
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide and a member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after differential splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:

Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.
Physalaemin is a tachykinin peptide obtained from the Physalaemus frog, closely related to substance P. Its structure was first elucidated in 1964.

Kassinin is a peptide derived from the Kassina frog. It belongs to tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It is secreted as a defense response, and is involved in neuropeptide signalling.
Neurokinin 1 (NK1) antagonists (-pitants) are a novel class of medications that possesses unique antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antiemetic properties. NK-1 antagonists boost the efficacy of 5-HT3 antagonists to prevent nausea and vomiting. The discovery of neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonists was a turning point in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy.

Neurokinin A (NKA), formerly known as Substance K, is a neurologically active peptide translated from the pre-protachykinin gene. Neurokinin A has many excitatory effects on mammalian nervous systems and is also influential on the mammalian inflammatory and pain responses.
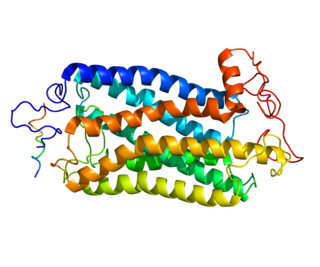
The tachykinin receptor 1 (TACR1) also known as neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) or substance P receptor (SPR) is a G protein coupled receptor found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endogenous ligand for this receptor is Substance P, although it has some affinity for other tachykinins. The protein is the product of the TACR1 gene.

Panadiplon (U-78875) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure that is not closely related to other drugs of this type. It has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and relatively little sedative or amnestic effect, and so is classified as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

Imidazenil is an experimental anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and is most closely related to other imidazobenzodiazepines such as midazolam, flumazenil, and bretazenil.

Substance-K receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TACR2 gene.

Tachykinin receptor 3, also known as TACR3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TACR3 gene.

Osanetant (developmental code name SR-142,801) is a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist which was developed by Sanofi-Synthélabo and was being researched for the treatment of schizophrenia but was discontinued. It was the first non-peptide NK3 antagonist developed in the mid-1990s.

Zacopride is a potent antagonist at the 5-HT3 receptor and an agonist at the 5-HT4 receptor. It has anxiolytic and nootropic effects in animal models, with the (R)-(+)-enantiomer being the more active form. It also has antiemetic and pro-respiratory effects, both reducing sleep apnea and reversing opioid-induced respiratory depression in animal studies. Early animal trials have also revealed that administration of zacopride can reduce preference for and consumption of ethanol.
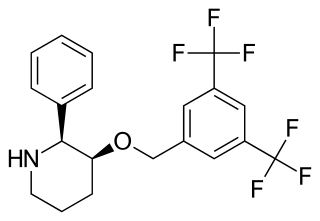
L-733,060 is a drug developed by Merck which acts as an orally active, non-peptide, selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, binding with a Ki of 0.08 nM. Only one enantiomer is active which has made it the subject of several asymmetric synthesis efforts.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

Neuropeptide S (NPS) is a neuropeptide found in human and mammalian brain, mainly produced by neurons in the amygdala and between Barrington's nucleus and the locus coeruleus, although NPS-responsive neurons extend projections into many other brain areas. NPS binds specifically to a G protein-coupled receptor, NPSR. Animal studies show that NPS suppresses anxiety and appetite, induces wakefulness and hyperactivity, including hyper-sexuality, and plays a significant role in the extinction of conditioned fear. It has also been shown to significantly enhance dopamine activity in the mesolimbic pathway, and inhibits motility and increases permeability in neurocrine fashion acting through NO in the myenteric plexus in rats and humans.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

MGS-0039 is a drug that is used in neuroscientific research, which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for group II of the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3). It produces antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and has been shown to boost release of dopamine and serotonin in specific brain areas. Research has suggested this may occur through a similar mechanism as that suggested for the similarly glutamatergic drug ketamine.

HA-966 or (±) 3-Amino-1-hydroxy-pyrrolidin-2-one is a molecule used in scientific research as a glycine receptor and NMDA receptor antagonist / low efficacy partial agonist. It has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antinociceptive and sedative / hypnotic effects in animal models. Pilot human clinical trials in the early 1960s showed that HA-966 appeared to benefit patients with tremors of extrapyramidal origin.

Vofopitant (GR205171) is a drug which acts as an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic effects as with other NK1 antagonists, and also shows anxiolytic actions in animals. It was studied for applications such as the treatment of social phobia and post-traumatic stress disorder, but did not prove sufficiently effective to be marketed.

















