
The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene.

Tetrabenazine is a drug for the symptomatic treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders. It is sold under the brand names Nitoman and Xenazine among others. On August 15, 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of tetrabenazine to treat chorea associated with Huntington's disease. Although other drugs had been used "off label," tetrabenazine was the first approved treatment for Huntington's disease in the U.S. The compound has been known since the 1950s.

The adenosine A2A receptor, also known as ADORA2A, is an adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

SCH-58261 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the adenosine receptor A2A, with more than 50x selectivity for A2A over other adenosine receptors. It has been used to investigate the mechanism of action of caffeine, which is a mixed A1 / A2A antagonist, and has shown that the A2A receptor is primarily responsible for the stimulant and ergogenic effects of caffeine, but blockade of both A1 and A2A receptors is required to accurately replicate caffeine's effects in animals. SCH-58261 has also shown antidepressant, nootropic and neuroprotective effects in a variety of animal models, and has been investigated as a possible treatment for Parkinson's disease.

Istradefylline, sold under the brand name Nourianz, is a medication used as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adults with Parkinson's disease (PD) experiencing "off" episodes. Istradefylline reduces "off" periods resulting from long-term treatment with the antiparkinson drug levodopa. An "off" episode is a time when a patient's medications are not working well, causing an increase in PD symptoms, such as tremor and difficulty walking.

ZM-241,385 is a high affinity antagonist ligand selective for the adenosine A2A receptor.

PSB-10 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the adenosine A3 receptor (ki value at human A3 receptor is 0.44 nM), with high selectivity over the other three adenosine receptor subtypes (ki values at human A1, A2A and A2B receptors are 4.1, 3.3 and 30 μM). Further pharmacological experiments in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay using hA3-CHO-cells indicated that PSB-10 acts as an inverse agonist (IC50 = 4 nM). It has been shown to produce antiinflammatory effects in animal studies. Simple xanthine derivatives such as caffeine and DPCPX have generally low affinity for the A3 subtype and must be extended by expanding the ring system and adding an aromatic group to give high A3 affinity and selectivity. The affinity towards adenosine A3 subtype was measured against the radioligand PSB-11.

Preladenant is a drug that was developed by Schering-Plough which acted as a potent and selective antagonist of the adenosine A2A receptor. It was being researched as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease. Positive results were reported in Phase II clinical trials in humans, but it did not prove itself to be more effective than a placebo during Phase III trials, and so was discontinued in May 2013.

CGS-15943 is a drug which acts as a potent and reasonably selective antagonist for the adenosine receptors A1 and A2A, having a Ki of 3.3nM at A2A and 21nM at A1. It was one of the first adenosine receptor antagonists discovered that is not a xanthine derivative, instead being a triazoloquinazoline. Consequently, CGS-15943 has the advantage over most xanthine derivatives that it is not a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and so has more a specific pharmacological effects profile. It produces similar effects to caffeine in animal studies, though with higher potency.

MGS-0039 is a drug that is used in neuroscientific research, which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for group II of the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3). It produces antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and has been shown to boost release of dopamine and serotonin in specific brain areas. Research has suggested this may occur through a similar mechanism as that suggested for the similarly glutamatergic drug ketamine.
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that blocks adenosine at the adenosine A2A receptor. Notable adenosine A2A receptor antagonists include caffeine, theophylline and istradefylline.
Monoamine-depleting agents are a group of drugs which reversibly deplete one or more of the monoamine neurotransmitters, serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. One mechanism by which these agents act is by inhibiting reuptake by the vesicular monoamine transporters, VMAT1 and VMAT2. Examples of monoamine-depleting agents include deutetrabenazine, oxypertine, reserpine, tetrabenazine, and valbenazine. Tetrabenazine selectively depletes dopamine at low doses and is used as an animal model of amotivation.
A motivation-enhancing drug, also known as a pro-motivational drug, is a drug which increases motivation. Drugs enhancing motivation can be used in the treatment of motivational deficits, for instance in depression, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They can also be used in the treatment of disorders of diminished motivation (DDMs), including apathy, abulia, and akinetic mutism, disorders that can be caused by conditions like stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), and neurodegenerative diseases. Motivation-enhancing drugs are used non-medically by healthy people to increase motivation and productivity as well, for instance in educational contexts.
CT-005404, or CT-5404, is an atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) that was derived from modafinil. It shows pro-motivational effects in animals and reverses motivational deficits induced by tetrabenazine and interleukin-1β. CT-005404 is described as being orally active in animals and having a long duration of action. It is under development by Chronos Therapeutics for treatment of motivational disorders. The drug was first described by 2018.

Lu AA47070 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist that was under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease but was never marketed. It has been found to reverse some of the effects of dopamine D2 receptor antagonists like pimozide and haloperidol, for instance tremulous jaw movements, catalepsy, locomotor suppression, and other anti-motivational effects, in animals. The drug is a prodrug of Lu AA41063. It was discontinued in phase 1 clinical trials because it lacked the intended pharmacological properties in humans. Lu AA47070 was first described by 2008.

3-Chlorostyrylcaffeine (CSC), or 8-(3-chlorostyryl)caffeine (8-CSC), is a potent and selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist which is used in scientific research.

MSX-4 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist used in scientific research. It is a water-soluble amino acid ester prodrug of MSX-2, the active metabolite of the drug. MSX-4 reverses the motivational deficits induced by the dopamine D2 receptor antagonist eticlopride in animals and hence has the capacity to produce pro-motivational effects. MSX-4 was first described in the scientific literature by 2008.
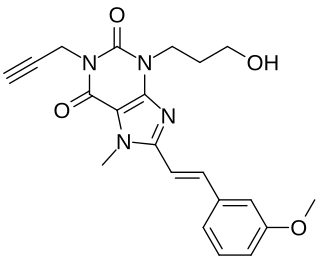
MSX-2 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist used in scientific research. It is a xanthine and a derivative of the non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist caffeine.

Lu AA41063 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist. Structurally, it is a non-xanthine.

The conditioned avoidance response (CAR) test, also known as the active avoidance test, is an animal test used to identify drugs with antipsychotic-like effects. It is most commonly employed as a two-way active avoidance test with rodents. The test assesses the conditioned ability of an animal to avoid an unpleasant stimulus. Drugs that selectively suppress conditioned avoidance responses without affecting escape behavior are considered to have antipsychotic-like activity. Variations of the test, like testing for enhancement of avoidance and escape responses, have also been used to assess other drug effects, like pro-motivational and antidepressant-like effects.


















