Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as highly efficacious anti-depressants, as well as effective therapeutic agents for panic disorder and social phobia. They are particularly effective in treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and several other disorders.

Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula N
2H
4. It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour.

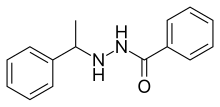
Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil, among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class which is used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use. It is taken by mouth.

Isocarboxazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.
Nialamide is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant. It was withdrawn by Pfizer several decades ago due to the risk of hepatotoxicity.

Iproniazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was later most prominently used as an antidepressant drug. However, it was withdrawn from the market because of its hepatotoxicity. The medical use of iproniazid was discontinued in most of the world in the 1960s, but remained in use in France until fairly recently.

Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Iproclozide is an irreversible and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant, but has since been discontinued. It has been known to cause fulminant hepatitis and there have been at least three reported fatalities due to administration of the drug.
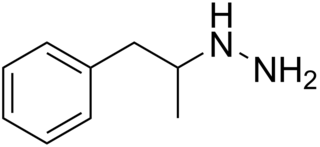
Pheniprazine is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant in the 1960s. It was also used in the treatment of angina pectoris and schizophrenia. Pheniprazine has been largely discontinued due to toxicity concerns such as jaundice, amblyopia, and optic neuritis.

Mebanazine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was previously used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.

Metfendrazine, also known as methphendrazine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class. It was investigated as an antidepressant, but was never marketed.

Phenoxypropazine is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family. It was introduced as an antidepressant in 1961, but was subsequently withdrawn in 1966 due to hepatotoxicity concerns.

Pivhydrazine, also known as pivalylbenzhydrazine and pivazide, is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family. It was formerly used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been discontinued.
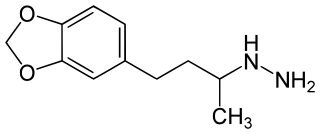
Safrazine (Safra) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was introduced as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been discontinued.

The hydrazine antidepressants are a group of non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which were discovered and initially marketed in the 1950s and 1960s. Most have been withdrawn due to toxicity, namely hepatotoxicity, but a few still remain in clinical use.
Octamoxin, also known as 2-octylhydrazine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant in the 1960s but is now no longer marketed.

Pipofezine, sold under the brand name Azafen or Azaphen, is an antidepressant approved in Russia for the treatment of depression. It was introduced in the late 1960s and is still used today.

Cimemoxin (INN), or cyclohexylmethylhydrazine, is a hydrazine monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant which was never marketed.

Domoxin (INN) is a hydrazine derivative monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant which was never marketed.
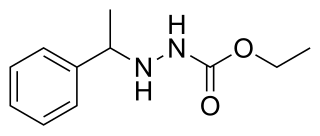
Carbenzide (INN), also known as carbazic acid, is a hydrazine derivative monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant which was never marketed.