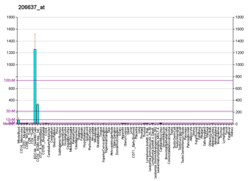
| P2RY14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | P2RY14 , BPR105, GPR105, P2Y14, purinergic receptor P2Y14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610116; MGI: 2155705; HomoloGene: 15769; GeneCards: P2RY14; OMA:P2RY14 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
P2Y purinoceptor 14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RY14 gene. [5]
Contents
The product of this gene, P2Y14 belongs to the family of G-protein coupled receptors, which contains several receptor subtypes with different pharmacological selectivity for various adenosine and uridine nucleotides. This receptor is a P2Y purinergic receptor for UDP-glucose and other UDP-sugars coupled to G-proteins. It has been implicated in extending the known immune system functions of P2Y receptors by participating in the regulation of the stem cell compartment, and it may also play a role in neuroimmune function. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. [5]