
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH.

Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.

Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to produce ions using an electrospray in which a high voltage is applied to a liquid to create an aerosol. It is especially useful in producing ions from macromolecules because it overcomes the propensity of these molecules to fragment when ionized. ESI is different from other ionization processes since it may produce multiple-charged ions, effectively extending the mass range of the analyser to accommodate the kDa-MDa orders of magnitude observed in proteins and their associated polypeptide fragments.
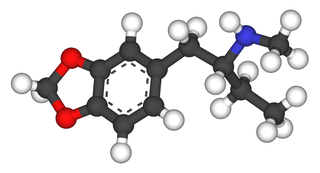
1,3-Benzodioxolyl-N-methylbutanamine (N-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine, MBDB, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-ethylphenylethylamine) is an entactogen of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is known by the street names Eden and Methyl-J. MBDB is a ring substituted amphetamine and an analogue of MDMA. Like MDMA, it has a methylene dioxy substitution at the 3 and 4 position on the aromatic ring; this is perhaps the most distinctive feature that structurally define analogues of MDMA, in addition to their unique effects, and as a class they are often referred to as "entactogens" to differentiate between typical psychostimulant amphetamines that (as a general rule) are not ring substituted. MBDB differs from MDMA by having an ethyl group instead of a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon; all other parts are identical. Modification at the alpha carbon is uncommon for substituted amphetamines. It has IC50 values of 784 nM against 5-HT, 7825 nM against dopamine, and 1233 nM against norepinephrine. Its metabolism has been described in scientific literature.

Electron-capture dissociation (ECD) is a method of fragmenting gas-phase ions for structure elucidation of peptides and proteins in tandem mass spectrometry. It is one of the most widely used techniques for activation and dissociation of mass selected precursor ion in MS/MS. It involves the direct introduction of low-energy electrons to trapped gas-phase ions.
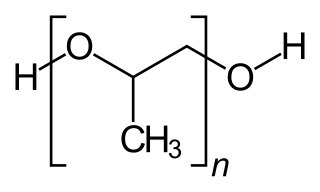
Polypropylene glycol or polypropylene oxide is the polymer of propylene glycol. Chemically it is a polyether, and, more generally speaking, it's a polyalkylene glycol (PAG) H S Code 3907.2000. The term polypropylene glycol or PPG is reserved for polymer of low- to medium-range molar mass when the nature of the end-group, which is usually a hydroxyl group, still matters. The term "oxide" is used for high-molar-mass polymer when end-groups no longer affect polymer properties. Between 60 and 70% of propylene oxide is converted to polyether polyols by the process called alkoxylation.
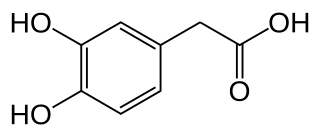
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) is a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine can be metabolized into one of three substances. One such substance is DOPAC. Another is 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT). Both of these substances are degraded to form homovanillic acid (HVA). Both degradations involve the enzymes monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), albeit in reverse order: MAO catalyzes dopamine to DOPAC, and COMT catalyzes DOPAC to HVA; whereas COMT catalyzes dopamine to 3-MT and MAO catalyzes 3-MT to HVA. The third metabolic end-product of dopamine is norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
Polysorbate 20 is a polysorbate-type nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of sorbitan monolaurate. Its stability and relative nontoxicity allows it to be used as a detergent and emulsifier in a number of domestic, scientific, and pharmacological applications. As the name implies, the ethoxylation process leaves the molecule with 20 repeat units of polyethylene glycol; in practice these are distributed across 4 different chains, leading to a commercial product containing a range of chemical species.

Ethylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylcathinone, is a recreational designer drug classified as an entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone chemical classes. It is the β-keto analogue of MDEA ("Eve"). Ethylone has only a short history of human use and is reported to be less potent than its relative methylone. In the United States, it began to be found in cathinone products in late 2011.

Propylene carbonate (often abbreviated PC) is an organic compound with the formula C4H6O3. It is a cyclic carbonate ester derived from propylene glycol. This colorless and odorless liquid is useful as a polar, aprotic solvent. Propylene carbonate is chiral, but is used as the racemic mixture in most contexts.

Methylenedioxypyrovalerone is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). It was first developed in the 1960s by a team at Boehringer Ingelheim. Its activity at the dopamine transporter is six times stronger than at the norepinephrine transporter and it is virtually inactive at the serotonin transporter. MDPV remained an obscure stimulant until around 2004 when it was reportedly sold as a designer drug. In the US, products containing MDPV and labeled as bath salts were sold as recreational drugs in gas stations, similar to the marketing for Spice and K2 as incense, until it was banned in 2011.

2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine is a lesser-known psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and was described in his book PiHKAL. Shulgin listed the dosage as 30–75 mg and the duration as 6–8 hours. He reported DMMDA as producing LSD-like images, mydriasis, ataxia, and time dilation. DMMDA isn't mentioned much in literature outside PiHKAL unlike 2C-B.

1,3-Benzodioxolylbutanamine is an entactogenic drug of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is the α-ethyl analog of MDPEA and MDA and the methylenedioxy analogue of α-ethylphenethylamine.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher activity as a monoaminergic neurotoxin, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

4'-Methyl-α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone is a stimulant drug and substituted cathinone. It is structurally very similar to α-PPP, with only one added methyl group in the para position on the phenyl ring. 4-MePPP was sold in Germany as a designer drug in the late 1990s and early 2000s, along with a number of other pyrrolidinophenone derivatives. Although it has never achieved the same international popularity as its better-known relations α-PPP and MDPV, 4-MePPP is still sometimes found as an ingredient of grey-market "bath salt" blends such as "NRG-3".

4'-Methoxy-α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (MOPPP) is a stimulant designer drug of the pyrrolidinophenone class. It has the potential to produce euphoria, an effect shared with other classical stimulants.

2,3-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (2,3-MDMA) is a positional isomer of the recreational drug 3,4-MDMA.

Dimethylone (βk-MDDMA) is a substituted cathinone derivative with stimulant and empathogenic effects. Unlike the corresponding amphetamine derivative MDDM which is thought to be practically inactive, dimethylone substitutes for methamphetamine and MDMA in animal studies and has been sold as a designer drug.
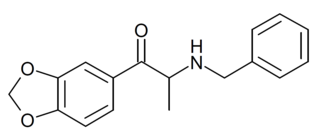
Benzylone, is a recreational designer drug from the substituted cathinone family, with stimulant effects. It has been commonly encountered in seizures of street drug samples but appears to have relatively low potency on its own, being mainly found as a component of mixtures with other related drugs.

Desmethylsibutramine is an active metabolite of the anorectic drug sibutramine. It is a more potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor than sibutramine and has been sold as an ingredient in weight loss products sold as dietary supplements, along with related compounds such as the N-ethyl and 3,4-dichloro derivatives.



















