 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MK-677; MK-0677; L-163,191; Oratrope |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 4–6 hours (in beagles); [1] IGF-1 levels remain elevated in humans with a single oral dose for up to 24 hours [2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.734 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
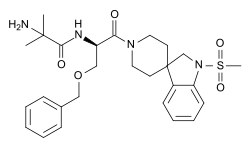
| Formula | C27H36N4O5S |
| Molar mass | 528.67 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ibutamoren (INN ; developmental code MK-677, MK-0677, LUM-201, L-163,191; former tentative brand name Oratrope) is a potent, long-acting, orally-active, selective, and non-peptide agonist of the ghrelin receptor and a growth hormone secretagogue, mimicking the growth hormone (GH)-stimulating action of the endogenous hormone ghrelin. [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] It has been shown to increase the secretion of several hormones including GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and produces sustained increases in the plasma levels of these hormones while also raising cortisol levels. [8]