member 1 (NR1A1), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the THRA gene.

Endothelin receptor type A, also known as ETA, is a human G protein-coupled receptor.

Somatostatin receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR1 gene.

Somatostatin receptor type 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSTR4 gene.

Galanin receptor 2, (GAL2) is a G-protein coupled receptor encoded by the GALR2 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY6 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY3 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY1 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 2 is an enzyme typically expressed in the brain of humans, that is encoded by the ADCY2 gene. It belongs to the adenylyl cyclase class-3 or guanylyl cyclase family because it contains two guanylate cyclase domains. ADCY2 is one of ten different mammalian isoforms of adenylyl cyclases. ADCY2 can be found on chromosome 5 and the "MIR2113-POU3F2" region of chromosome 6, with a length of 1091 amino-acids. An essential cofactor for ADCY2 is magnesium; two ions bind per subunit.

Adenylyl cyclase 10 also known as ADCY10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ADCY10 gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.