Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide and a type of neuropeptide, belonging to the tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It acts as a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator. Substance P and the closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after alternative splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:

Aprepitant, sold under the brand name Emend among others, is a medication used to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) and to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). It may be used together with ondansetron and dexamethasone. It is taken by mouth or administered by intravenous injection.

Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.
Physalaemin is a tachykinin peptide obtained from the Physalaemus frog, closely related to substance P. Its structure was first elucidated in 1964.

DNQX (6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione) is a competitive antagonist at AMPA and kainate receptors, two ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) subfamilies. It is used in a variety of molecular biology subfields, notably neurophysiology, to assist researchers in determining the properties of various types of ion channels and their potential applications in medicine.
Neurokinin 1 (NK1) antagonists (-pitants) are a novel class of medications that possesses unique antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antiemetic properties. NK-1 antagonists boost the efficacy of 5-HT3 antagonists to prevent nausea and vomiting. The discovery of neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonists was a turning point in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy.

Neurokinin A (NKA), formerly known as Substance K, is a neurologically active peptide translated from the pre-protachykinin gene. Neurokinin A has many excitatory effects on mammalian nervous systems and is also influential on the mammalian inflammatory and pain responses.
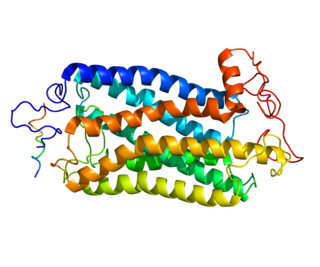
The tachykinin receptor 1 (TACR1) also known as neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) or substance P receptor (SPR) is a G protein coupled receptor found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endogenous ligand for this receptor is Substance P, although it has some affinity for other tachykinins. The protein is the product of the TACR1 gene.

The cholecystokinin B receptor also known as CCKBR or CCK2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCKBR gene.

Substance-K receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TACR2 gene.
In pharmacology, an indirect agonist or indirect-acting agonist is a substance that enhances the release or action of an endogenous neurotransmitter but has no specific agonist activity at the neurotransmitter receptor itself. Indirect agonists work through varying mechanisms to achieve their effects, including transporter blockade, induction of transmitter release, and inhibition of transmitter breakdown.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.

UH-232 ((+)-UH232) is a drug which acts as a subtype selective mixed agonist-antagonist for dopamine receptors, acting as a weak partial agonist at the D3 subtype, and an antagonist at D2Sh autoreceptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. This causes dopamine release in the brain and has a stimulant effect, as well as blocking the behavioural effects of cocaine. It may also serve as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, based on animal studies. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia, but unexpectedly caused symptoms to become worse.
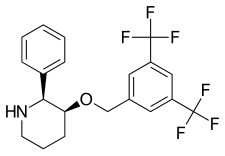
Vestipitant (INN) is a drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. It is under development as a potential antiemetic and anxiolytic drug, and as a treatment for tinnitus and insomnia.

Ezlopitant (INN, code name CJ-11,974) is an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic and antinociceptive effects. Pfizer was developing ezlopitant for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome but it appears to have been discontinued.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

Netupitant is an antiemetic medication. In the United States, the combinations of netupitant/palonosetron and the prodrug fosnetupitant/palonosetron are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of acute and delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, including highly emetogenic chemotherapy such as with cisplatin. In the European Union, the combinations are approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the same indication.

Vofopitant (GR205171) is a drug which acts as an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic effects as with other NK1 antagonists, and also shows anxiolytic actions in animals. It was studied for applications such as the treatment of social phobia and post-traumatic stress disorder, but did not prove sufficiently effective to be marketed.

Lanepitant (INN, code name LY303870) is a drug developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, and was one of the first compounds developed that act at this target. It was under development as a potential analgesic drug, but despite promising results in initial animal studies, human clinical trials against migraine, arthritis and diabetic neuropathy all failed to show sufficient efficacy to support further development, with the drug being only marginally more effective than placebo and inferior to older comparison drugs such as naproxen. Failure of analgesic action was thought to be due to poor penetration of the blood–brain barrier in humans, but research has continued into potential applications in the treatment of other disorders with a peripheral site of action, such as corneal neovascularization.
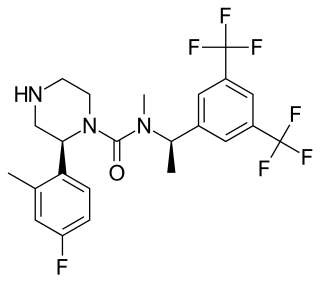
Burapitant (SSR-240,600) is a drug developed by Sanofi-Aventis which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. While burapitant itself did not proceed beyond early clinical trials and was never developed for clinical use in humans, promising animal results from this and related compounds have led to a number of novel drugs from this class that have now been introduced into medical use.