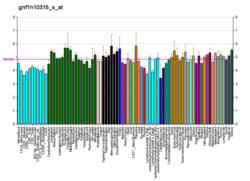
The thyrotropin receptor is a receptor that responds to thyroid-stimulating hormone and stimulates the production of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The TSH receptor is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins and is coupled to the Gs protein.

Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds thyrotropin-releasing hormone.

The adrenocorticotropic hormone receptor or ACTH receptor also known as the melanocortin receptor 2 or MC2 receptor is a type of melanocortin receptor (type 2) which is specific for ACTH. A G protein–coupled receptor located on the external cell plasma membrane, it is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase. The ACTH receptor plays a role in immune function and glucose metabolism.

The nuclear receptor 4A3 (NR4A3) also known as neuron-derived orphan receptor 1 (NOR1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A3 gene. NR4A3 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling the activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A1 gene, a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily, located on the long arm of chromosome 9 at position 33.3. It was originally identified as a regulator of genes encoding cytochrome P450 steroid hydroxylases, however, further roles in endocrine function have since been discovered.

The growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone-releasing hormone. The GHRHR activates a Gs protein that causes a cascade of cAMP via adenylate cyclase. GHRHR is distinct from the growth hormone secretagogue receptor, where growth hormone releasing peptides act to release growth hormone.
The prokineticin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the peptide hormone prokineticin. There are two variants each encoded by a different gene. These receptors mediate gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction and angiogenesis.

The KiSS1-derived peptide receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the peptide hormone kisspeptin (metastin). Kisspeptin is encoded by the metastasis suppressor gene KISS1, which is expressed in a variety of endocrine and gonadal tissues. Activation of the kisspeptin receptor is linked to the phospholipase C and inositol trisphosphate second messenger cascades inside the cell.

Kinase insert domain receptor also known as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) is a VEGF receptor. KDR is the human gene encoding it. KDR has also been designated as CD309. KDR is also known as Flk1.

Neuropilin 2 (NRP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRP2 gene.
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a protein that is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor / vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. It is encoded in humans by the VEGFC gene, which is located on chromosome 4q34.

G-protein coupled receptor 39 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR39 gene.

Prokineticin receptor 1, also known as PKR1, is a human protein encoded by the PROKR1 gene.

Putative gonadotropin-releasing hormone II receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNRHR2 gene.

Placental growth factor(PlGF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PGF gene.

Insulin-like 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the INSL3 gene.

C-fos-induced growth factor (FIGF) is a vascular endothelial growth factor that in humans is encoded by the FIGF gene.
Vascular endothelial growth factor B also known as VEGF-B is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the VEGF-B gene. VEGF-B is a growth factor that belongs to the vascular endothelial growth factor family, of which VEGF-A is the best-known member.

Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VEGFA gene.

Fms-related tyrosine kinase 4, also known as FLT4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FLT4 gene.