
Ghrelin is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid.

Motilin is a 22-amino acid polypeptide hormone in the motilin family that, in humans, is encoded by the MLN gene.
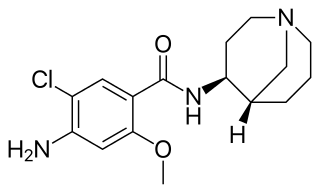
Renzapride is a prokinetic agent and antiemetic which acts as a full 5-HT4 agonist and partial 5-HT3 antagonist. It also functions as a 5-HT2B antagonist and has some affinity for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors.

Motilin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds motilin. It was first cloned in 1999 by Merck Laboratories. and scientists have since been searching for compounds to modify its behavior.

Growth hormone-releasing peptide 6 (GHRP-6), also known as growth hormone-releasing hexapeptide, is one of several synthetic met-enkephalin analogues that include unnatural D-amino acids, were developed for their growth hormone-releasing activity and are called growth hormone secretagogues. They lack opioid activity but are potent stimulators of growth hormone (GH) release. These secretagogues are distinct from growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) in that they share no sequence relation and derive their function through activation of a completely different receptor. This receptor was originally called the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR), but due to subsequent discoveries, the hormone ghrelin is now considered the receptor's natural endogenous ligand, and it has been renamed as the ghrelin receptor. Therefore, these GHSR agonists act as synthetic ghrelin mimetics.
Mosapride is a gastroprokinetic agent that acts as a selective 5HT4 agonist. The major active metabolite of mosapride, known as M1, additionally acts as a 5HT3 antagonist, which accelerates gastric emptying throughout the whole of the gastrointestinal tract in humans, and is used for the treatment of gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome. It is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach (i.e. at least one hour before food or two hours after food).

Itopride (INN; brand name Ganaton) is a prokinetic benzamide derivative. These drugs inhibit dopamine and acetylcholine esterase enzyme and have a gastrokinetic effect. Itopride is indicated for the treatment of functional dyspepsia and other gastrointestinal conditions. It is a combined D2 receptor antagonist and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.

Ibutamoren is a potent, long-acting, orally-active, selective, and non-peptide agonist of the ghrelin receptor and a growth hormone secretagogue, mimicking the growth hormone (GH)-stimulating action of the endogenous hormone ghrelin. It has been shown to increase the secretion of several hormones including GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and produces sustained increases in the plasma levels of these hormones without affecting cortisol levels.
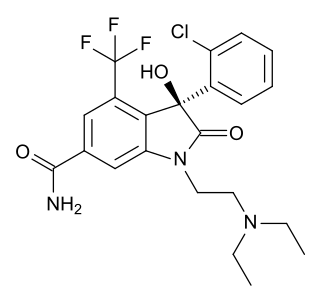
SM-130686 is a small-molecule drug which acts as a potent, orally-active agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) and growth hormone secretagogue, with around half the potency of the endogenous agonist ghrelin as a stimulator of growth hormone release. It produces dose-dependent increases in muscle mass and decrease in body fat, and is under investigation for the treatment of growth hormone deficiency and other medical conditions. Concerns about its potential use as a performance-enhancing drug for athletes have led to the development of urine tests for SM-130686 and other GHSR agonists, even though no drugs from this class have yet progressed to clinical use.

Tabimorelin (INN) is a drug which acts as a potent, orally-active agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) and growth hormone secretagogue, mimicking the effects of the endogenous peptide agonist ghrelin as a stimulator of growth hormone (GH) release. It was one of the first GH secretagogues developed and is largely a modified polypeptide, but it is nevertheless orally-active in vivo. Tabimorelin produced sustained increases in levels of GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), along with smaller transient increases in levels of other hormones such as adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, and prolactin. However actual clinical effects in adults with growth hormone deficiency were limited, with only the most severely GH-deficient patients showing significant benefit, and tabimorelin was also found to act as a CYP3A4 inhibitor which could cause it to have undesirable interactions with other drugs.

Prucalopride, sold under brand names Resolor and Motegrity among others, is a medication acting as a selective, high affinity 5-HT4 receptor agonist which targets the impaired motility associated with chronic constipation, thus normalizing bowel movements. Prucalopride was approved for medical use in the European Union in 2009, in Canada in 2011, in Israel in 2014, and in the United States in December 2018. The drug has also been tested for the treatment of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction.
A prokinetic agent is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency or strength of contractions, but without disrupting their rhythm. They are used to treat certain gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal discomfort, bloating, constipation, heart burn, nausea, and vomiting; and certain gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia.
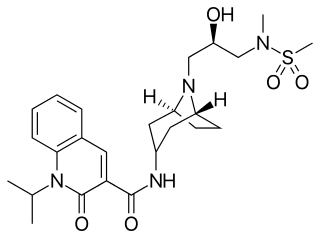
Velusetrag (INN, USAN; previously known as TD-5108) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of gastric neuromuscular disorders including gastroparesis, and lower gastrointestinal motility disorders including chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome. It is a potent, selective, high efficacy 5-HT4 receptor serotonin agonist being developed by Theravance Biopharma and Alfa Wassermann. Velusetrag demonstrates less selectivity for other serotonin receptors, such as 5-HT2 and 5-HT3, to earlier generation 5-HT agonists like cisapride and tegaserod.
Growth hormone secretagogues or GH secretagogues (GHSs) are a class of drugs which act as secretagogues of growth hormone (GH). They include agonists of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR), such as ghrelin (lenomorelin), pralmorelin (GHRP-2), GHRP-6, examorelin (hexarelin), ipamorelin, and ibutamoren (MK-677), and agonists of the growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR), such as growth hormone-releasing hormone, CJC-1295, sermorelin, and tesamorelin.

Pralmorelin (INN), also known as pralmorelin hydrochloride (JAN) and pralmorelin dihydrochloride (USAN), as well as, notably, growth hormone-releasing peptide 2 (GHRP-2), is a growth hormone secretagogue (GHS) used as a diagnostic agent that is marketed by Kaken Pharmaceutical in Japan in a single-dose formulation for the assessment of growth hormone deficiency (GHD).
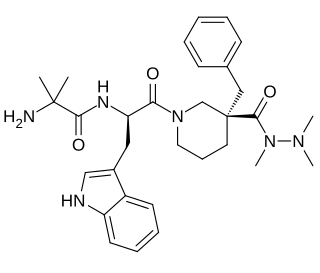
Anamorelin (INN), also known as anamorelin hydrochloride, is a non-peptide, orally-active, centrally-penetrant, selective agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) with appetite-enhancing and anabolic effects which is under development by Helsinn Healthcare SA for the treatment of cancer cachexia and anorexia.

Ipamorelin (INN) (developmental code name NNC 26-0161) is a peptide selective agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS) and a growth hormone secretagogue. It is a pentapeptide with the amino acid sequence Aib-His-D-2-Nal-D-Phe-Lys-NH2 that was derived from GHRP-1.

Examorelin (INN) (developmental code names EP-23905, MF-6003), also known as hexarelin, is a potent, synthetic, peptidic, orally-active, centrally-penetrant, and highly selective agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) and a growth hormone secretagogue which was developed by Mediolanum Farmaceutici. It is a hexapeptide with the amino acid sequence His-D-2-methyl-Trp-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys-NH2 which was derived from GHRP-6. These GH-releasing peptides have no sequence similarity to ghrelin, but mimic ghrelin by acting as agonists at the ghrelin receptor.

Ulimorelin is a drug with a modified cyclic peptide structure which acts as a selective agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR-1a).. Unlike many related drugs, ulimorelin has little or no effect on growth hormone (GH) release in rats. However, like ghrelin and other ghrelin agonists, ulimorelin does stimulate GH release with concomitant increases in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in humans. It has been researched for enhancing gastrointestinal motility, especially in gastroparesis and in aiding recovery of bowel function following gastrointestinal surgery, where opioid analgesic drugs used for post-operative pain relief may worsen existing constipation. While ulimorelin has been shown to increase both upper and lower gastrointestinal motility in rats, and showed promising results initially in humans, it failed in pivotal clinical trials in post operative ileus.

Camicinal is a motilin agonist for the treatment of gastroparesis.


















